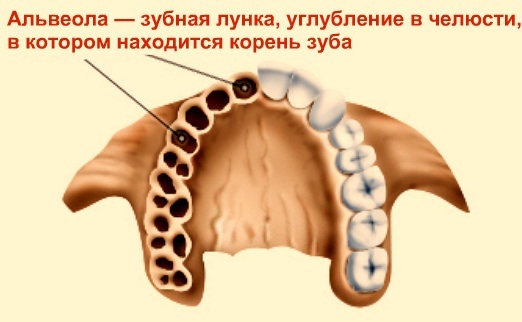
In the bone structure of the upper and lower jaw, the alveoli are anatomical depressions. In to the mouth, they are designed to fix the teeth. Otherwise, they are called tooth sockets. They are located on the surface of the bones of the upper and lower jaw.
The wells are composed of connective tissue, covered with a mucous membrane. Normally, they are filled with a healthy tooth. The main diseases occur after tooth extraction (post-extraction alveolitis). But there are also more rare pathologies.
What are the alveoli of the teeth
The alveoli in the mouth are located in the bone tissue of the alveolar processes of both jaws. These are depressions called sockets. In them, with the help of connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves, first the milk teeth, and then the molars are fixed.
Normally, their mucous membrane is not exposed. After extraction or loss of a tooth, a "hole" is formed. This is the hole or alveolus. Gradually, the exposed surface is covered with granulation tissue and epithelialized, that is, it becomes covered with connective tissue.
The hole is not involved in the chewing process. But during healing, food can get there. This slows down the healing process, causing alveolitis and other inflammatory changes in the mouth.
Record content:
-
1 Alveoli in the mouth
- 1.1 Structure
- 1.2 Functions and location
- 1.3 Upper alveoli of teeth
- 1.4 Alveolitis of the tooth socket
- 2 The causes of the appearance of alveolitis
- 3 Symptoms
- 4 Possible complications
- 5 Power features
- 6 Hygiene rules
- 7 How to treat
- 8 Oral Anatomy Videos
Alveoli in the mouth
The structure of the alveolar bone is simple. These are the alveolar processes. Teeth are attached to them with the help of root cement. The wells are made up of walls. The inner oral wall (otherwise called the lingual), as well as the outer wall (buccal) are counted.
At the edges of the process, they are visible in the form of arches. They are separated from each other by partitions. Complex molars also have internal partitions, usually up to 4 pieces. They are called inter-root.
Structure
The alveolar process itself consists of cortical bone plates. This is the so-called compact bone substance. Its structure also has room for blood vessels that feed the tissues of the tooth. Arteries and veins are located in the central canals, which are made of bone plates oriented concentrically.
Approaching the edge of the jaw process, the mentioned bony cortical plate acquires a more mottled structure. This is necessary to conduct smaller and more numerous vessels and nerve endings to the tooth tissue.
There is a space between the cortical plates of the alveolar process and the walls of the hole. It is made of chaotically oriented cancellous bone fibers. Between its cells is the substance of the red bone marrow in children, which in the adult state is replaced by yellow bone marrow.
The alveoli in the mouth are on the border with the dental tissue. The walls of the hole are strong. They are made of bony plates that release a large number of nerve endings. This leads to a high sensitivity of the alveolar mucosa.
Functions and location
The main purpose of the dental alveoli is to correctly orient the tooth and fix it in this anatomically and physiologically correct position. This is important for the formation of the correct bite.
This ensures the normal functioning of the entire oral cavity and its participation in digestion. But this does not limit the significance and role of the tooth socket. In case of violation of interdental and other anatomical relationships, there is a risk of impaired diction and speech.
In case of violations of the fixation of the tooth, it begins to stagger. This entails the risk of periodontitis and other inflammation in the oral cavity. Ultimately, the teeth will not last as long as possible, but will deteriorate, necessitating premature dentures.
Upper alveoli of teeth
The anatomical structure of the sockets of the upper and lower teeth is practically the same. The structure is absolutely identical.
The only difference lies in the anatomical proximity of the alveolar process to the tissues of the soft palate. With diseases and defects of the alveoli of the upper teeth, diction and speech disorders are formed. In addition, the infection from there quickly spreads to the neighboring ENT organs.
Alveolitis of the tooth socket
It is an inflammation of the mucous membrane and soft tissues of the dental alveoli. Among other diseases, this pathology is currently in first place in terms of frequency of occurrence.
The main cause of the phenomenon is the spread of infection after tooth extraction. But there are other etiological factors.
The causes of the appearance of alveolitis
The inflammatory process develops due to the effect on the mucous membrane and soft tissues of the alveoli of the bacterial flora. As a rule, these are own bacteria, which are opportunistic. That is, in a healthy person, under normal conditions, they do not cause an infectious process.
But when favorable for the activation of their pathogenic properties, they cause inflammation.
The reasons for the development of alveolitis:
| Risk factors | Description |
| Tooth extraction and its consequences. | There are several possible factors. First of all, there is a danger of traumatic damage to the walls of the hole. They are very thin and contain a large number of small vessels and nerve endings. It is quite easy to damage them, especially if the dentist does not have sufficient experience in extractions. Often, for this reason, alveolitis develops when eights are removed, or the so-called "wisdom teeth". They have many roots, the arrangement of which is very ornate.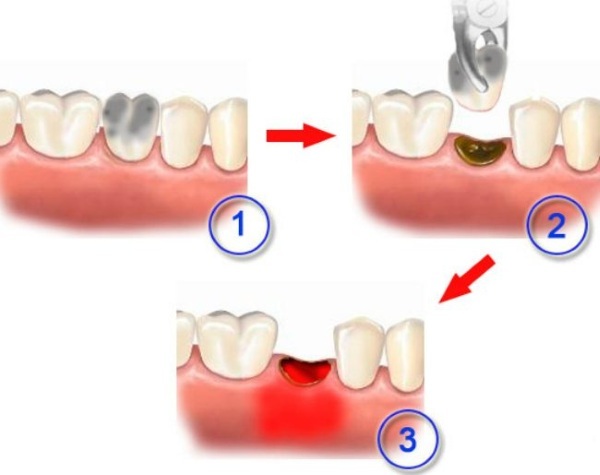 Fragments of a tooth may remain in the exposed hole. Therefore, X-rays are included in the standards of treatment and examination before and after tooth extraction. |
| Reduced immune status of the body. | This applies to malnourished patients (old age, severe somatic diseases), as well as those with immunodeficiency (HIV infection, patients with cancer or systemic diseases requiring treatment with drugs that inhibit immunity). Own protection factors do not work, and the conditionally pathogenic flora of the oral cavity causes active inflammation of the tissues of the tooth socket. |
| Violation of sanitary and epidemiological standards. | Bacteria can also be introduced into the oral cavity due to insufficient adherence to the principles of antisepsis and asepsis. Therefore, it is extremely important to choose clinics where these conditions are met to the extent required. When removing molars, it is recommended to visit large regional or city clinics. |
| Inflammatory processes in the oral cavity and ENT organs. | Against the background of acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections, tonsillitis and other inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity and ENT organs, it is not recommended to remove teeth. Otherwise, these foci can become the source of infection. The condition will be complicated by bacterial post-extraction alveolitis of the tooth socket. |
The main factor contributing to normal, timely healing after removal is an adequate blood supply to the injured area, as well as the formation of a blood clot.
This process can be hampered due to the following possible reasons:
- food ingress into the alveolar cavity;
- taking anticoagulants, drugs that reduce blood clotting ("thin"), for example, Warfarin, Clopidogrel, Cardiomagnyl;

- diabetes mellitus (a condition in itself that prevents normal healing, especially without proper blood glucose control).
Failure to follow the doctor's recommendations entails the risk of complications. This is especially true of the rules of hygiene of the naked hole and the prophylactic intake of antibacterial agents.
Symptoms
The pain in this condition is quite pronounced, intensifies during meals. May not be relieved by low-dose analgesics. Pain syndrome is localized at first in the area of the extracted tooth.
When the infection spreads to adjacent tissues, the area of pain impulses also increases. The immune system responds by increasing the concentration of white blood cells and lymphocytes. Therefore, regional lymph nodes increase. They can also be painful, including on palpation.
When pain spreads to the temporal region or to the ear, one should think that the infection has spread to the ENT organs. This requires the consultation of an ENT or maxillofacial surgeon for timely and adequate treatment, possibly operative.
Sometimes alveolitis begins gradually with discomfort when opening the mouth. Further, pain joins, the nature of the same as described above.
The inflammatory process is manifested by weakness, fatigue. The body temperature rises. If the febrile level is reached (above 38.5 degrees), then chills are worried. In addition to local pain in the gum region, a headache appears as a sign of a systemic inflammatory process.
An unpleasant odor appears from the mouth. When a purulent component is attached, it intensifies and becomes specific. Sometimes the smell resembles rot. If a sweetish, sugary smell appears, one should be wary of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection, which is very difficult to treat.
Alveoli externally with inflammation look edematous. The mucous membrane in the mouth at the site of the alveolitis is clearly reddened. There may be a grayish coating on the surface. If cyanotic mucosa is visible, then it may be necrotic tissue.
Possible complications
Among the most common complications of alveolitis, there is a lesion of the facial nerve. It can be caused by compression by inflamed tissues. This condition is manifested by paresthesias in the chin area. This is a kind of burning sensation, crawling "goose bumps".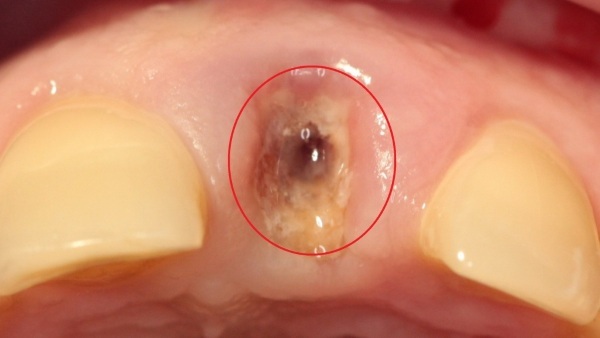
A more severe complication is associated with the spread of infection to adjacent tissues and the attachment of pyogenic flora. This is how a limited area of purulent infection appears - an abscess, and an unlimited area - phlegmon. In the latter case, the risk of developing odontogenic sepsis increases.
The inflammation can spread to the jawbone. In this case, osteomyelitis is formed. In this case, it can arise acutely, after a long time after the transferred alveolitis.
When the molars of the upper jaw are removed, an anastomosis is sometimes formed between the hole and the maxillary sinus. This is fraught with the occurrence of chronic sinusitis refractory to antibacterial treatment. In this situation, it is also odontogenic.
Power features
Therapeutic recommendations for alveolitis and for the prevention and development of alveolitis contain recommendations for food intake. After tooth extraction, the fasting time should be about 3 hours. If the figure eight was removed, then this period increases to 4-5 hours.
The first snack should be light. It is better if you use products with a homogeneous semi-liquid consistency. For example, pastas, yoghurts or purees. Hot food should not be eaten, as high temperatures prevent the formation of blood clot as a necessary factor for the timely and physiological healing of the resulting mucosal defect shell.
For the next two days, the principles of nutrition are the same. Food should be thermally and mechanically gentle. It is necessary to exclude the ingress of solid food into the well. It is advisable to protect yourself from seeds, nuts, fruits with small hard seeds.
The food temperature should be between 27 and 40 degrees. Hot or overly cold foods can interfere with tissue healing.
Hygiene rules
It is not necessary to remove the gauze swab immediately after tooth extraction. After 15 minutes. it can be removed. You do not need to re-place a dry swab on your own in the area of the well. The risk of infection and the formation of a dry socket increases.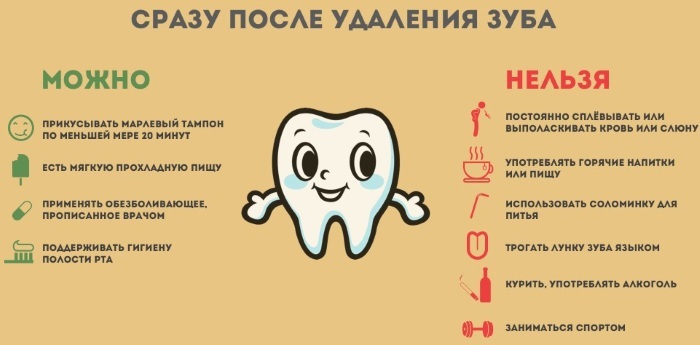
You should not touch the place of the extracted tooth with your tongue. Thus, you can deprive the alveoli of the protective clot. It is not recommended to chew food on the side where the tooth was extracted during the day. After eating, the mouth is washed with water at room temperature.
Brushing your teeth during the first 2 days on the side of the extraction should be extremely careful, without using hot water.
For the first 3 days, it is advisable to use antiseptic solutions instead of water for rinsing. An aqueous solution of Chlorhexidine, Hexoral and Stomatidin are well suited for this. Furacilin is dangerous to use, since according to recent studies, irrigation of the oral cavity with it creates favorable conditions for the colonization of the mucous membrane by fungi.
How to treat
The alveoli in the mouth are located near the facial nerve, therefore, most often there is acute pain in the symptomatology, in most cases, grasping and trigger points. Pain syndrome with alveolitis is stopped by non-steroidal analgesics. Nimesulide helps best. If the pain is severe, Ketorol or Diclofenac can be injected.
Antibacterial drugs are used as etiotropic drugs. The choice should be based on whether any antibiotics have been taken in the past 2 months, as well as options for intolerance.
In the initial stages, Lincomycin helps well. Dentists also prescribe Tsifran OD. The standard dose is 500 mg once a day.
The course of admission should not be less than 7 days. If these terms are not met, resistance to this group of antibacterial agents is usually formed. With the pathology of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, Flemoxin solutab is used.
Local treatment is performed by a dentist. At the same time, food debris and necrotic tissue, if any, are carefully removed. Then the mucosal area is treated with antibiotics and antiseptics.
If the facial nerve is damaged, physiotherapy is prescribed. This is usually an ultrasound or laser. Warming up is not recommended.
From folk remedies, only rinsing with chamomile infusion is allowed. An alternative is irrigation of the oral cavity using an alcoholic solution of Eucalyptus tincture diluted with water.
Wells (alveoli) in the mouth after tooth extraction should be processed correctly as much as possible. After all, they are close to the ENT organs, to which inflammation spreads in case of infection. Therefore, you should not ignore the doctor's advice on hygiene and prevention of complications. This is important for keeping your teeth healthy for a long time.
Oral Anatomy Videos
Oral cavity:



