Prescribed antibiotics with intestinal infections bacterial nature, affect the cause of the disease. If they are selected correctly, then the patient is recovering quickly, otherwise a lethal outcome is possible.
Record content:
- 1 The mechanism of action of antibiotics
- 2 Requirements for antibiotics for intestinal infections
- 3 When are they shown?
- 4 Contraindications and side effects
- 5 How is the selection of the drug
-
6 List of the best drugs
- 6.1 In tablets
- 6.2 In ampoules
- 6.3 For acute intestinal infection
- 7 What is prescribed during pregnancy?
- 8 Antibiotics for children
- 9 Recovery after taking antibiotics
- 10 Prices in Moscow, St. Petersburg and regions
- 11 Video about antibiotics for intestinal infection
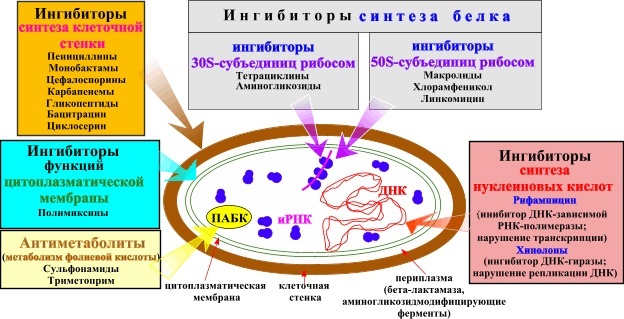
The mechanism of action of antibiotics
An antibiotic for intestinal infection can have a bactericidal or bacteriostatic effect.
The drugs of the first group cause the death of pathogenic microorganisms. Medicines of the second group stop the growth of pathogenic bacteria. It happens that the same antibiotic, depending on the dose, can have both bacteriostatic and bactericidal effects.
The benefits of antibiotics include:
- they destroy pathogenic microorganisms that cause infection, that is, they eliminate the cause of the disease;
- if the medication is selected correctly, then the infection is treated quickly;
- antibiotics are available in various dosage forms, which allows you to choose the most convenient, for example, a person cannot, for any reason, take pills and capsules, perhaps an appointment injections;
- there are antibiotics that are allowed for children and women in position;
- different cost of medicines, you can choose a budget option.
The disadvantages include the following:
- the presence of contraindications to the initiation of therapy;
- the occurrence of side effects, including life-threatening ones.
Requirements for antibiotics for intestinal infections
An antibiotic for intestinal infection must meet the following requirements:
- After oral administration, the drug should not be destroyed by gastric juice, but retain its effectiveness in order to act in the intestines.
- Do not be absorbed in the upper digestive tract in order to sanitize the entire large intestine.
- It is good to combine with sulfa drugs such as Phthalazol, Sulfadimethoxin and enterosorbents, for example, with Neosmectin.
- Do not adversely affect the patient.
When are they shown?
Antibiotics should act on the following pathogens of intestinal infections:
- proteas;
- salmonella, including those that cause typhoid fever;
- cholera vibrio;
- shigella;
- enterobacteria;
- Escherichia coli.
The indications for the appointment of antibiotics are as follows:
- typhoid and paratyphoid fever;
- cholera;
- shigellosis;
- salmonellosis;
- escherichiosis.
Be sure to prescribe antibiotics in the following cases:
- The patient is in serious condition when, due to an intestinal infection, signs of dehydration have appeared, especially in children of the first year of life.
- Symptoms of blood poisoning have appeared.
- Intestinal infection has appeared in patients with cancer, immunodeficiency, or hemolytic anemia.
- The appearance of mucus and blood in the feces, the detection of a large number of leukocytes in them.
- Detection in the blood of high ESR and leukocyte count.
Contraindications and side effects
With intestinal infection, antibiotics of various groups are used, which have various contraindications and adverse reactions.
Tetracyclines are contraindicated in women in position and breastfeeding, in children under 8 years of age, as well as in patients with severe liver dysfunction. Tetracycline is prohibited in renal failure.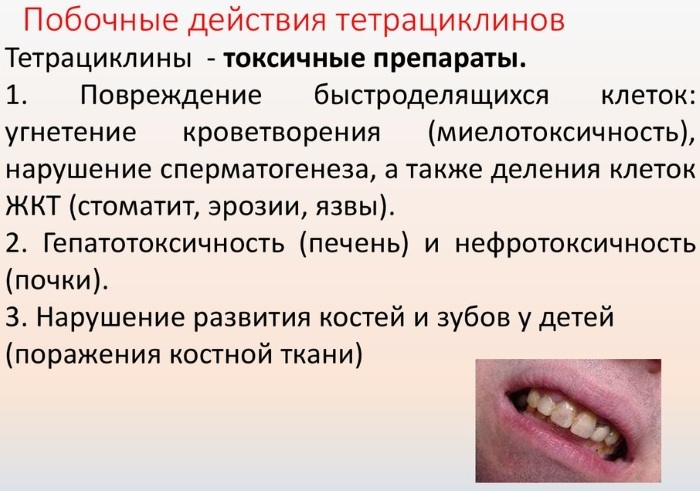
Tetracyclines can cause a number of side effects, such as:
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, pain and discomfort in the abdominal cavity;
- intracranial hypertension, vertigo, instability;
- liver disease;
- slowing bone growth in children, problems with bone formation;
- enamel defects, gray-brown or yellow staining of the teeth;
- violation of protein metabolism;
- allergy;
- increased nitrogen content in the blood with kidney dysfunction;
- photoallergy;
- thrombophlebitis if tetracyclines are injected into a vein;
- inflammation of the tongue, esophageal mucosa and pancreas;
- erosion of the esophagus;
- intestinal and vaginal dysbiosis;
- antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
Penicillins are contraindicated in case of intolerance, they can provoke the following undesirable effects:
- allergy;
- headaches, tremors of certain parts of the body, cramps, mental problems;
- abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, indigestion, pseudomembranous colitis;
- an increase in sodium and potassium content, due to which there may be edema and hypertension;
- pain and infiltration with the introduction of an antibiotic into the muscle;
- inflammation of the vein wall;
- increased activity of liver enzymes, which may be accompanied by high fever, nausea, vomiting;
- anemia, a decrease in the number of platelets and neutrophils;
- violation of platelet adhesion;
- the appearance of blood in the urine;
- tubulointerstitial nephritis;
- dysbiosis of the oral cavity and vagina.
Quinolones and fluoroquinolones are contraindicated in pregnancy and in the presence of the following pathologies:
- allergy to their composition;
- lack of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
In addition, quinolones should not be drunk by patients with health problems such as:
- severe liver and kidney dysfunction;
- severe atherosclerosis of the head vessels
Fluoroquinolones should not be given to children or taken by women who are breastfeeding.
The following problems may arise due to treatment with quinolones:
- stomach pain, heartburn, loss of appetite, indigestion, vomiting, nausea;
- hearing and vision problems;
- allergy;
- violation of sensitivity, trembling of the limbs and other parts of the body, drowsiness, insomnia;
- headaches, dizziness, convulsions;
- a decrease in the number of platelets and leukocytes, a decrease in hemoglobin;
- liver inflammation, intrahepatic cholestasis.
Fluoroquinolones can still provoke:
- reactive arthritis, joint and muscle pain, inflammation and tendon rupture;
- the appearance of crystals in the urine, inflammation of the kidneys;
- lengthening the QT interval on the ECG;
- thrush;
- pseudomembranous colitis.
 Levomycetin is contraindicated in pregnancy, lactation, allergies to it.
Levomycetin is contraindicated in pregnancy, lactation, allergies to it.
It can provoke a number of negative reactions, such as:
- lowering the amount of all blood cells;
- aplastic anemia, myeloid leukemia;
- cardiovascular syndrome in newborns, including premature infants, which is manifested by vomiting, increased gas production, respiratory failure, blue skin, fever, acidosis, neurogenic shock, it can cause the death of the baby;
- impaired consciousness, pain in the head, mental problems, inflammation of the optic nerve, which can cause blindness, peripheral polyneuropathy;
- inflammation of the tongue, stomatitis, nausea, vomiting, loose stools, pain and discomfort in the abdominal cavity;
- Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction.
How is the selection of the drug
When choosing a medication, one must take into account the sensitivity of pathogenic microorganisms to antibiotics. To do this, it is necessary to sow bacteria on a nutrient medium and determine which drugs act on it.
But unfortunately, there is not always time to wait, therefore, most often, the treatment of intestinal infection begins empirically, giving preference to medications of a wide spectrum of action. If 3 days have passed since the moment of therapy and the patient's well-being has not improved, then the medicine is changed.
In addition to the sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics, it is necessary to take into account the patient's age, the presence of contraindications and the tolerance of antibiotic therapy.
General rules of application and dosage
After the antibiotic for intestinal infection is selected, the following treatment rules must be observed:
- It is necessary to strictly follow the therapy regimen. It is impossible to reduce the dosage of the drug, since in this case it will not have the desired effect, but microorganisms may develop resistance to antimicrobial agents.
- You cannot interrupt the course of treatment after the patient's well-being improves, it must be completed to the end. Depending on the specific drug, it can last from 5 to 10 days, and sometimes even longer. After the signs of intestinal infection disappear, it is recommended to drink the antibiotic for another 2 days.
- It is necessary to take the antimicrobial agent by mouth or inject it at regular intervals.
- To prevent the development of dysbiosis, antibiotics are recommended to be taken in combination with probiotics.
For intestinal infections, antibiotics should be taken in the following doses:
- Penicillins. From this group, Ampicillin and Amoxicillin can be used. The first drug should be taken orally 4 times a day, and injected into a vein or muscle every 4 or 6 hours. For children, a single dosage is 12.5-50 mg / kg, and for adults it can vary from 0.25 to 0.5 g. Amoxicillin is prescribed for adults at a dose of 250 mg to 1 three times a day. For children weighing less than 40 kg, it is prescribed in a daily dosage of 20 to 100 mg per kg of body weight, it must be divided by 2 or 3 times.
- Tetracyclines. This group includes Tetracycline and Doxycycline. The first should be taken every 6 hours. For adults, a single dose of Tetracycline is 250 or 500 mg. Doxycycline on the first day should be taken at 200 mg, then it should be taken in a dose of 200-100 mg.
- Fluoroquinolones. This group includes medicines based on ciprofloxacin. The regimen is selected individually, depending on the severity of the infection. The daily dosage can vary from 500 to 1500 mg, it must be divided into 2 doses. The course of treatment can last from 1 to 4 weeks. Also, the antimicrobial agent can be administered intravenously at 200 mg or 400 mg twice a day for 1 to 2 weeks, when the duration of therapy is required, it can be increased. Ciprofloxacin can be injected into a vein in a stream, but it is better to drip within half an hour.
- Levomycetin. Adults need to take 0.5 g three or four times a day for 7-10 days.
List of the best drugs
An antibiotic for intestinal infection can be in pills and injections.
In tablets
-
Ampicillin (Zetsil). It has a bactericidal effect against Shigella, Salmonella, Escherichia coli.
- Amoxicillin (Amosin, Flemoxin Solutab). It causes the death of Shigella, Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Clostridium.
- Tetracycline. It has a bacteriostatic effect against Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Salmonella, Shigella, Clostridium.
- Doxycycline (Unidox Solutab). It stops the growth of Escherichia coli, Shigella, Salmonella, Enterobacteriaceae, Klebsiella.
- Ciprofloxacin (Tsifran, Tsiprolet). This antimicrobial agent causes the death of Escherichia coli, Shigella, Salmonella.
- Levomycetin. Shigella, Salmonella, Klebsiella, Proteus, Escherichia coli, including strains resistant to penicillins and sulfonamides, are sensitive to it. Resistance in microorganisms to chloramphenicol develops slowly.
In ampoules
The following antibiotics can be used in ampoules for intestinal infections:
- Ampicillin.
- Doxycycline (Vidoccin).
- Ciprofloxacin (Basigen, Ifitsipro, Quintor)
For acute intestinal infection
Acute intestinal infections can be caused by various microorganisms, and only if they are of a bacterial nature, then it is advisable to prescribe antibiotics.
The disease begins abruptly. It is characterized by indigestion, nausea, vomiting, high fever, and weakness. When these symptoms appear, the patient should be isolated. He was advised to drink plenty of fluids, take enterosorbents, prescribe bacteriophages, and follow a special diet. When the patient's condition is stable, then such procedures are sufficient.
If, after 48 hours, no positive dynamics is observed, then antibiotic therapy should be connected. If the patient has severe signs of infection, then the antibiotic can be prescribed from the first days of the illness.
What is prescribed during pregnancy?
During gestation, intestinal infections are treated with penicillin antibiotics, such as Ampicillin, Amoxicillin (Flemoxin Solutab). They are prescribed for typhoid fever, paratyphoid fever, salmonellosis, dysentery.
With their intolerance, women in the position are prescribed nitrofurans, for example, Enterofuril, containing as the main component of nifuroxazide, to which Vibrio cholerae, Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Shigella are sensitive, clostridia.
For adults, the medication is available in capsules that need to be drunk for an upset stomach of bacterial etiology, 200 mg four times a day for a week.
They should not be taken in case of intolerance to their composition, impaired absorption of dextrose and galactose, deficiency of sucrase and isomaltase.
Enterofuril is practically not absorbed by the digestive tract, so it is usually well tolerated, only sometimes it can become cause of the following adverse reactions:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- allergy, manifested by a rash, angioedema, nettle fever, anaphylaxis.
In addition, women expecting a child with an upset stomach can drink enterosorbents, which on their surfaces adsorb toxins, microorganisms and their waste products and accelerate their removal from organism. These are medicines such as Smecta, Neosmectin, Enterosgel (except for sweet paste, which is contraindicated for pregnant patients).
Antibiotics for children
In pediatric practice, penicillins can be used from birth, which are sold in suspension and dissolving tablets. These are drugs such as Amoxicillin, Flemoxin Solutab.
The dosage of drugs based on amoxicillin is selected individually, depending on the severity of the disease, the age of the child, and kidney function.
- Infants of the first year per day are prescribed them in doses of 30 to 60 mg per 1 kg of body weight, dividing the dosage into 2-3 doses.
- Children from one to 3 years old are prescribed in a dose of 250 mg twice a day or 125 mg three times a day.
- For patients from 3 to 10 years old, drink amoxicillin at a dose of 375 mg 2 r per day or 250 mg 3 r. per day.
- For children over 10 years old, the daily dosage can vary from 1 to 1.5 g, which must be divided by 2 or 3 times.
- If the child has kidney pathology, then the daily dose should be reduced by 15-50%.
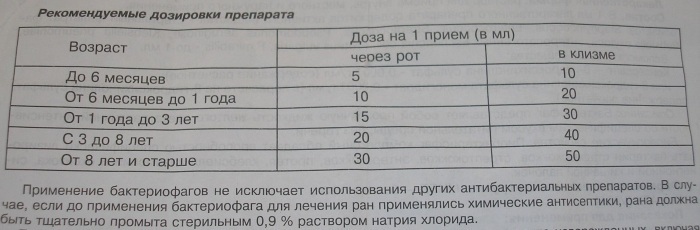
- Also, in children older than 1 month with penicillin intolerance, drugs based on nifuroxazide (Enterofuril, Stopdiar) in suspension can be taken.
They need to be given in the following doses:
| Age | Single dose in ml | Frequency rate of admission per day |
| 1 to 6 months | 2,5 | Twice, thrice |
| 7 months to 2 years | 2,5 | Four times |
| 3-7 years | 5 | Three times |
| From 7 years old | 5 | Three or four times |
The second-line drug is Levomycetin, which can only be used in a hospital under the control of the drug level in the blood serum.
The dose is selected depending on age:
- An antibiotic for intestinal infection is given to infants up to 14 days at 6.25 mg per kg of body weight every 6 hours.
- Children over this age are prescribed medication at a dose of 12.5 mg per kg of body weight every 6 hours or 25 mg per kg of body weight twice a day.
- If the infection is severe, the daily dose may be increased to 75 or 100 mg per kg of patient weight.
- Patients over 8 years of age may be prescribed tetracycline. It is prescribed in a single dose of 20 or 25 mg per kg of body weight. Tetracycline should be given to the child every 6 hours.
- Children over 12 years old and weighing over 45 kg are allowed Doxycycline in injections and capsules. On the first day, the daily dose is 0.2 g, it must be taken at a time or divided into 2 doses, then it is reduced to 0.1 g.
Recovery after taking antibiotics
Antibiotics act not only on harmful, but also on beneficial microorganisms, which causes a violation of the intestinal microflora.
To eliminate the unwanted effects of antibiotic therapy, such as dysbiosis, and to normalize the digestion of food, the following groups of medicines are prescribed:
- Enterosorbents, which on their surface adsorb toxic compounds and accelerate their excretion from the body through the intestines. From the first days of life, Smecta or Neosmectin in powder can be prescribed, from which a suspension for oral administration is prepared.
- Probiotics - These are medicines that contain bacteria necessary to restore the intestinal microflora. Linex belongs to this group.
- Prebiotics - these are medicines that, after oral administration, create an optimal environment in the digestive tract for the growth and reproduction of beneficial microorganisms. From birth, you can take drops of Hilak forte. They can be taken by pregnant and lactating patients, of course, in the absence of an allergy to the composition of the medication.
Prices in Moscow, St. Petersburg and regions
The cost of antibiotics depends on the manufacturer, dosage, dosage form, pharmacy margin.
Approximate prices for medicines:
| City | Ampicillin 250 mg No. 20 | Flemoxin Solutab 125 mg No. 20 | Tetracycline 0.1 g No. 20 | Tsiprolet 500 mg No. 20 | Levomycetin Actitab 500 mg, 20 tablets per pack |
| Moscow | RUB 23 | 224 r | 51 rbl. | RUB 101 | 104 rbl. |
| St. Petersburg | 28 RUB | 254 r 50 kopecks. | RUB 55 | RUB 99 | 123 r |
| Kazan | RUB 26 | 236 r | RUB 56 | 106 RUB | 113 r |
Antibiotics quickly help with intestinal infection, but a specialist should prescribe them, as only a doctor can determine how appropriate their intake is, as well as select the optimal dose, taking into account the age and weight of the patient, function kidneys.
Also, the doctor can determine which drug the pathogen is sensitive to, since many microorganisms have acquired resistance to antimicrobial agents.
Video about antibiotics for intestinal infection
When antibiotics are prescribed for intestinal infection: