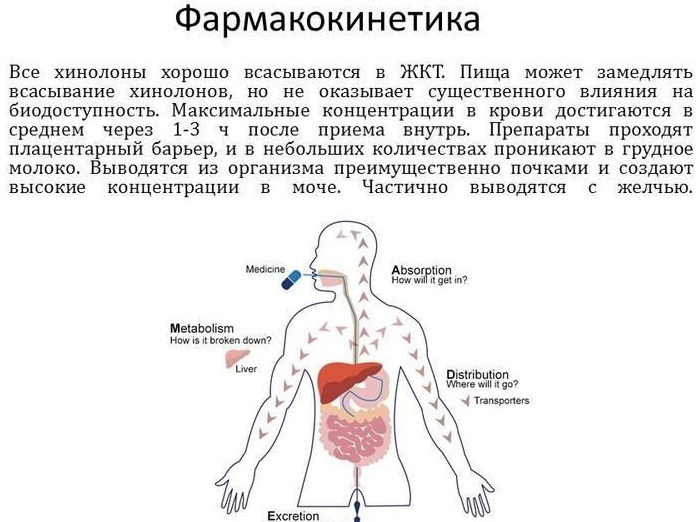
Antibiotic groups are replenished daily with new medicines aimed at combating pathogenic microorganisms. Classification involves the separation of funds depending on the mechanism and spectrum of action. Each type of medication can be aimed at destroying one or several types of bacteria, which makes it possible to select the most effective drug for different diseases.
Record content:
- 1 What are antibiotics, for what purpose are they prescribed?
-
2 Classification of antibiotics
- 2.1 By the mechanism of action
- 2.2 By chemical structure and origin
- 2.3 By the spectrum of action and purposes of application
- 3 Modern classification of antibiotics
-
4 The action of antibiotics of different groups. Essential drug lists
- 4.1 Penicillins
- 4.2 Cephalosporins
- 4.3 Carbapenems
- 4.4 Monobactams
- 4.5 Aminoglycosides
- 4.6 Macrolides
- 4.7 Sulfonamides
- 4.8 Quinolones
- 4.9 Tetracyclines
- 5 Antibiotic videos
What are antibiotics, for what purpose are they prescribed?
Antibiotics are substances that can affect the growth and reproduction of cells, as well as destroy them by stopping all life processes. Some funds are aimed solely at slowing growth and development, while others directly at the destruction of microorganisms.
The funds do not have any effect on viruses, therefore they are absolutely useless for treatment diseases of viral origin, even in the case of their severe course with a significant increase body temperature.
Experts today call antibiotics antimicrobial drugs, since the first term was given to drugs that were of natural origin, that is, they were derivatives of penicillin.
Synthetic medicines are today called antibacterial chemotherapy drugs. They are prescribed for inflammatory diseases that are provoked by microorganisms that are sensitive to one or another group of antibiotics. The main goal of such drugs is to stop the growth and development of microbes, followed by complete destruction.
In this case, the tissues are cleansed from the decomposition products of bacteria and the inflammatory symptoms are eliminated. In addition, drugs are prescribed in order to localize the focus of infection and prevent the spread of bacteria to healthy tissues and into the systemic circulation.
When ingested, the active components quickly accumulate in the affected area and begin to act. This improves the patient's condition, normalizes body temperature and gradually cleansing the body of toxins.
Classification of antibiotics
Groups of antibiotics, the classification of which has been improved over many decades, differ depending on their mechanism of action, as well as their structure and origin.
By the mechanism of action
Depending on the mechanism of action on living pathogenic cells, bacteriostatic and bactericidal groups of drugs are isolated. The former are considered to be more gentle, since they stop the growth of cells and disrupt the processes that support their vital activity.
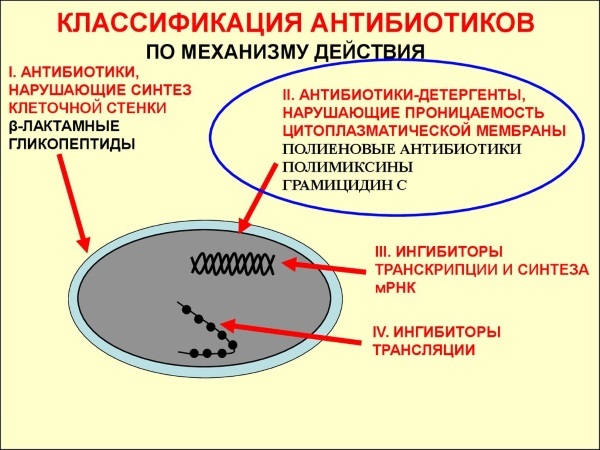
However, this group is also divided into several subgroups, depending on what processes in disease-causing cells they violate:
- Drugs that disrupt the synthesis of polymers, which are necessary for building a cell membrane.
- Drugs affecting the permeability of the cell membrane. This allows the active ingredients to enter the cell and gradually destroy it.
- Medicines that suppress the synthesis of nucleic acids necessary for the normal functioning of a microorganism.
- Medicines that inhibit the synthesis of proteins in the cell.
Any type of bacteriostatic antimicrobial drugs can quickly eliminate the pronounced symptoms of the disease, provoked by the excessive activity of pathogenic bacteria.
Bactericidal drugs do not affect the processes in the cell, but immediately after a collision with pathogens, they destroy microbes that are sensitive to them. There are antibiotics that simultaneously have a bacteriostatic and bactericidal effect. They are the most effective.
By chemical structure and origin
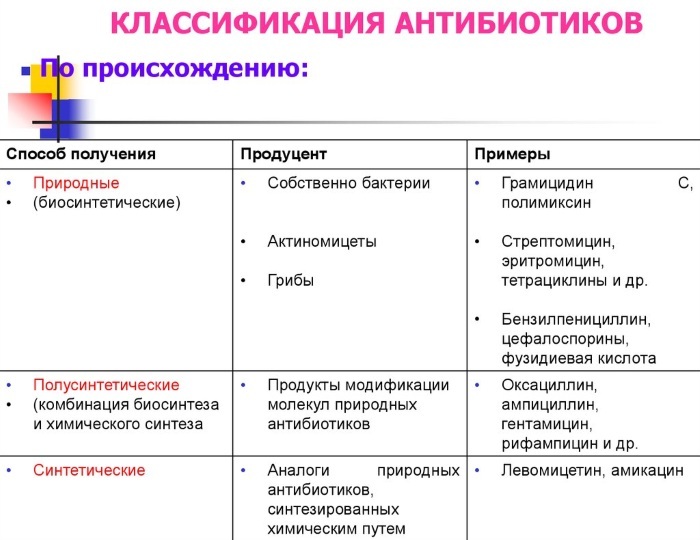
Taking into account the origin, antibacterial drugs are divided into natural, semi-synthetic and synthetic. The former, in most cases, are derivatives of penicillin, since it was this substance that was isolated at the end of the 19th century.
Semi-synthetic are obtained by synthesizing a substance that was obtained naturally in the initial stages. Synthetic agents can no longer be called antibiotics, since this group includes only those drugs whose active component is obtained in a completely natural way.
That is why synthetic antibiotics are classified as antimicrobial or antibacterial drugs.
Depending on the chemical structure, specialists also allocate several groups of funds:
- Beta-lactam antibiotics can be of natural, semi-synthetic or synthetic origin. The first representatives of the flock are penicillins with the addition of potassium or sodium salt, as well as benzylpenicillin procaine. After that, semisynthetic penicillins of a narrow and broad spectrum of action appeared, as well as funds aimed directly at the destruction of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, as well as gram-negative bacteria. This group also includes cephalosporins, as well as other medicines that have a lactam ring in their structure.
- Macrolides and azalides are represented by a small group of agents that are highly effective due to their structure. The drugs are synthetically obtained and are active against various groups of microorganisms.
- Aminoglycosides have special components in the structure that allow you to synthesize the most effective means. The group includes natural and semi-synthetic drugs.
- Tetracyclines can be semi-synthetic and natural. They contain quaternary structures that provide high efficiency and speed, as well as influence on several groups of microorganisms.
- Dioxyaminophenylpropane derivatives.
- Cyclic polypeptides formed as a result of the synthesis of peptide chains.
- Polyene the funds contain antifungal components.
- Steroid drugs in the base they contain components that in their action are similar to hormonal agents.
-
Lincosamides are of natural and semi-synthetic origin.

In addition, specialists single out in one group agents that may contain polypeptide chains, as well as lactam rings and other components, which does not allow them to be attributed to any group.
By the spectrum of action and purposes of application
Groups of antibiotics, the classification of which has changed over the years, are distinguished depending on the spectrum of action. The most commonly used drugs are a narrow spectrum, the active component of which is aimed at combating a certain type of microorganism, as well as broad-spectrum drugs.
The latter are considered the most popular because they help get rid of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, as well as many other types of microbes that can provoke inflammatory process.
Depending on the purpose of use, antibiotics are isolated, which are prescribed to prevent postoperative complications. For example, during a planned operation, the patient undergoes a course of antibiotic therapy. In addition, there are medications used for emergency prevention of sexually transmitted diseases.
Most often, drugs are used, the action of which is aimed at localizing microorganisms only in the area of inflammation. This minimizes the risk of complications and prevents the spread of bacteria through the systemic circulation.
Additionally, there are antibiotics in the form of external agents that are used to prevent the spread of infection into deep tissues and internal organs. They are necessary when the body is not affected by bacteria, and the focus is located on the skin or in one of its layers.
Modern classification of antibiotics
The modern classification of antibacterial drugs does not divide funds depending on the spectrum of action, as well as the purpose of use. Experts have compiled a table, it contains all the drugs that are well studied and used most often.
| Group | Subgroups and subclasses |
| Beta-lactams | This group includes natural penicillins, drugs with a combined composition and a wide spectrum of action. In addition, 4th generation monobactams, carbapenems and cephalosporins are also part of the group. |
| Aminoglycosides | All 3 generations of drugs in this group. |
| Macrolides | These include azalides, as well as 14- and 16-membered drugs. |
| Sulfonamides | In the group, local funds are allocated, short-acting drugs. But the most popular are long-term and ultra-long-acting medicines. |
| Quinolones | The group consists of funds of the 1st, 2nd, 3rd and 4th generations. |
| Anti-tuberculosis | The groups include funds from the reserve subgroup. |
| Tetracyclines | Semi-synthetic and natural medicines for local, systemic use. |
There is also a rather long list of products that are not included in any of the groups. Doctors examine them separately, but do not classify them in the modern classification of antibacterial agents.
The action of antibiotics of different groups. Essential drug lists
Groups of drugs with antimicrobial action consist of antibiotics with different properties. The classification includes many medicines, but several groups are considered basic, therefore they are used in the overwhelming majority of cases.
Penicillins
Penicillins are the first class of drugs, they can be called full-fledged antibiotics, since most drugs are of natural origin. They were discovered several decades ago. Experts pay attention to the fact that the funds were just discovered, since penicillin has always existed in nature and is produced by fungi from the genus Penicillins.
Preparations of natural origin are effective in combating gram-positive microorganisms:
- Streptococci are hemolytic.
- Meningococci.
- Pneumococci.
- Corynebacterium diphtheria.
- Pale treponema.
- Leptospira.
- Anthrax pathogens.
When using benzylpenicillins, it should be borne in mind that they are destroyed in the acidic environment of gastric juice, therefore, the funds are available only in the form of a powder for the preparation of a solution for intramuscular introduction.
A feature of natural penicillins is the ability to spread throughout the body, except for the stomach and meninges. This feature allows the use of agents for the destruction of bacteria in different tissues and organs.
The most popular representatives of penicillins:
- Oxacillin.
- Benzylpenicillin.
- Augmentin.
- Amoxicillin.
- Ampicillin.
The principle of action of penicillins is based on the effect they have on processes in pathogenic cells. Their gradual destruction occurs due to the destruction of the cell membrane.
However, the lack of drugs from this group is the lack of effect on cells at rest. That is, in the event of the multiplication of microbes, some of them will continue to actively divide, while others do not manifest themselves. Therefore, penicillins are not capable of destroying them.
Cephalosporins
Cephalosporins are represented by four generations of antibiotics, the action of which is aimed at destroying gonococci, Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. They also effectively fight Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella and Salmonella. In recent decades, funds have been withdrawn that allow you to destroy Proteus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Haemophilus influenzae.
The mechanism of action of the funds is based on suppressing the activity of microorganisms, stopping their growth and complete destruction. The drugs affect not only active microorganisms, but also bacteria that do not multiply. This explains their effectiveness in the treatment of acute inflammatory processes.
Most often, patients are prescribed the following medications:
- Tsiprolet.
- Ceftazidime.
- Cefuroxime.
- Cefotaxime.
- Cefepim.
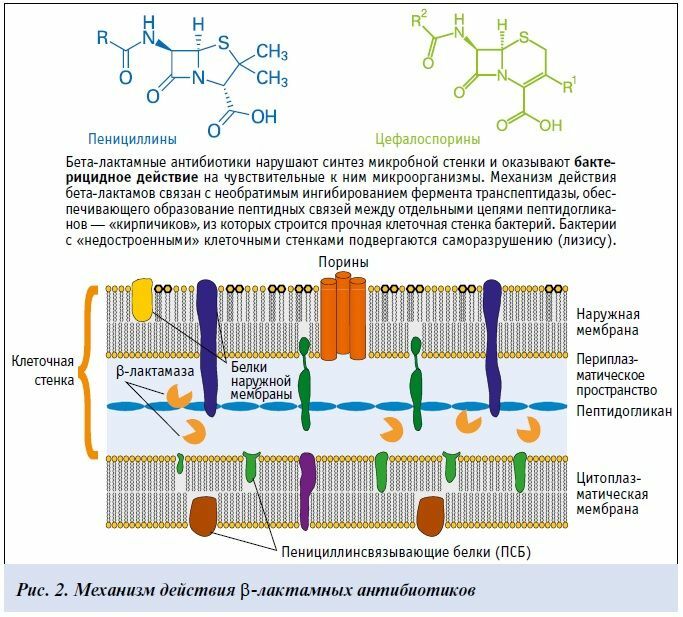
Representatives of the first two generations are used at the initial and progressive stages of the disease, when there are no signs of complications. Preparations of the 3rd and 4th generations are indicated in the case of advanced inflammation with the spread of microorganisms in the systemic circulation or localization in healthy tissues.
Carbapenems
Broad-spectrum drugs that affect most types of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. The mechanism of action is based on stopping the growth of microorganisms with their subsequent destruction. Due to this, the inflammatory process is localized and the spread of microbes to healthy tissues is prevented.
The most commonly prescribed are Biapenem, Meropenem, Ertapenem. They also use Faropenem, Imipenem.
Monobactams
Groups of antibiotics (the classification is complete and expanded or modern) include monobactams, which are considered quite effective. However, in clinical practice, only one medication is used - Aztreonam. It is taken orally, quickly absorbed in the human body.
A feature of monobactams is the ability to penetrate the placental barrier, the membranes of the brain and into breast milk. The drugs have bacteriostatic activity, that is, they disrupt the formation of the cell wall, which prevents bacteria from multiplying and spreading through the systemic circulation.
Monobactams have a rather narrow spectrum of action. They are ineffective against anaerobes and gram-positive cocci. That is why the funds are used in rare cases, when experts are sure that the disease is caused by microorganisms sensitive to monobactams.
Aminoglycosides
The drugs in this group are considered to be quite effective. The mechanism of action is based on the disruption of the process of protein formation in the ribosomes of microorganisms. Due to this, there is a gradual decrease in the activity of bacteria, followed by their destruction. Aminoglycosides allow you to fight against gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms.
Unlike monobactams, drugs from this group penetrate tissue barriers much worse. Active components are not concentrated in bone tissue, cerebrospinal fluid and bronchial secretions. Experts distinguish 3 generations of aminoglycosides. The first includes Kanamycin and Neomycin, the second - Streptomycin and Gentamicin. The third generation includes Amikacin, Hemamycin.
Macrolides
This group of funds is considered the most effective and safe. Many medicines can be used during pregnancy, since they do not have a toxic effect on the fetus and the mother's body.
Means from the group of macrolides in a low dosage have a bacteriostatic effect by suppressing the formation of protein in the ribosomes of pathogenic microorganisms. However, with an increase in dosage, the drugs have bactericidal properties, they can quickly destroy pathogens.
Most often, experts prescribe Azithromycin, Sumamed or Josamycin. The latter medication is considered to be very effective and relatively safe. In addition, Erythromycin and Clarithromycin are prescribed. They appeared earlier than other drugs in this group, but are not considered safe for pregnant women.
Sulfonamides
Groups of antibiotics, the classification of which allows you to get a general idea of the variety of drugs, have sulfa drugs on their list. As the main method of therapy, medicines are not used, since today many gram-positive and gram-negative microbes have developed resistance to them.
However, as an additional method of therapy, drugs are quite effective. The mechanism of action is based on bacteriostatic activity, which prevents the growth and development of pathogens. Specialists also allocate funds for short, medium, long and ultra-long action. The latter are considered the most effective.
Most often, patients are prescribed Sulfodimethoxine, Sulfazim, Sulfalene. In addition, Sulfanilamide and Biseptol are used. The last medication is a combined remedy.
Quinolones
One of the most popular and frequently used groups of funds. Quinolones have bactericidal activity, therefore they quickly destroy pathogens. They are effective against many gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria that provoke inflammatory pathologies of the respiratory, urinary, and digestive systems.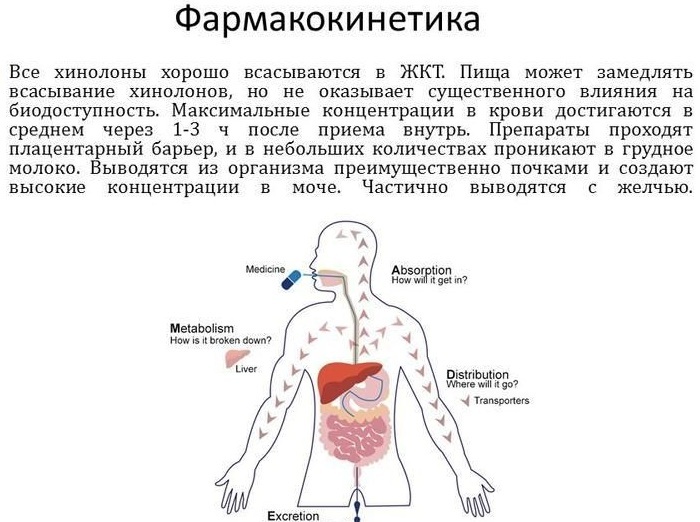
Among the most popular products in the group are the following:
- Levofloxacin.
- Ciprofloxacin.
- Moxifloxacin.
- Sparfloxacin.
- Ofloxacin.
In the composition of medicines there is nolidix or oxolinic acid, in the new generation of drugs there are also other substances that provide high efficiency.
Tetracyclines
Drugs from the tetracyclines group are not often used in therapeutic practice today, since they provoke many negative reactions, especially in pregnant women.
The mechanism of action of the drugs is based on suppressing the growth and development of pathogenic bacteria. Due to this, there is a sharp decrease in the concentration of bacteria in the body, which leads to gradual death.
Among the tetracyclines are Doxycycline, Tetracycline, Oxytetracycline. Sometimes monocycline and metacyclin are prescribed. The danger of drugs from this group is the ability to penetrate the placental barrier and have a toxic effect on the fetus, especially on the skeletal system.
Groups of medicines with antimicrobial activity include many antibiotics that have different effects on the body and help fight inflammatory diseases. The classification of funds helps specialists to choose the most effective medicines and those that can be used for specific pathologies.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Antibiotic videos
Basic pharmacology of beta-lactams: