Method of determination Treponema pallidum total antibodies refers to one of the most common and diagnostically valuable research methods. The low cost and high availability of the analysis allows you to confirm the diagnosis with high accuracy, which is important for the early detection of syphilis.
But, it must be borne in mind that the enzyme immunoassay used to determine total antibodies does not provide information about the stage of the pathological process and the duration of infection. To do this, you should perform a study that will determine them separately.
Record content:
- 1 Indications for research
- 2 How is it determined?
- 3 Preparation and analysis
- 4 Analysis decoding
- 5 When to see a doctor
- 6 Possible complications
- 7 Treponema pallidum video
Indications for research
A study for the determination of total antibodies to treponema is a publicly available research method. This analysis can be prescribed to patients if there are indications or on an individual basis at personal request. The patient can independently come to the doctor for a referral or perform the analysis in a private laboratory.
Treponema pallidum, whose total antibodies are detected at different stages of the disease, are classified as diseases, requires examination not only of the sexual partners of the infected person, but also of family members.
Among the main indications, against the background of which it is necessary to perform a study aimed at detecting antibodies, include:
- Pregnancy planning stage. When performing pre-gravid preparation, a woman needs to pass a biomaterial to exclude infections, which are predominantly sexually transmitted and lead to infection of the child or interruption pregnancy. If syphilis is detected, treatment is required before conception.
- Pregnancy management. The analysis during the period of bearing a child is performed three times in each of the trimesters. The need for dynamic control is associated with the possible implementation of the study in the incubation period or infection at any of the terms. A positive result during pregnancy requires urgent treatment in order to exclude intrauterine infection.
- Preventive screening of a patient at risk. These can be patients who are sexually active, an asocial lifestyle, who use drugs regularly in contact with infected people or biological materials. When a patient contacts a doctor who had a history of unprotected sexual intercourse without use barrier methods, it must be borne in mind that within a month and a half, symptoms can absent.
-
Preparing the patient for surgical interventions of varying severity. Any manipulation involving contact with blood requires a preliminary examination.
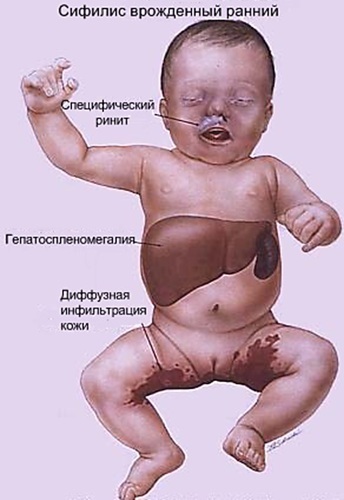
- Exclusion of congenital syphilis. When a child is born from a woman who has syphilis during pregnancy, or has symptoms characteristic of the disease, a study is required.
- Diagnosis of the disease in the presence of symptoms of the disease. In this case, the indications include the identification of formations resembling a hard chancre, as well as rashes or signs of damage to internal organs or various systems.
A doctor of any specialty can prescribe an analysis to determine antibodies to pale treponema. Most often, the study is performed in the direction of a therapist, surgeon, obstetrician-gynecologist, dermatovenerologist.
How is it determined?
Treponema pallidum, total antibodies to which are determined by enzyme immunoassay, is subject to screening.
This research method, performed in laboratory conditions, is based on the reaction of antigens with antibodies. This allows you to identify substances that have a protein nature, for example, an enzyme, a fragment of a virus, bacteria or other components that make up biological fluids.
Antigens are a particle foreign to the body that gets along with an infectious agent. In the human body, they trigger an immune response, which is aimed at protecting the integrity of the internal environment.
In response, antibodies are produced, which combine with antigens to form immune complexes. There are several types of them, initially, class M immunoglobulins are synthesized, then class G is formed. As a result, the infection is completely destroyed while maintaining immunity to re-infection.
Thanks to the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, it is possible to determine the qualitative and quantitative composition of antibodies contained in the body. For the purpose of its reproduction, a biological fluid is taken.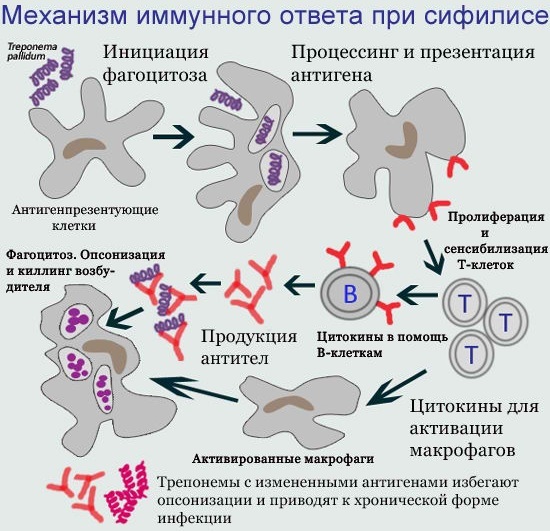
Most often, blood serum is used, which is applied to the wells on plastic plates, pre-treated with purified antigens. An enzymatic reaction leads to a change in the color of the substance in the wells.
Due to the high sensitivity and specificity of the method, it is possible to identify the causative agent of the infection even in cases where its concentration in the test material is insignificant. This significantly reduces the risk of diagnostic errors and ineffectively selected treatment, since the study carried out in the first days of the disease already depletes antibodies to the pathogen.
Preparation and analysis
When prescribing an analysis or an independent desire to pass biological material to detect a disease, it is necessary to take into account the timing of the appearance of antibodies. After infection, it takes several weeks for the test to detect antibodies.
The method of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay allows them to be detected as soon as possible. In this case, it takes up to 3 weeks from the moment of infection. In this case, the patient does not note clinical manifestations.
Performing an analysis with the determination of antibodies refers to indirect research methods, since it detects not the genetic material of the pathogen, but traces of its presence — antibodies. For this, blood is taken from a vein.
To eliminate diagnostic errors and reduce the risk of obtaining a false positive result, you must follow the preparation rules. There are no specific recommendations for performing the analysis.
It is enough for the patient:
- Limit the consumption of fatty foods for 24 hours before taking the biomaterial. It is preferable to take the test if the last meal was no later than 8 hours before the study.
- Avoid smoking for 30 minutes. before the blood is drawn.
- Refuse to take alcoholic beverages during the day.
- Eliminate the intake of medicines with antibacterial activity against the causative agent of syphilis.
If a result is obtained that does not correspond to clinical manifestations or anamnesis data, the study must be repeated. This is due to possible false positive or false negative data.
A false negative result may be due to insufficient time from infection to antibodies. In this case, the determination of the total antibodies of Treponema pallidum is prescribed later, taking into account the data of the anamnesis or exposure to risk factors.
A false positive reaction can be associated with:
- The presence of concomitant infectious pathologies, such as hepatitis of various types, human immunodeficiency virus, respiratory viral infection;
- Oncological diseases;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- myocardial infarction;
- cirrhotic liver damage;
- recent vaccinations;
- pregnancy.
If necessary, the patient is assigned additional research methods aimed at confirming or excluding the disease.
Analysis decoding
With the help of enzyme immunoassay, several types of immunoglobulins are detected.
Among them:
| Immunoglobulins M | Their production is carried out from the early stages of the disease. Detection using additional research methods is possible 14 days after the introduction of the pathogen into the body. The most accurate is the concentration, which is determined after 1.5 months. The production is characteristic for the primary and secondary periods, in the tertiary, its decrease is observed. |
| Immunoglobulins G | These specific compounds of a protein nature are classified as late, since their production begins no earlier than one month from the moment of infection. It should be borne in mind that synthesis is possible after a long time from the moment of infection, even after effective pharmacotherapy has been carried out. |
A positive result indicates that immunoglobulins are present in the blood serum. At the same time, there is no distinction into their individual types. Therefore, the technique confirms the fact of infection in the anamnesis, even after the therapy, or the presence of an acute course of syphilis at any of the stages.
When to see a doctor
Treponema pallidum, the total antibodies of which are examined regardless of the indications, provides for decoding by a specialist.
For an accurate diagnosis, the doctor must compare the clinical manifestations of pathology with the data of additional research methods, risk factors and anamnestic indicators. In this case, contacting a specialist is mandatory.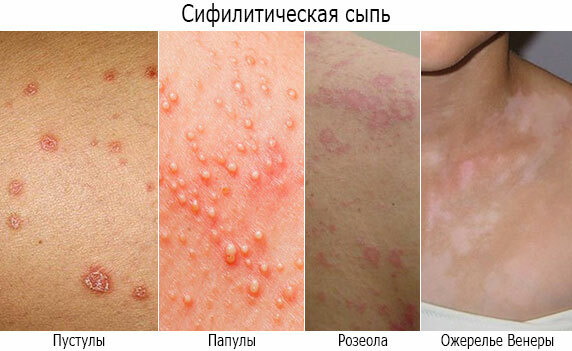
A doctor of any specialty can decipher the results. With information about a possible infection in the history, when the patient is unaware of the previous disease, as well as the acute course of the pathology, it is required to consult a dermatovenerologist.
The doctor will give a detailed transcript, prescribe additional studies if necessary, and also determine the tactics of further patient management. Self-decryption can lead to diagnostic errors and the progression of syphilis without treatment. This increases the risk of complications.
Possible complications
Treponema pallidum, whose total antibodies are detected using a publicly available enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, refers to bacteria that cause severe consequences for the patient. It is this method, due to its availability, aimed at early diagnosis, which allows starting treatment as soon as possible, preventing complications.
In many ways, the manifestations of complications of syphilis depend on the stage at which they arose and how the disease was treated.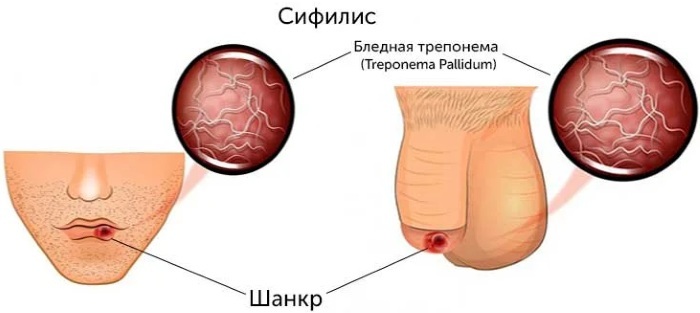
The most typical complications arising in the early and primary form are:
- Gangrene with subsequent self-amputation of the penis. This pathology can develop against the background of a hard chancre, as well as the attachment of a secondary infection to the wound surface. It is manifested by a change in the color of the organ, starting from the distal areas. In this case, necrosis can be dry or wet. He is accompanied by severe pain syndrome due to the presence of a large number of nerve endings, impaired sensitivity and loss of erectile function.
- Damage to the renal and hepatic tissues. Complications are characterized by the development of nephrotic syndrome with proteinuria and edema syndrome. Blood pressure does not change. Syphilitic hepatitis is manifested by jaundice, itching, poor appetite, nervousness. The inflammatory process proceeds painlessly with a significant increase in the size of the liver and its pronounced functional disorders. There is often a transition to cirrhosis.
- Neurosyphilis with impaired visual and auditory function. The defeat of the nervous system is accompanied by the clinic of meningitis, meningomyelitis, inflammation of the cords and roots in the spinal cord, as well as symptoms of focal brain damage.
- Testicular affection. For syphilitic changes in the testicles or their appendages, the appearance of focal seals or interstitial inflammation is characteristic. The patient does not experience pain, discomfort, fever and signs of an inflammatory reaction. The development of the disease is slow, as is the dysfunction.
- Skin changes with hair loss, skin rashes, and scar formation. Baldness can be diffuse or patchy. Scars are formed as a result of tissue destruction. They have a rough and drawn-in character with a change in the shade of the skin.
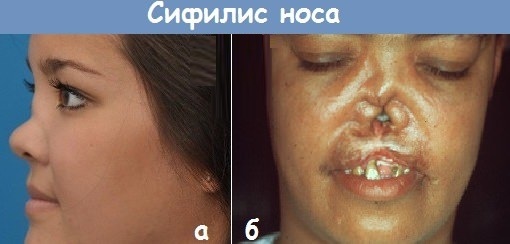
With tertiary or late syphilis, complications such as:
- Damage to the connective tissue, leading to inflammatory processes and manifestations in the vessels. Most often, arteries are involved in the pathological process, followed by aortitis and the formation of aneurysms. Also, patients may experience bronchiectasis and pneumosclerosis. These complications are often fatal.
- Destructive changes in bone and cartilage tissue, causing osteomyelitis, osteitis and periostitis. Saddle nose deformities, palatal perforation, or damage to other bone structures are common. Persons with destruction of bone structures not only experience serious psychological problems, but also severe impairment of motor function.
- Neuropsychiatric disorders in the form of tabes of the spinal cord, progressive paralysis or meningovascular syphilis.
Patients with similar complications in tertiary or late syphilis face disability and need outside care, as often develops loss of motor activity and the impossibility of independent service.
A special group is made up of the consequences of syphilis, which a woman suffered during pregnancy or against the background of congenital infection.
Often, pregnancy ends with early termination, infection of the chorion with its subsequent death.
Intrauterine infection in the second and third trimesters causes multiple organ failure with damage to the respiratory tract and nervous system. In addition, damage to the cornea and auditory nerve is possible, followed by deafness and impaired tooth structure. Children who have had congenital syphilis lag behind in physical and mental development.
With the help of enzyme immunoassay against Treponema pallidum, total antibodies are determined with high accuracy. Due to the early detection of the disease, the technique is widely used in clinical practice.
To reduce diagnostic errors and prevent complications, the interpretation of the results obtained should performed by the attending physician, if necessary, it is required to consult a dermatovenerologist or infectious disease specialist.
Treponema pallidum video
About the causative agent of syphilis - treponema:



