A mandatory study for routine diagnostics and various diseases is a complete blood count. In decoding the results the ICSU parameter appears, which reflects the level of concentration of hemoglobin in erythrocytes. If the value is lowered, the development of iron deficiency anemia or other pathologies is suspected.
Record content:
- 1 Significance for the body
- 2 Indications for research
- 3 Calculation features
- 4 Reasons for deviations
- 5 Why is lowering dangerous?
-
6 How to get it back to normal?
- 6.1 Medication
- 6.2 Diet
- 7 Video about ICSU
Significance for the body
By this English-language abbreviation, clinicians mean the erythrocyte index. It displays the average saturation of red blood cells with protein components - hemoglobin.
This is an important biological indicator that allows timely diagnostics of pathologies of hemostasis, cardiovascular apparatus and other functional systems of the body.
MCHS in the blood test is lowered extremely rarely for natural reasons. Usually this is an alarming signal that indicates the development of systemic pathologies associated with a violation of hemoglobin synthesis.
To study the laboratory indicator, not the entire blood mass is used, but only the erythrocyte fraction isolated from it. The study allows you to assess the biochemical and physiological activity of the uniform cells.
The MCHS parameter provides information on the saturation of erythrocytes with protein compounds responsible for the transfer of oxygen and iron ions. Deviation from the norm in any direction is a good reason for the appointment of an additional examination.
A decrease in the erythrocyte index indicates:
- dysfunction of the endocrine glands;
- liver diseases;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- endocrine disorders;
In adult patients who receive a balanced diet, there are no malfunctions of organs and functional systems, the hemoglobin content in erythrocytes is always in the established limits.
The variations of this parameter are MVC and MCH. They display the level of concentration of a protein protein in cells. MVC shows the average content of erythrocyte blood fragments.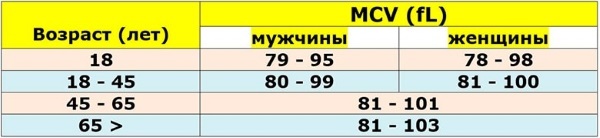
In a laboratory report, it is indicated in cubic micrometers or femtoliters. MCH is considered to be no less clinically important type of erythrocyte index. This parameter displays the average distribution of hemoglobin in each studied red blood cell separately.
It is important in determining the ability of red blood cells to transport oxygen. These indicators are indicated in the results of an extended biochemical blood test and are assessed comprehensively.
MCHS provides general information about the state of hemostasis, while MVC and MCH clarify it and make it possible to determine the functional parameters of each cell involved in the transfer of oxygen and iron.
Indications for research
A laboratory study of hematological fluid is not carried out only to determine the erythrocyte index. The doctor pays attention to this parameter when interpreting a general blood test. Such a study is prescribed for patients with obvious anemic symptoms, especially in the exacerbation phase.
This pathological condition is characterized by:
- frequent dizziness;
- loss of strength;
- decreased performance;
- general weakness of the body.
The erythrocyte index has a significant effect on the physical and psycho-emotional state.
Direct indications for a blood test for ICSU:
- obstructed respiratory function;
- shortness of breath after walking a short distance or with minimal physical activity;
- change in the shade of fecal masses in the absence of diagnosed disorders of the digestive system;
- an increase in the size of the parenchymal lymphoid organ (spleen) and a change in its contours;
- increased heart rate;
- cardiac arrhythmia and tachycardia;
- permanent arterial hypotension;
- chronic fatigue;
- regular fainting;
- decreased muscle tone;
- unhealthy pallor of the skin.
MCHS in the blood test can be lowered with other characteristic etiological signs. Such symptoms are characteristic of diseases of internal organs, vitamin and oxygen starvation of tissues.
Hemoglobin is responsible for transporting oxygen and iron ions, as well as removing carbon dioxide. With a decrease in the amount of protein protein in erythrocytes, dysfunctions of internal organs and a state of tissue intoxication occur.
Due to the content of atomic iron, hemoglobin effectively binds toxins and provides gas exchange. Violation of these functions is manifested by pathological symptoms, which is the reason for the appointment of a blood test for MCHS.
The study of the hematological coefficient is carried out when the attending physician suspects the presence of genetic pathologies. The decrease in hemoglobin content is often due to an increase in the plasma concentration of highly osmotic compounds such as glucose and sodium ions, which gives noticeable clinical symptoms.
Calculation features
When studying the obtained biological material, the laboratory assistant determines the erythrocyte index using a special technological method and indicates this parameter in the conclusion.
Use an automatic analyzer with data processing by a computer program and displaying the result on a monitor screen along with other key hematological characteristics.
The calculation of the MCHS parameter is performed in g / l of blood. The interpretation of the result is comparative. If the erythrocyte index is deviated from the established norm, clarifying diagnostic tests are prescribed.
The calculation formula is simple - the total volume of the detected protein is divided by the number of red blood cell fragments. This is how the average value is obtained. This indicator is stable and in an adult it is 32-36%.
The concentration of hemoglobin is established upon reaching puberty and after the onset of the menstrual cycle in girls. Some fluctuations are possible in older women in the menopause stage.
ICSU standard indicators:
| Age | The norm for men in g / l | Value for women |
| Newborns up to 2 weeks | 280-350 | 280-350 |
| 2 weeks-4 months | 280-370 | 280-370 |
| From 4 months to 12 years | 320-370 | 320-370 |
| 12-18 | 320-380 | 320-360 |
| 18-45 | 320-360 | 320-360 |
| 45-65 | 320-360 | 310-360 |
| From 65 years old | 310-360 | 320-360 |
In adolescence, boys have a slightly higher hemoglobin content in erythrocytes than girls. The reason is the onset of menstruation, during which blood is lost, and with it part of the protein protein.
In old age, fluctuations are due to the natural aging processes that lead to the destruction of hemoglobin. The results of a hematological study can be distorted under the confluence of certain conditions and factors.
ICSU is falsely lowered or raised in the blood test under such circumstances, distributed according to the degree of influence as follows:
- Failure to comply with the rules of preparation for the procedure.
- Taking coagulants and other medications that change the rheological properties and blood formula.
- Incorrect operation of the automatic analyzer used to study biological material.
- Laboratory assistant error.
The probability of the last 2 factors is negligible. ICSU is an accurate analysis, and the technology is well developed. The probability of getting an unreliable result is no more than 3%. If in doubt, there is always the possibility of re-donating blood for analysis.
Such a study is not a definitive diagnosis.
If the erythrocyte index deviates from the norm, carry out:
- consultation with a hematologist and other specialists;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs;
- oral questioning of the patient and taking anamnesis;
- extended biochemical blood test;
If you suspect a hereditary nature of the pathology, consultation of a geneticist is required.
Reasons for deviations
A decrease in the level of hemoglobin in erythrocytes provokes many etiological factors. This condition is called hypochromia. A rare cause of deficiency of iron-containing protein protein in red blood cells is thalassemia. This is a genetic pathology of the recessive type.
It is characterized by a decrease in the production of polypeptide chains that form the basis of hemoglobin. Hypochromia is also triggered by other hereditary diseases. It is not considered a separate nosological unit, but is a symptom of systemic disorders.
A common factor in reducing the concentration of hemoglobin in red blood cells is a lack of adermine, better known as vitamin B6. The accompanying symptoms are not fundamentally different from the signs of folic acid deficiency. In both cases, a biochemical blood test will show hypochromia.
A separate category of factors that affect this hematological indicator is chronic liver disease. These include sluggish inflammation, cirrhosis, hepatitis. Cell death is observed, which provokes generalized disorders of the hematopoietic mechanism.
Men suffer from such violations more often. In women, iron deficiency anemia is common, which develops due to insufficient consumption of foods containing this chemical element. This pathology occurs due to systemic disorders that interfere with the normal absorption of iron.
In children, anemia of this type develops against the background of helminthic invasions. Hypochromia often serves as a complication of chronic diseases associated with internal bleeding - pulmonary tuberculosis, stomach ulcers, and others.
Deviation of the erythrocyte index downward occurs when:
- violation of water-salt balance;
- lead and mercury intoxication;
- hemolytic pathology in newborns, which is accompanied by the disintegration of erythrocyte cells;
- post-hemorrhagic anemia;
MHCS in the blood test is lowered in premature infants, often due to the partially suppressed ability of the bone marrow to synthesize hemoglobin. In girls during puberty, hypochromia develops due to heavy menstrual bleeding.
Violation of the erythrocyte blood index in newborns is often observed due to intrauterine infection. A factor encountered in clinical practice is hemoglobinopathy. This pathological condition is hereditary or congenital in nature and is provoked by the replacement of some amino acids in the protein structure.
Why is lowering dangerous?
With a deficiency of iron-containing protein protein in the erythrocyte mass, an atrophic state of the mucous membranes of organs develops, which inhibits their barrier function. This increases the risk of bacterial and viral diseases and the development of inflammatory processes.
With a lack of hemoglobin and iron carried by it, the risk of occurrence of:
- rhinitis;
- sinusitis;
- gastritis;
- esophygitis.
Dysfunctions of the muscular system develop, which lead to an increase in convulsive readiness in children and myocardial dystrophy in adults. Deficiency of hemoglobin in erythrocyte cells provokes a decrease in blood pressure, tachycardia, and complicates respiratory function.
A low concentration of iron-containing protein in red blood cells causes functional failure of the hepatic organ, which leads to suppression of the synthesis of albutamine, prothrombin and glucose. In pregnant women, this pathological condition provokes placental dystrophy.
With a deficiency of hemoglobin, oxygen starvation of epithelial cells and tissues of vital organs occurs. The volume of the lungs is reduced, the atherosclerotic state of the cerebral arteries develops. Hypochromia is especially dangerous for adolescents, whose bodies are in the phase of active formation.
How to get it back to normal?
The therapy regimen and measures aimed at stabilizing the erythrocyte index are determined by the reasons that caused such a pathological condition. Hypochromia is often situational and occurs after stress or profuse blood loss.
In such cases, rest and the use of sedatives are prescribed. With thalassemia, hemosorption and symptomatic correction are performed. A specific therapy for this rare pathology has not been developed. For liver dysfunctions, hepatoprotective agents are used. It is necessary to be constantly monitored by a gastroenterologist.
In case of lead and mercury poisoning, detoxification measures are performed in a medical hospital. In each case, an individual therapy is developed depending on the causes of hypochromia. To clarify the diagnosis, an additional examination is prescribed by laboratory and hardware methods.
Medication
MCHS in the blood test can be lowered for several pathological reasons at once. In such a situation, combined drug therapy is used. Iron deficiency anemia is most easily eliminated.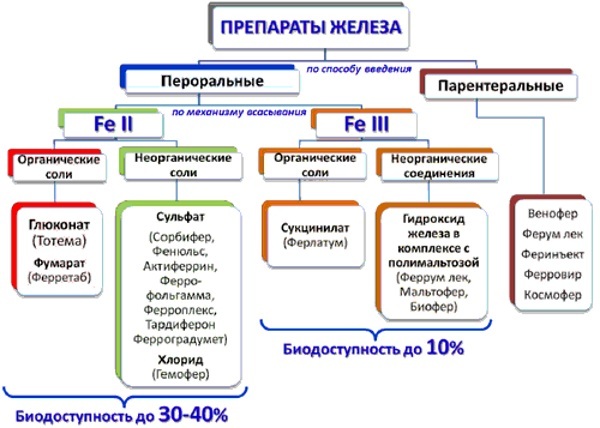
Shock doses of this chemical element of 2- and 3-valent modification are prescribed. Injectable drugs are quickly absorbed. The duration of the course and the frequency of use depend on the hematological indicator.
The body quickly recovers and begins to produce hemoglobin on its own. If hypochromia is due to poor absorption of iron, medications that stimulate the digestive function are prescribed.
The most effective drugs for eliminating anemic pathology:
- Actoferrin, produced in capsules and saturated with sulfonated iron monohydrate, as well as serine - a nonessential amino acid, which is an important component of cell membranes;
- Ferratab - an effective medicine for the treatment and prevention of iron deficiency conditions;
- Ferroplex, stimulating hematopoiesis - the formation, development and maturation of blood corpuscles;
- Tardiferon - antianemic drug saturated with iron atoms;
- Fenuls - a drug containing a multivitamin complex and improves the functioning of the hemostasis system.
If the deviation of the erythrocyte index from the norm is caused by vitamin starvation, the appropriate complexes are prescribed in combination with enzyme medications.
To fully restore the balance, several therapeutic courses are carried out throughout the year. With post-hemorrhagic anemia, surgery may be required to eliminate the cause of blood loss by surgery.
According to the plan of further treatment, iron-containing preparations and agents that affect the rheological properties of blood are prescribed. If functional disorders of the liver act as an etiological factor in reducing hemoglobin in erythrocytes, Karsil, Essentiale and other drugs of the category of hepatoprotectors are prescribed.
They restore the functioning of the organ and prevent further progression of the disease. For infectious infections that violate the hematological indicator, antibiotics, stimulants of interferon synthesis, and fungicidal preparations are used.
The choice of medicines for complex therapy is determined by the composition of the pathogenic microflora. Blood transfusion and regulation of water-salt balance allow to restore the normal value of the hemoglobin content.
Diet
The stabilization of MCHS can be accelerated by a competent combination of drug therapy with diet correction. Correctly selected dietary food will help to quickly restore the balance of hemoglobin.
It is recommended to include apples, bell peppers, seafood in your own diet. A high concentration of iron is observed in ocean fish. Citrus crops are saturated with vitamin C, which is necessary to improve the rheological properties of blood.
It is recommended to regularly consume tomatoes, beef, cod liver. Cauliflower contains a lot of iron. Useful systematic use of walnuts, buckwheat, peanuts.
If in the blood test the MCHS indicator has a deviation from the norm towards a decrease, it is often possible to do only with diet therapy without the use of drugs. Beetroot, rosehip broth and nutria meat will help stabilize the hematological parameter in the shortest possible time.
Video about ICSU
ICSU in the blood test:



