If pain occurs in the hip joint during exercise, the orthopedic surgeon must rule out impingement syndrome. According to unofficial data, the specified pathology of the musculoskeletal system is diagnosed in everyone the fourth patient who complained of prolonged painful sensations in this part body.
Record content:
- 1 What is impingement syndrome?
- 2 Causes
- 3 Stages
- 4 Symptoms
-
5 Diagnostic methods
- 5.1 Physical examination
- 5.2 X-ray
- 5.3 MRI
- 5.4 Other methods
-
6 Methods for treating the disease
- 6.1 Conservative treatment
- 6.2 Surgical intervention
- 6.3 Rehabilitation
- 7 Video about impingement syndrome
What is impingement syndrome?
This violation can occur not only in the hip, but also in the shoulder joint. Impingement syndrome makes itself felt at the time of physical activity involving a specific muscle group. This disease has another official medical name - femoroacetabular conflict.
Impingement syndrome of the hip joint is an injury to parts of the joint, which, as a rule, occurs in a chronic form and arises from their permanent deformation. The most commonly diagnosed violation of the femoral-acetabular joint, in which bone fragments rub against each other, causing discomfort.
The disease proceeds according to a certain pattern. The forming osteophytes (bone micro-growths) on the surface of the femoral head interfere with the full sliding of the joint elements interacting with it. During movement or physical exertion, they constantly confront, as a result of which the acetabular lip, which serves as the edging of the upper part of the pelvic cavity, is constantly damaged.
If the problem is not eliminated, after a while it begins to worsen by the rupture of the acetabular lip, erasure and destruction of the cartilage and articulating bones of the pelvis, due to which a person feels pain, aggravated by walking.
Diagnoses with the prefix "impingement" in traditional medicine are made not so long ago, since their discovery is associated with the use of the latest research methods.
It is impossible to study in detail the structure of the hip joint, which consists of bones, cartilage and soft elastic connective tissues, on the X-ray picture. The correct treatment of this disease has become possible thanks to the use of modern technologies (CT, MRI).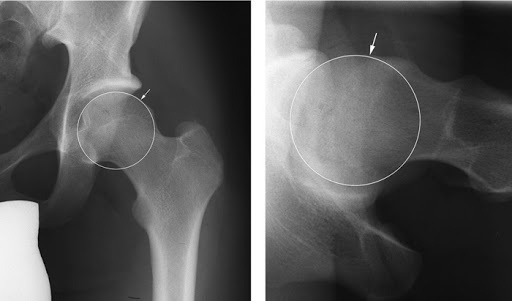
If you ignore the symptoms of impingement syndrome for a long time or refuse professional medical care, there is a huge risk of developing irreversible complications.
In this disease, destruction of the joint can lead to its complete dysfunction and unsuitability. However, with timely referral to specialists, impingement syndrome can be cured by conservative or surgical methods.
Causes
In the overwhelming majority of cases, the factor that predisposes to femoroacetabular conflict between the hip and the pelvic bone is the abnormal structure of the joint. We are talking about both congenital anomalies and acquired diseases and injuries.
Hip impingement is often provoked due to the following structural features of the joint:
- irregularly shaped femoral head;
- the convexity of the body of the bone at the point of articulation with the neck of the femur;
- defective length of the femur tubular bone;
- defective joint configuration.
Structural disorders of the hip joint are often the consequences of injuries and a number of diseases, for example:
- avascular necrosis;
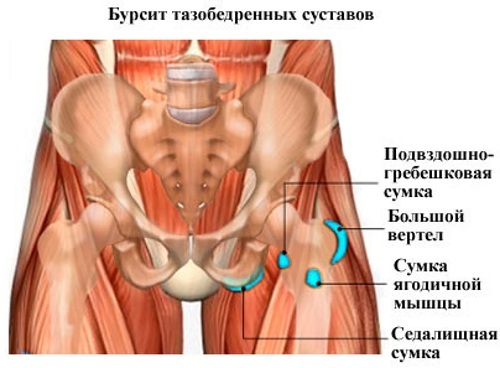
- fractures;
- dislocations;
- sprains and tendon ruptures;
- epiphysis;
- bursitis and other types of inflammation of the synovial bag;
- avascular necrosis (femoral head bone infarction);
- Perters disease (osteochondropathy);
- atrophy of muscle tissue within the hip joint.
In rare cases, the cause of this pathology is malfunction of the endocrine system. For example, in diabetes mellitus, the structure of bones, cartilage and soft tissues in the joints suffers due to poor metabolism and circulatory problems.
A separate category should include diseases that are not a direct cause of the development of impingement, but increase the likelihood of its occurrence.
First of all, these are chronic diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue, which include:
- arthritis and arthrosis;
- gout;
- rachiocampsis;
- intervertebral hernia.
The risk group includes people who regularly experience excessive physical exertion on their legs and pelvis. Also, impingement syndrome can be the result of an unsuccessful operation on the pelvic bones or lower extremities.
Stages
For such a disease as impingement, a staged course is characteristic.
Orthopedists distinguish the pathological process into 3 main stages: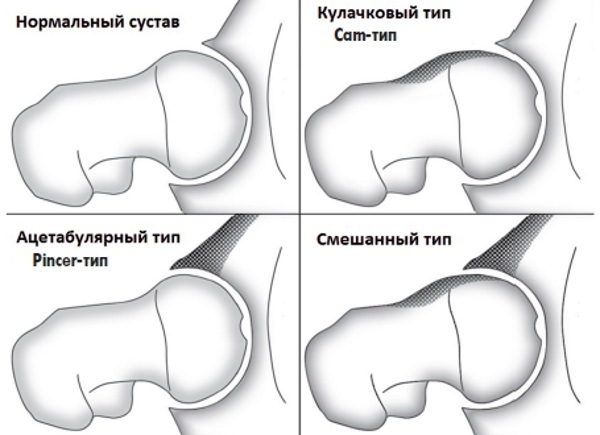
| Stage | Patient age | Symptoms and manifestations |
Reversible or not | Treatment type |
| The first | up to 25-28 years old | Swelling, joint hemorrhage, pain after physical activity. | Lovers | Conservative |
| The second | 28 to 40 years old | Persistent inflammation of the tendons, leading to tendinitis and fibrosis of the cartilage tissue. | Irreversible | Complex (medicines and acromioplasty) |
| Third | After 40 years | The presence of bone spurs, cuff ruptures, degenerative changes in the joint and adjacent soft tissues. | Irreversible, leading to disability | Surgical |
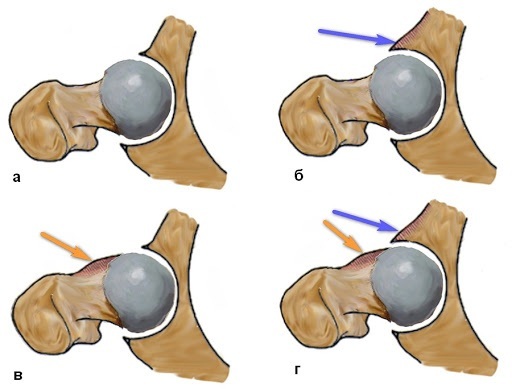
Patients under the age of 30 are most likely to cure impingement syndrome. At the initial stage, the symptoms of the disease are easily stopped by drugs and physiotherapy.
With the progression of the pathology, the pain spreads to the entire groin area, causing discomfort in the outer thighs and difficulty in movement. In the second stage, it becomes difficult for patients to bend over, squat and perform other elementary movements. Sometimes the pain radiates to the knee joint.
It is important to understand that the treatment of the second stage of femoroacetabular conflict is not intended to achieve a full recovery of the affected tissues. An excellent result of complex therapy will be the lack of dynamics of the disease.
In patients at the third stage of impingement syndrome, bone spurs are formed, destructive and irreversible consequences occur in the cartilage and bone tissues of the joint. Often this form of the disease is found in people over 40-45 years old. The prognosis for recovery is usually unfavorable, the disease leads to complete disability.
Symptoms
Hip impingement syndrome is accompanied by the following clinical signs:
- a constant feeling of pulling pain in the groin;
- cramps and discomfort during motor activity of the thigh, bending of the leg;
- inability to bring the hip joint to its extreme positions (turn inward, bend);
- increased pain after prolonged sitting and weakening in the supine position;
- limited range of motion at the joint;
- difficulties arising even with calm measured walking.
The presence of one or more of these symptoms indicates the development of a pathological process, therefore, in order to establish an accurate diagnosis, it is imperative to visit an orthopedist.
With impingement, pain is localized, as a rule, in only one hip joint. The minimal impact on the leg provokes an increase in pain syndrome.
Depending on the severity of the symptoms of the disease, the attending physician selects an individual treatment program. In addition, in the early stages, signs of the disease may be completely absent, therefore, some patients do not notice discomfort, therefore, they are not aware of the presence of pathology.
And yet, in most cases, impingement syndrome is manifested by limited mobility of the hip joint and pain that increases with movement and physical exertion. Such symptoms are typical for a number of disorders of the musculoskeletal system, therefore, when making a diagnosis, the doctor must be able to differentiate the disease.
Diagnostic methods
First of all, the doctor must make sure that the pathological process, manifested by typical symptoms, is localized precisely in the tissues of the hip joint. For the diagnosis, the type and genesis of the femoroacetabular conflict, its stage, and the presence of concomitant diseases matter.
Impingement syndrome, in which patients complain of pain in the hip joint, is often mistaken by doctors for developing coxarthrosis. However, unlike this disease, femoroacetabular conflict occurs in patients at an earlier age.
Physical examination
Diagnosis of the disease begins with a test for the functionality of the hip joint. During the examination, the doctor must obtain an objective assessment of the joint performance during flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, rotation. The orthopedist tests the leg with the diseased articulation in any physiologically possible trajectories.
So, the doctor's conclusion after the examination is based on the results of 4 main tests:
-
"Rolling a log". The patient needs to lie on his back, put his hands along the body and relax the limbs. The doctor manually tries to roll the leg from the outside to the inside and in reverse order. If a characteristic crunch is heard during the experiment, the specialist will suspect damage to the articular lip.
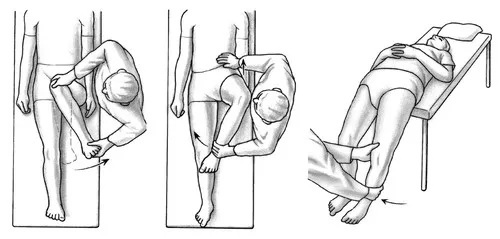
- "Right angle". To identify impingement, the patient needs to bend the leg at the hip joint, trying to form a right angle. The limb is first pressed to the inside of the joint, then to the outside. If during the test the patient complains of pain, it means that the anteroposterior acetabular site collides with the surface of the femoral neck.
- Dremann's Syndrome. The main diagnostic criterion is the patient's ability to painlessly flex the leg at the joint from the position of external rotation.
- C-symptom. The disease is confirmed in case of uncomfortable sensations when clamping the suprauterine zone with the thumb and forefinger.
X-ray
Today, radiography is not considered an advanced method for studying diseases of the musculoskeletal system. However, it is the X-ray that remains the mandatory initial diagnostic measure for suspected hip impingement.
This exploratory procedure does not produce cross-sectional images, however in percentage terms, the level of its information content is considered to be quite high (85-90%).
In order to make a correct diagnosis using X-ray, the study is performed in several projections at once.
In case of femoroacetabular conflict, projections are mandatory:
- anteroposterior (standard);
- Launstein (frog pose);
- lateral;
- when bending the hip at right and sharp angles;
- oblique (technique of "false" profile).
MRI
Impingement syndrome of the hip joint using magnetic resonance imaging is determined with an accuracy of 100%. This type of examination allows you to determine even microscopic changes in the size, shape, location of bones and cartilage.
During an MRI, a complete picture of the disease is revealed, it becomes clear which parts of the joint rub against each other, what symptoms this disorder provokes.
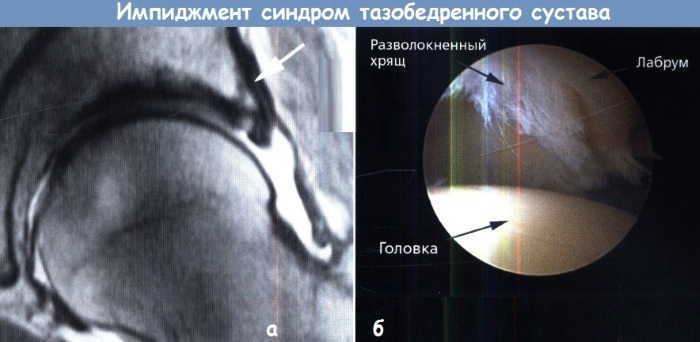
Magnetic resonance imaging is used in complicated generalized forms of joint impingement, requiring a detailed assessment of each fragment of the osteochondral joints.
In addition, MRI allows you to get a clearer picture of the condition of soft tissues, including the synovial membrane and lip. During the diagnosis, cystic and polyposis formations, inflammation of muscle fibers, tendons and bone marrow edema are easily visualized.
Other methods
In addition to radiography and MRI, computed tomography is often used to diagnose femoroacetabular impingement. The advantage of this research method is the ability to obtain volumetric 3D images and a detailed examination of anomalies in bone structure.
Along with instrumental types of diagnostics, if impingement syndrome is suspected, patients are given directions for laboratory blood tests to determine biochemical parameters, as well as to confirm or exclude the inflammatory process in the body.
Methods for treating the disease
The choice of treatment tactics largely depends on the stage of the pathology. The decision to use a particular therapy is applied by the attending physician.
In the initial stages, the treatment of the hip joint is carried out in a conservative way. A medical course and physiotherapy procedures are capable of producing the expected therapeutic effect in an uncomplicated course of the disease.
Otherwise, in parallel with conservative methods, surgical intervention is carried out, which will help correct the structure of the deformed joint and restore its performance.
Conservative treatment
Hip impingement syndrome is a disease that must be dealt with in a complex manner.
Conservative treatment programs for femoroacetabular conflict usually include the following items:
- abstaining from physical activity that causes joint pain;
- temporary immobilization of the limb (with severe edema, inflammation);
- remedial gymnastics, necessary to increase the range of motion and strengthen the muscles that support the work of the joints;
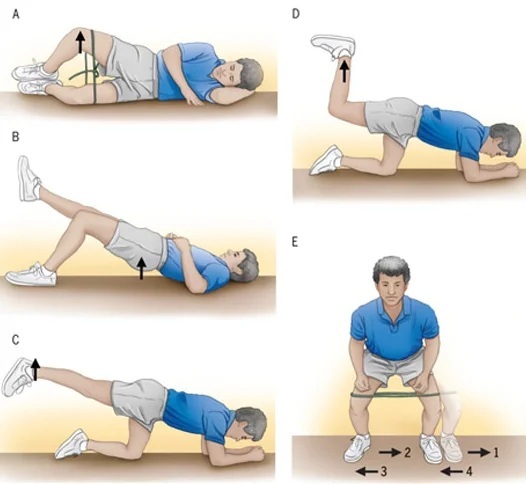
- physiotherapy procedures (exposure to ultrasound, laser, electrophoresis, shock wave therapy);
- a medication course consisting of drugs of the NSAID series, anesthetics and pain relievers, hormonal drugs for intra-articular blockade.
Injection of steroids and hyaluronic acid into the articular space is justified only in the case of confirmed cartilaginous lesions, the pathogenesis of which is revealed using MRI. On the basis of radiographic images indicating the presence of impingement, no drugs with intra-articular administration are prescribed to patients.
If the course of conservative treatment did not allow achieving positive dynamics and arresting painful symptoms, the doctor has no choice but to prescribe a surgical operation to the patient. At the same time, it is important to establish the true cause provoking the impingement.
Without its elimination, there is a risk of recurrence of the disease. Moreover, impingement of the hip joint can turn into a more severe pathology - deforming arthrosis, in which total arthroplasty of the joint is often required.
The use of medications for limiting the mobility of the limbs allows you to achieve only a temporary result. As soon as physical activity resumes and drugs that block pain receptors stop entering the blood, symptoms will return. If conservative treatment for 3-4 months turns out to be useless, then it is not used in the future.
Surgical intervention
With the complete destruction of the hip joint, the only way to put the patient on his feet is an expensive operation to install the endoprosthesis. However, it is important to take into account that not in all cases impingement is a direct indication for surgical intervention.
When deciding on the appointment of an operation to a patient, the doctor must establish whether the disease actually creates for the patient, serious difficulties in everyday life, professional activity, sports and other branches of everyday life life.
Surgical intervention is performed with an open or arthroscopic approach. The task of the surgeon is to eliminate bone growths, thanks to which it will be possible to eliminate the cause of the constant pathological effect of the articular elements with each other.
In open surgery, the surgeon makes a standard incision at least 8 cm long. This type of radical treatment is indicated for idiopathic acetabular impingement, where it is important to get maximum access to the articulation.
When opening the joint, the surgeon has the ability to cut off the greater trochanter in case of hip dislocation. Open surgery is performed in the case of cartilage tissue resection followed by plastic surgery of the proximal glenoid cavity.
Arthroscopy is a medical and diagnostic procedure that is performed using a special apparatus. This manipulation makes sense to carry out with impingement, poorly expressed on X-ray images.
The algorithm for performing arthroscopy is as follows:
- The tube of the optical device is inserted into the joint cavity through a skin incision no more than 1-1.2 cm in size.
- The arthroscope displays an image of the intra-articular surfaces on the screen.
- The surgeon, carefully looking at the monitor, performs a modeling resection: removes excess bone growths, corrects defects with autoplasty.
In 9 out of 10 cases, surgery can help relieve a hip problem. However, the high cost of such manipulations is not suitable for everyone. The minimum price for arthroscopy in Russian clinics is $ 15,000. rubles, maximum - more than 100 thousand. In the capital, the average cost is about 60 thousand. rub.
Foreign medical centers are also ready to accept Russian patients for surgical treatment of impingement syndrome. Promising to carry out the operation in a minimally invasive, safe and effective way, Israeli specialists are requesting at least 14 thousand. dollars, and in Germany - from 10 thousand. Euro.
Rehabilitation
No complicated rehabilitation is required after arthroscopy. Observing all the prescriptions of specialists, the patient will be able to quickly return to a full life.
After open surgery, the hip joint must remain immobilized for a certain period. Its duration is set by the doctor on an individual basis.
Upon completion of the immobilization, the patient should begin to exercise to develop the joint. In combination with physical education, a course of myostimulation and intake of vitamin and mineral preparations are prescribed.
It is possible to avoid hip impingement syndrome only with regular physical activity of moderate intensity. Athletes should pay attention to the correctness of the technique of the exercises performed, and use special bandages for increased loads.
Video about impingement syndrome
About hip impingement syndrome: