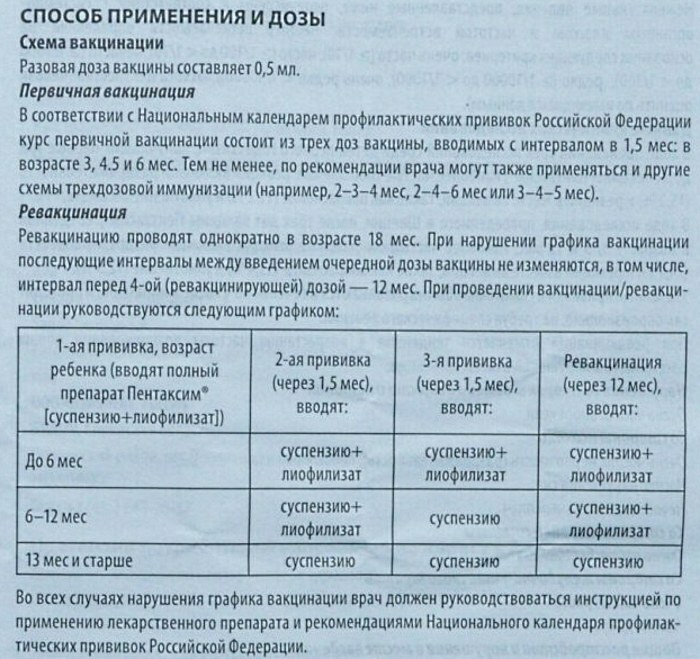
Pentaxim vaccine administration leads to the emergence of a pronounced immune response in a child to causative agents of such dangerous diseases as tetanus, diphtheria, whooping cough, poliomyelitis and hemophilic infection. Like other vaccines that include acellular pertussis component, it is well tolerated and causes few adverse reactions.
This vaccine was first registered in 1997. in Sweden and is now widely used all over the world. It is administered in a three-fold scheme (the first vaccination is in the first year of the child's life, and the revaccination is in the second). Antibodies to these diseases persist for about 5 years.
Record content:
- 1 Features of the composition of Pentaxim
- 2 What is the vaccine for?
- 3 Contraindications to use
- 4 How long can there be a reaction to Pentaxim?
- 5 Normal reaction to Pentaxim in children
-
6 Causes and possible side effects of vaccination
- 6.1 Fever and moodiness
- 6.2 Local allergic manifestations
- 6.3 Neurological phenomena
- 6.4 The child's leg is swollen
- 6.5 Lump (induration) at the injection site
- 7 How can complications be eliminated?
- 8 What is forbidden to do
- 9 How long is the post-vaccination period?
- 10 How is the 2nd and 3rd revaccination tolerated?
- 11 Compatibility with other vaccines
- 12 Vaccine reaction videos
Features of the composition of Pentaxim
The composition of the vaccine (1 dose is 0.5 ml) includes the substances indicated in the table:
| A type | Component | Quantity |
| Main active substances (microbial agents) | ||
| Purified toxins from microbial cells | from a diphtheria bacillus (Corynebacterium diphtheriae) | ≥30 IU |
| from a tetanus stick (Clostridium tetani) | ≥40 IU | |
| from whooping cough (Bordetella pertussis) | 25 mg | |
| Inactivated polio vaccine | the first type (culture of the Mahoney virus) | 40 D units |
| the second type (culture of the MEF-1 virus) | 8 D units | |
| the third type (culture of the Saukett virus) | 32 D units | |
| Pertussis pathogen adhesin (pertussis microbial cell antigen) | Adsorbed purified filamentous hemagglutinin | 25 mg |
| Hemophilus influenza vaccine | Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide | 10 mg |
| Additional components | ||
| Immune response enhancer | Aluminum hydroxide | 0.3 mg |
| Preservatives | 2-Phenoxyethanol in ethanol | 2.5μl |
| Formaldehyde | 12.5 mcg | |
| Acidity regulator | Trometamol | 0.6 mg |
| Stabilizer | Sucrose | 42.5 mg |
| Solvents | Wednesday Hanks 199 | 0.05 ml |
| Water for injections | <0.5 ml |

The reaction to Pentaxim in a child can be associated with any of the main components, since the drug is a combination vaccine used to prevent several diseases.
The medicine is made in the form of a set - a lyophilisate (dried powder) and a suspension (it contains the polysaccharide of the hemophilic rod). Before the procedure, they are mixed in a syringe. This composition is administered intramuscularly.
What is the vaccine for?
Vaccination provides protection against 5 diseases at the same time:
- Diphtheria. This infection is transmitted by airborne droplets and affects the baby's oropharynx and airways. The classic sign of the disease is an off-white film on the palate. In severe cases, intoxication of the body, myocardial damage, paralysis due to damage to the nervous system by toxins that are secreted by the bacteria that cause diphtheria can occur.
- Tetanus. The causative agent of tetanus is widespread in soil contaminated with human and animal faeces. The highest number of infections occurs in infants, the elderly and adolescent boys, as they are most susceptible to trauma. The infection primarily affects the nervous system. Patients die from spasm of the respiratory muscles, paralysis of the heart muscle, myocardial infarction, pneumonia, sepsis and other complications.
- Whooping cough. This disease is also referred to as respiratory disease. A characteristic symptom is a paroxysmal, debilitating cough. About 1 million die from whooping cough each year. children, most of them under the age of 1 year. In them, this disease can lead to respiratory arrest, loss of consciousness, convulsions, paralysis and organic brain damage. The pathogen is easily transmitted from one person to another. In older children, whooping cough is often complicated by pneumonia, urinary incontinence, a sharp drop in blood pressure, and rib fractures.
- Polio. This disease is viral in nature. It leads to damage to the gray matter of the spinal cord and paralysis. Infection occurs through contaminated hands or food, as well as airborne droplets. Most often, the disease affects children aged from six months to 5 years.
- Hemophilic infection. Haemophilus influenzae leads to damage to the respiratory and nervous systems, the development of foci of purulent inflammation in various organs. The infection is transmitted by airborne droplets. Children under the age of 2 years, as well as patients with weakened immunity, are especially often affected.
The reaction to Pentaxim in a child in most cases poses less threat to the patient than the infection itself. The study of Pentaxim around the world shows that the vaccine helps to form a high titer of antibodies and prevent the development of the above diseases.
After 3-5 years after its introduction, the immune system weakens. However, these diseases are usually milder. For example, when infected with whooping cough, complications develop 4 times less often.
Contraindications to use
Contraindications include the following conditions:
- Encephalopathy of the newborn, which is progressive. This condition can occur for various reasons: hypoxia at birth, metabolic disorders (disorders of the metabolism of bilirubin, glucose, magnesium, sodium and other types), intoxication (when taking medications by the mother, with complicated pregnancy), with injuries and other non-inflammatory lesions of the head brain. This diagnosis can only be made by a neurologist. It should be borne in mind that some of the symptoms of encephalopathy may be signs of natural adaptation. newborn, therefore, in the early period, the correct diagnosis is a certain difficulties.

- Encephalopathy (non-inflammatory brain damage), with or without seizures, following a previous vaccination with a composition that contains a pertussis component. Encephalopathy may appear within a week after the procedure. Contraindications are also crying, lasting for a long time, convulsions, sluggish child syndrome (a significant decrease in muscle tone).
- Allergic reactions after the introduction of other vaccines - against diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio and hemophilus influenza, and also when using drugs containing auxiliary components Pentaxim, glutaraldehyde, Neomycin, Streptomycin, Polymyxin.
- Taking immunosuppressive drugs, immunodeficiency states.
- Acute infectious and inflammatory pathologies or a state of exacerbation of chronic diseases.
The last 2 types of contraindications are relative. After such conditions have been eliminated, the administration of the vaccine is permitted. This procedure is also carried out with caution in cases of blood coagulation disorders (bleeding may occur). With the development of acute polyradiculoneuritis or neuritis of the brachial nerve after tetanus vaccination, the appointment of this drug must be justified taking into account the possible consequences.
How long can there be a reaction to Pentaxim?
A reaction to Pentaxim can develop in a child both in the first minutes after its introduction, and in subsequent hours (usually in the first three days).
Normal reaction to Pentaxim in children
Normal reactions to the vaccine include:
- redness and thickening of tissues at the injection site (15% of children under the age of 1 year);
- increased irritability, anxiety of the child;
- disruption of the digestive tract (diarrhea);
- an increase in body temperature up to 38 ° C.
These signs do not require specific treatment and disappear in 1-2 days.
Causes and possible side effects of vaccination
The reaction to Pentaxim in a child can be of 2 types:
- local (pain, redness, swelling, rash, lump at the injection site);
- general (systemic disorders).
In most children, the post-vaccination period is asymptomatic, that is, there are no signs of a violation of the normal state. In very rare cases (less than 0.01% of patients), children develop a rash, severe itchy pink blisters (urticaria), seizures, lethargy associated with a drop in blood pressure, anaphylactic shock (edema Quincke).

Most often, complications are observed in weakened children with a burdened history and other diseases.
At an early age, adverse reactions may be associated with the transferred intrauterine infections, which lead to suppression of cellular immunity. This condition is a risk factor for allergic reactions.
Fever and moodiness
An increase in body temperature after vaccination occurs due to the activation of the immune system.
The prevalence of this side effect is as follows:
- more than 38 ° C - 1-10% of children;
- over 39 ° С - 0.1-1%;
- more than 40 ° C - 0.01-0.1%.
This reaction of the body can develop in the first 3 days after the administration of the vaccine. If the body temperature does not exceed 37.5 ° C, then this is considered a weak reaction and does not require medical intervention. At temperatures exceeding 38.6 ° C, intoxication may occur. This is considered a strong common vaccine reaction.
Anxiety or, conversely, drowsiness, loss of appetite develop in 23% of children. The child may become more moody, often wakes up at night.
Local allergic manifestations
Local reactions to the introduction of foreign biological components of any vaccine can develop according to the following mechanism:
- The appearance of redness of the skin in the area of injection (1-2 days).
- The onset of hypersensitivity or soreness, especially with finger pressure (2-4 days).
- The formation of edema and tissue compaction (starting from the 2nd day).
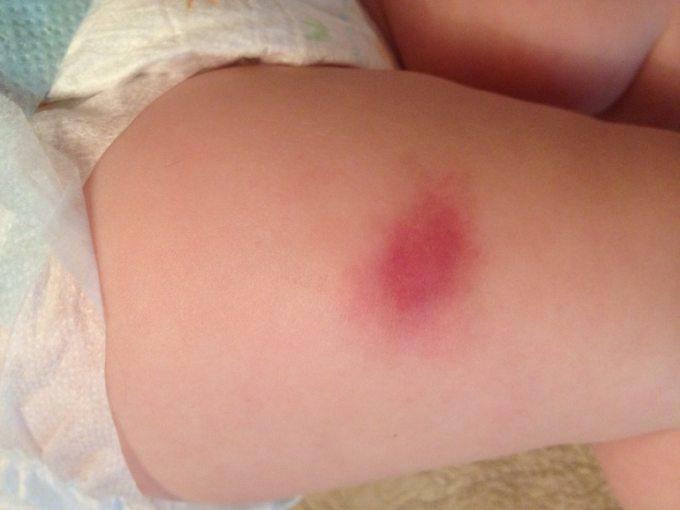
Reaction to Pentaxim in a child
These phenomena go away on their own within 5-7 days. No additional treatment is required. The critical value is the size of local reactions 5-8 cm in diameter (strong local reactions). The incidence of these side effects increases with repeated administration of pertussis vaccines.
Neurological phenomena
As side effects of a neurological nature, the following manifestations may occur:
- increased irritability, anxiety;
- prolonged or unusual crying;
- deterioration in sleep;
- convulsions (with or without fever);
- decreased muscle tone.
Both live and inactivated vaccines can lead to:
- encephalitis (inflammation of the brain);
- encephalopathy (impaired consciousness or behavior lasting more than 6 hours);
- myelitis (inflammation of the spinal cord);
- neuritis (inflammation of the peripheral nerves);
- polyradiculoneuritis (multiple lesions of peripheral nerves and their roots).
These complications appear within 10 days after the injection. In many cases, this drug is only a triggering factor for the development of neurological symptoms, and the disorder itself already existed before.
Encephalitis often occurs against the background of a viral infection that has joined, therefore, in case of diseases of an infectious and inflammatory nature, this procedure should be postponed until the child is fully recovered.
Anaphylactic shock can develop in the first minutes or 3-4 hours after the administration of the drug, but this happens extremely rarely.
The child's leg is swollen
The appearance of a pronounced swelling of tissues larger than 5 cm is a prognostically unfavorable reaction of the body and requires a visit to a doctor. If the redness or swelling is less and there is no tendency to increase, then this does not require medical intervention.
Lump (induration) at the injection site
Tissue thickening at the injection site is a common complication. If it is accompanied by tissue redness, soreness, fever, then you need to see a doctor.
The causes of lumps are the following:
- rapid administration of the drug and compression of the surrounding tissues;
- the reaction of the immune system - the flow of lymphocytes to foreign agents and the development of a protective inflammatory response;
- when injected into the subcutaneous fat, and not into the muscle.
How can complications be eliminated?
To eliminate the above conditions, the following methods are used:
- When the temperature rises above 38.5 ° C - antipyretic drugs (Panadol, Tsefekon D, Nurofen and others). To prevent dehydration of the body, the child can be given Regidron, Hydrovit. Body temperature should be monitored for at least 2 days after drug administration.
- To eliminate allergic reactions: in 1-2 days, the child is given antihistamines (Fenistil or Zyrtec drops from 6 months). Their reception continues for another 2 days after the introduction of the drug. Fenistil gel is used to eliminate local irritation.
- In case of malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract - Polysorb. It is diluted in breast milk and given to the child for 3-5 days at the dosage indicated in the instructions.
What is forbidden to do
It is not recommended to do the following:
- introduce new foods into the child's diet before and after vaccination;
- use analgesics and antipyretic drugs that are not intended for use by age (Aspirin and Nimesulide are prohibited until 12 years old);
- wet the injection site during the day, bathe the child;
- wipe the skin with vodka in order to lower body temperature;
- walk the first day after vaccination, actively contact people, as this can contribute to infection;
- rub the injection site or use lotions, creams, ointments.
How long is the post-vaccination period?
The post-vaccination period lasts no more than 1 month. If after this period there are undesirable reactions, then they are not associated with the vaccine.
How is the 2nd and 3rd revaccination tolerated?
With repeated revaccination, the incidence of local adverse reactions increases. However, general adverse events are noted at the same low level as with the initial administration of Pentaxim.
Compatibility with other vaccines
This vaccine combines well with other drugs that are used for immunization of hepatitis B, measles, rubella and mumps, pneumococcal infection.
Medical research shows that the reaction to Pentaxim in most children does not occur or manifests itself in a mild form. This drug has a good safety profile.
Most often, the child has local undesirable phenomena in the form of redness, itching, and slight edema. They go away on their own within a week. Weakened and sick children may experience general complications.
Vaccine reaction videos
How are local reactions to vaccinations: