Today glaucoma is considered incurable and the 2nd after cataract cause of blindness. However, there are techniques that allow you to stop the development of the disease and minimize the risk of loss of vision. One of them is laser iridectomy (LIE).
Record content:
- 1 What is the danger of an acute attack of glaucoma?
- 2 Risk group
- 3 Laser iridectomy for glaucoma
- 4 Advantages and disadvantages of the technique
- 5 Indications for the operation
- 6 Contraindications
- 7 Examination before iridectomy
- 8 Preparation for laser surgery
- 9 Stages of iridectomy
- 10 Feelings of the patient
- 11 Postoperative period, restrictions
- 12 Possible complications
- 13 Forecast
- 14 Iridectomy price
- 15 Video about laser iridectomy
What is the danger of an acute attack of glaucoma?
The term "glaucoma" in ophthalmology is understood as a number of diseases that lead to obstruction of the outflow of ocular fluid and increased intraocular pressure (IOP). In the absence of adequate treatment, increased pressure over time causes irreversible changes in the optic nerve and blindness.
The ocular fluid is a jelly-like transparent substance produced by the ciliary body. This is the part of the lining of the eye behind the lens.
The eye fluid has the following functions:
- nourishes the elements of the eye that do not contain blood vessels (lens, inner surface of the cornea);
- protects the eye from damage;
- creates a refractive environment.
Normally, the ophthalmic fluid enters through the opening of the pupil from the posterior chamber of the eye to the anterior chamber. After that, it is removed through the drainage canal located in the corner of the anterior chamber of the eye - where the junction of the cornea and the iris is located. The amount of liquid present in the front and rear chambers remains unchanged. IOP does not change either, amounting to 10-20 mm Hg. Art.
The physiological norm is considered small (no more than 2.75 mm Hg. Art.) fluctuations in the value of intraocular pressure during the day.
As a rule, it is higher in the morning and lower in the evening. With glaucoma, this process is disrupted, the outflow of the eye fluid slows down, while the ciliary body continues to produce it. As a result, IOP increases several times, increasing pressure on the optic nerve, which gradually leads to its atrophy.
For reasons causing impaired outflow, there are 2 types of glaucoma:
| View | Description |
| Open angle | There is access to the drainage channel, but the liquid suction function is impaired. In the initial stages, it is asymptomatic, causing a slow, gradual and subtle narrowing of the visual field and a decrease in its acuity. Pathology can be diagnosed with an ophthalmologic examination. |
| Closed-angle | The Schlemm canal is blocked by the iris: the angle of the anterior chamber of the eye narrows or completely overlaps. The disease develops quickly, but it is paroxysmal in nature, so it is difficult to identify it upon examination. Angle-closure glaucoma accounts for about 10% of cases. |
Glaucoma is also distinguished:
- primary, developing due to the anatomical features of the eye;
- secondary, which is a consequence of diseases of the organs of vision, injuries, previous operations;
- mixed.
Attacks of angle-closure glaucoma are usually observed at night (dark) time, when the pupil dilates and the iris thickens and blocks the drainage canal.
Acute attacks are especially dangerous, for which the following chain of changes is characteristic:
- The iris obstructs the drainage canal.
- Ocular fluid accumulates in the back of the eye and begins to press on the lens.
- The lens is pressed into the pupil, making it difficult for fluid to drain from the posterior to the anterior. This is how the pupillary block is formed - a pathological condition of the eye in which the pupil is partially or completely blocked by the lens.
In the light, the pupil cannot narrow due to the fact that the lens interferes with this, and the eye pressure continues to grow and reaches values of 70-100 mm Hg. Art. If an acute attack is not stopped within the next 2 days, it will cause irreversible changes in the optic nerve and complete loss of vision, which cannot be restored later.
Risk group
No one is immune from glaucoma, even those with excellent eyesight who have no complaints about their eyes.
However, there are factors that increase the risk of developing the disease:
- old age (over 60 years old) and thickening of the lens characteristic of old age;
- the presence of relatives in the ascendant with glaucoma;
- hyperopia;
- features of the anatomical structure of the eye: anterior attachment of the lens, narrow anterior chamber, small dimensions of the angle of the anterior chamber.
The following circumstances are capable of provoking the onset of an acute attack:
- unusual physical activity;
- work associated with the need to keep your head tilted for a long time;
- high load on the eyes: reading in low light, long-term work with small objects;
- intense excitement;
- hypertension;
- damage to the cornea;
- the use of medicines for the common cold with vasoconstrictor properties, antidepressants, eye drops that dilate the pupil;
- alcohol, smoking;
- one-time consumption of a large amount of liquid;
- excessive passion for salty foods.
It is difficult to diagnose an acute attack of glaucoma on your own, because many of its symptoms are characteristic of other diseases.
You should urgently consult a doctor if:
- the pupil has acquired a greenish color and does not respond to light (does not narrow);
- the cornea turns red or has lost transparency;
- the eye has become hard to the touch (“stone” eye effect).
These phenomena are usually accompanied by:
- severe migraine;
- sharp pain in the area of the orbit, radiating to the bridge of the nose, forehead, temples, eyebrows;
- sudden visual impairment (blurring);
- the appearance of rainbow circles around light sources;
- general deterioration of health: weakness, sometimes - nausea, vomiting.
Laser iridectomy for glaucoma
To suspend or slow down the pathological process in the treatment of mild forms of glaucoma, eye drops, the action of which is aimed at normalizing the outflow of eye fluid or reducing its production.
Laser iridectomy is the creation of an additional drainage hole (coloboma) by perforating the iris in one or more places. It is carried out if the patient is diagnosed with a closed-angle form of the disease, accompanied by a pupillary block, or the likelihood of an acute attack is high.
Through the formed hole, excess fluid from the posterior chamber of the eye passes into the anterior chamber, which makes it possible:
- equalize the pressure in them;
- remove the pupillary block;
- release access to the Schlemm channel;
- restore the natural way of the outflow of the eye fluid.
By the type of instrument used to create the hole, iridectomy is distinguished: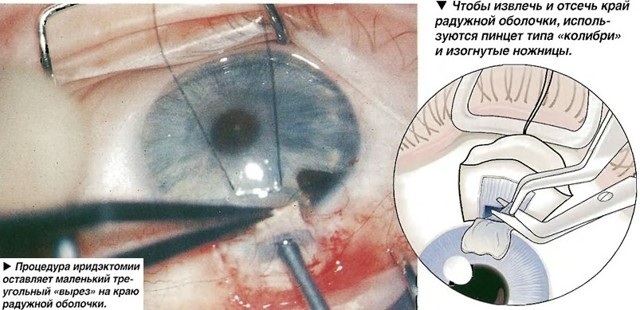
| View | Description |
| Surgical | It is performed using microsurgical scissors and requires opening the eyeball |
| Laser (LIE) | With it, the iris is exposed to a laser beam, without an incision in the cornea. This option is currently considered the best treatment for angle-closure glaucoma. |
Advantages and disadvantages of the technique
Compared to conservative treatments for glaucoma and surgical iridectomy, the use of a laser beam offers the following benefits:
- almost instant effect;
- painlessness;
- no need for hospitalization;
- the ability to perform the procedure in both eyes at once;
- rapidity;
- easy recovery period;
- a small number of complications and contraindications;
- the minimum number of restrictions imposed on the patient who underwent the procedure;
- affordable price.
The disadvantages of LIE include the inability to perform it in case of corneal opacity or edema caused by excessive pressure inside the eye. Sometimes, due to the large thickness or high density of the iris, it is not possible to create a coloboma of the required size. In the 1st and 2nd cases, it is necessary to resort to a surgical method of correction.
Indications for the operation
Laser iridectomy is the optimal treatment option for primary and secondary angle-closure glaucoma. It gives the best effect in the initial stages of the disease, when damage to the optic nerve is insignificant: in this case, it is possible to completely stop its destruction.
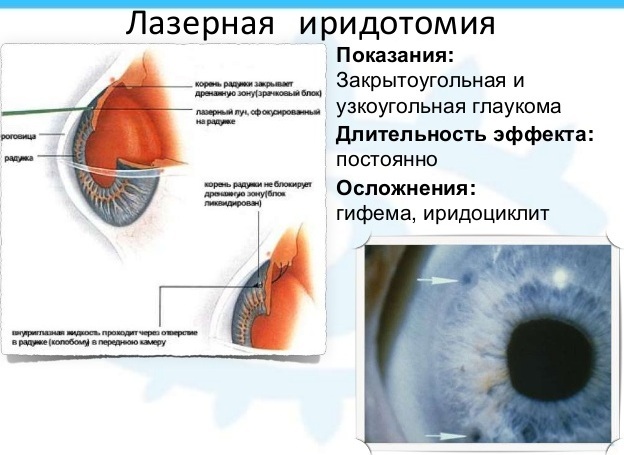
The procedure is shown under the following circumstances:
- in the early stages - in the absence of a response to conservative treatment or the impossibility of using drugs due to allergies;
- with a forming or formed pupillary block - for emergency treatment of the patient, a rapid decrease in IOP and preservation of vision;
- in the presence of symptoms indicating the approach of an acute attack of glaucoma - in order to prevent it;
- with chronic angle-closure glaucoma and previous seizures;
- with mixed type of glaucoma;
In preparation for other eye treatments, such as before a laser trabeculoplasty, LIE can be prescribed to a patient with open-angle glaucoma and a narrow anterior angle cameras.
As a prophylaxis for angle-closure glaucoma, LIE can be performed on a healthy eye if there are:
- factors that increase the risk of developing the disease: old age, already existing pathology of the other eye;
- genetic predisposition;
- structural features of the eyeball (narrow angle between the iris and the cornea).
Contraindications
Laser iridectomy will not work:
- with open-angle glaucoma;
- in the later stages of the disease;
- to restore the optic nerve in whole or in part.
Also, this procedure cannot be performed and is replaced by other methods of vision correction if:
- the eye fluid has lost its transparency due to increased pressure;
- with severe corneal edema;
- with a slit form of the anterior chamber of the eye;
- with paralytic mydriasis (pathological dilation of the pupil associated with a violation of the muscles that regulate its size);
- if the patient is unable to keep his head motionless for a long time;
- in the presence of diseases of the immune system or viral infections;
- with diabetic retinopathy: a complication of diabetes mellitus, causing damage to the vessels located in the shell of the eyeball;
- with neovascular glaucoma - a secondary form of glaucoma, characterized by proliferation of the vessels of the iris located in the corner of the anterior chamber of the eye.
During pregnancy, laser iridectomy is performed when it is the only way to preserve the eyesight of the expectant mother.
The procedure does not affect the course of pregnancy, but the drugs used as anesthetics during its implementation and eye drops, excluding the development of the inflammatory process in the postoperative period, have a teratogenic effect and can disrupt the formation process embryo.
If complex treatment of cataracts and glaucoma is required, preference is given to surgical methods that make it possible to solve 2 problems through the 1st operation.
Examination before iridectomy
The decision on the need for laser iridectomy or replacing it with another type of treatment is made by a specialist based on the results of a preliminary ophthalmological examination.
During it:
- the diagnosis is specified;
- the level of IOP is determined;
- factors that can interfere with the procedure are identified.
The survey may include the following stages:
- conversation with the patient, collection of anamnesis;
- gonioscopy - visual examination of the eye;
- perimetry - checking peripheral vision;
- ophthalmoscopy - examination of the fundus;
- biomicroscopy - diagnostics of the state of individual elements of the eye: lens, cornea, retina, iris, optic nerve;
- contact or non-contact tonometry - determination of IOP indicators;
- Ultrasound and CT of the organs of vision to clarify the anatomical features of the eye.
The listed diagnostic methods provide the necessary information about:
- the presence or absence of pathology;
- type of glaucoma;
- stage of the disease.
This allows you to select the optimal method of treatment and, if a decision is made to conduct LIE, to determine the area for making a drainage hole.
Preparation for laser surgery
Laser iridectomy is a procedure that requires preparation.
The patient needs:
- take tests if necessary: general blood test, blood for PW, hepatitis, HIV;
- stop using contact lenses a week before the procedure, stop taking eye drops and any medications. If it is impossible to cancel them, consult an ophthalmologist;
- during 2 days preceding the procedure, do not consume alcoholic beverages;
- limit work associated with high physical activity;
- sleep well before iridectomy, stay calm, avoiding strong emotional experiences.
Going to the clinic, you should:
- thoroughly cleanse your eyes and face from decorative cosmetics;
- take sunglasses with you;
- refuse to use deodorants;
- wear comfortable clothes with a fastener in the front or with an open collar.
Stages of iridectomy
LIE does not require hospitalization. It is performed on an outpatient basis using a YAG laser capable of operating in a pulsed mode, less often a continuous argon laser.
The procedure is performed as follows:
- The patient sits in a special chair so that his chin is on the support, and his head is fixed motionless.
- The eye is treated with an anesthetic, after which a miotic is instilled into it - a drug for narrowing the pupil. Usually a 1% solution of pyrocarpine is used.
- A special optical lens (goniolins) is installed in the eye to focus the laser beam on the desired area of the iris. Typically, this is a place on the periphery at the top.
- For the formation of a coloboma, a zone is selected where the membrane is thinner or there are natural depressions.
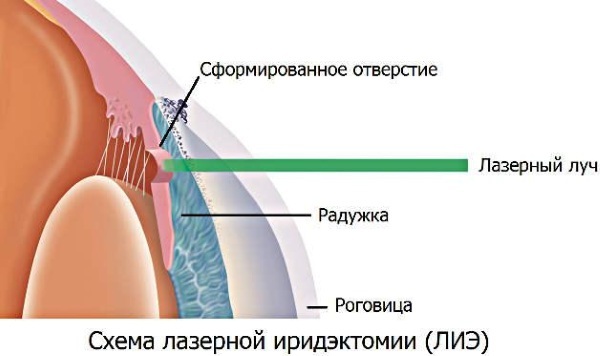
- After performing the described manipulations, a laser beam is directed into the patient's eye and he is asked to follow the "green light". Due to the special convex-concave shape of the lens, the laser beam passing through the cornea is scattered (its diameter increases twice), so it does not harm it, and then focuses on the iris, burning a microscopic hole.
The whole procedure takes about 10-15 minutes, of which 25 seconds are required to create a hole using a laser.
Depending on the characteristics of the iris (its color, thickness, density), various techniques for creating an artificial drainage hole are used:
| Technique | Description |
| Layered | Indicated for patients with brown eyes. The hole is formed layer by layer, gradually deepening. Argon or YAG laser can be used |
| Phased | It is used in the case of a very light color of the iris. The procedure requires 2 to 5 sessions |
| One-time | Can be used for patients with any eye color. Only a YAG laser is used, which creates a hole in 3 pulses. Today, simultaneous iridectomy is the most popular |
Feelings of the patient
Laser iridectomy is a painless procedure. Light flashes accompanying laser operation can cause slight discomfort. In the first 10-15 seconds of exposure to the beam, vision remains clear, then becomes blurred.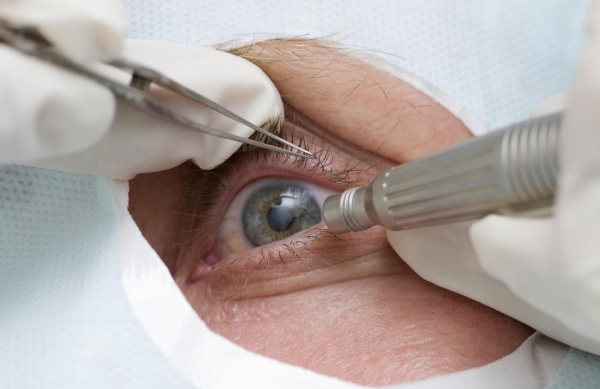
This persists for 1-2 minutes after the procedure, then the clarity is partially restored. Full recovery will take about 1 hour. If there were symptoms of an acute attack of glaucoma, then they should disappear in a few minutes after performing LIE.
Postoperative period, restrictions
After the end of the procedure, the patient remains under the supervision of a doctor for 20-30 minutes, then he can go home. Visually, the eye looks usually, the hole made is so small that it can be seen under a microscope. However, it is usually hidden under the upper eyelid. If the procedure is performed correctly, there should be no vivid painful or unpleasant sensations.
In the first 1-2 days it is possible:
- slight redness of the eye;
- tearing;
- slight swelling;
- increased sensitivity to light;
- slight distortion of vision.
To avoid complications, you must:
- within a week after the procedure, instill anti-inflammatory and decongestant drugs prescribed by a doctor into the eye;
- regularly visit an ophthalmologist to monitor the condition of the organs of vision;
- exclude prolonged reading and work at the computer;
- do not keep your head tilted for a long time;
- do not rub your eyes;
- do not use contact lenses;
- do not sleep on your stomach. This position can disrupt blood circulation in the eye and cause swelling. If the procedure was performed on the right eye, it is advisable to sleep on the left side, and vice versa;
- in the first 2-3 days, refrain from washing your hair, washing your face with soap, visiting saunas and swimming pools;
- exclude work associated with high physical activity;
- remove from the diet foods that provoke fluid stagnation;
- wear dark glasses on sunny days;
- do not use decorative cosmetics (mascara, shadows).
As a rule, after a week, the described restrictions are removed after consulting an ophthalmologist. The exceptions are sports involving heavy lifting (weightlifting) and activities that involve a high risk of injury. It is advisable for a person who has undergone LIE to give them up forever.
Rehabilitation
LIE is one of the non-invasive procedures, does not cause tissue injury and does not leave external sutures that require long-term healing. For these reasons, during the recovery period, it is enough for the patient to observe the restrictions described above and regularly (1-2 times a year) visit an ophthalmologist in order to monitor the condition of the eye.
Possible complications
With a properly performed iridectomy procedure and competent follow-up care, the likelihood of complications is minimal.
Doctor's mistakes can cause:
- persistent distortion of vision (with too large coloboma);
- no effect (insufficient hole size);
- burn of the iris.
Neglecting the advice of an ophthalmologist in the period after the procedure greatly increases the risk of the following complications:
- the appearance of adhesions in the area of the holes;
- overgrowth with colobomas or accumulation of pigment in them;
- a sharp increase in IOP;
- inflammation (swelling and redness) of the cornea;
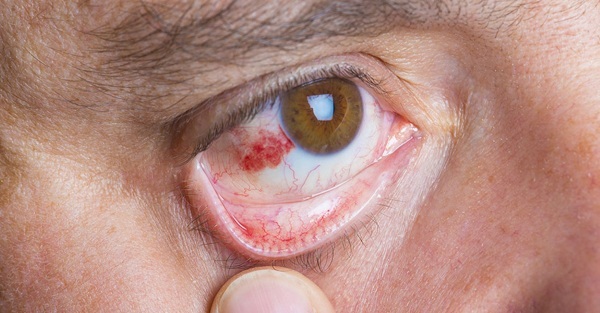
In the first 3 cases, a second procedure will be required, in the latter case, long-term treatment of the inflammatory process.
Forecast
According to medical statistics, in 96% of cases it is possible with the help of laser iridectomy to achieve normalization of intraocular pressure and suspension of the process of destruction of the optic nerve.
The subsequent prognosis largely depends on the patient and his attitude towards his health. With regular examinations by an ophthalmologist and fulfilling all his requirements, there is a high chance of maintaining vision.
However, it should be remembered that:
- the likelihood of complications and the associated need to repeat the procedure can be minimized;
- the LIE procedure does not give a 100% guarantee that the patient will not develop another form of glaucoma over time or that it will not affect the second eye;
- laser iridectomy is unable to prevent age-related changes in the organs of vision, as well as the appearance of symptoms of other eye diseases, such as cataracts.
Iridectomy price
The cost of laser iridectomy ranges from 5,000 to 15,000 rubles. The average is 9,000 rubles. for a procedure performed on 1 eye.
The exact amount depends on several factors:
- the complexity of the upcoming procedure;
- type of equipment used;
- the level of qualifications of the personnel.
To date, there is no way to completely recover from glaucoma and restore the optic nerve. But there are ways to stop the development of the disease in the early stages. Laser iridectomy is one such technique. Among its advantages are efficiency, painlessness, quick results, affordable prices.
Video about laser iridectomy
Laser iridectomy:



