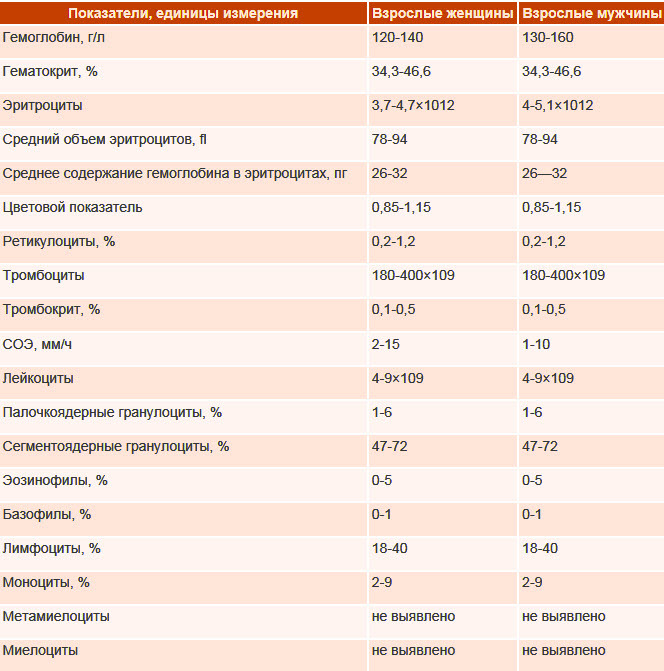
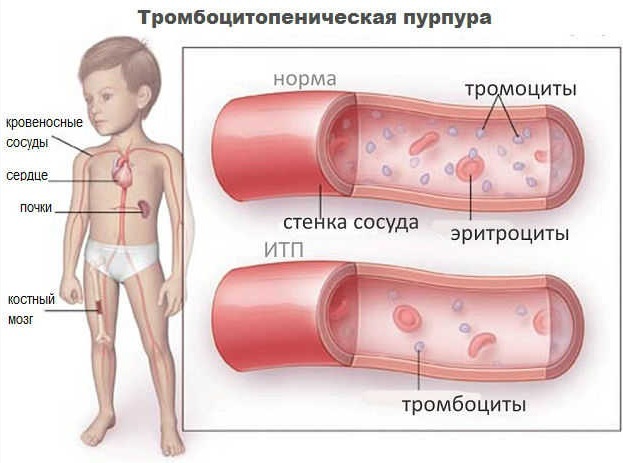
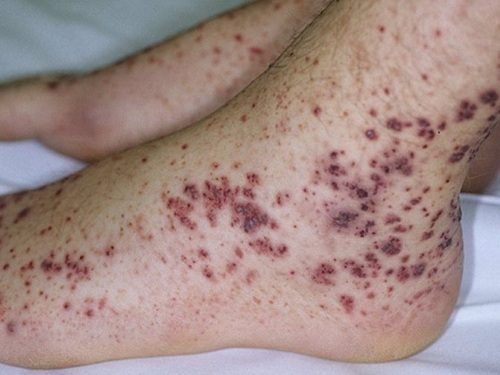
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (Werlhof disease) is a pathological condition in which the level of platelets in the blood changes. Most often, the disease is diagnosed in children aged 2 to 10 years.
In adults, a decrease in the number of platelets is rare, but in most cases it occurs in women. Pathological abnormalities will show the results of the study, which will be prescribed by the hematologist, taking into account the existing complaints of the patient. Treatment is selected in each case individually based on the information received.
Record content:
- 1 The reasons for the development of the disease
- 2 Risk factors
- 3 Pathogenesis
- 4 Classification of the disease
- 5 Symptoms of pathology
- 6 Differential diagnosis
-
7 Treatment of the disease
- 7.1 Medication
- 7.2 Folk remedies
- 7.3 Diet
- 7.4 Surgical intervention
- 8 Prognosis and complications
- 9 Video about the disease
The reasons for the development of the disease
Doctors cannot say for sure what causes the development of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in humans, but there are provoking factors in the background
which pathological changes are triggered:- a viral or bacterial infection that a person has suffered earlier (chickenpox, infectious mononucleosis);
- vaccination (BCG);
- hypothermia of the body;
- prolonged exposure to the sun;
- trauma, damage, surgery;
- autoimmune disorders;
- the use of certain drugs.

Provoking factors affect the level of platelets, reducing their number and contributing to the production of antibodies to them. An insufficient concentration of blood cells leads to damage to the blood vessels. Bleeding appears, a malfunction occurs in the formation of a blood clot, and the contractility of the vessels is impaired.
Risk factors
Scientists continue to study the reasons behind the destruction of blood cells.
In addition to the main sources, negative influences should also be highlighted that contribute to the development of pathological processes:
- frostbite of the lower and upper extremities;
- hereditary predisposition;
- stressful situations, nervous strain, overwork;
- ultraviolet irradiation and radiation;
- violation of material metabolism in the human body;
- malignant processes;
- anemia;
- stagnant processes in the blood;
- a tendency to allergic reactions to chemicals, heavy metals, salts or active ingredients of drugs.
Against the background of all these factors, there is an insufficient production of platelets by the cells of the bone marrow due to its impaired functioning. It should also be noted that the disease occurs in women 3 times more often than in the stronger sex.
Pathogenesis
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (treatment at an early stage of the disease will help stop progressive pathological processes and prevent serious consequences) develops gradually:
| Name | Description |
| Hemorrhagic crisis | The stage of pathological processes, at which severe bleeding appears, a bruised rash. The indicators of the general blood test also change. Thrombocytopenia appears, the level of hemoglobin decreases. |
| Clinical remission | The stage of development of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, when there are no visible clinical signs. But CBC results will show changes. |
| Clinical and hematological remission | Laboratory blood counts are restored, while there are no symptoms of the pathological condition. |
In 45% of cases, doctors cannot accurately determine the cause of the disease. In other situations, purpura is a consequence of an infectious lesion of the human body. The first signs of pathological processes appear 2 weeks after recovery.
Classification of the disease
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (treatment is prescribed by a hematologist after a comprehensive examination) occurs as a result of a reduced level of platelets in the blood. Blood cells live 7-10 days. In idiopathic purpura, this period is shortened to several hours by suppressing platelet production by the immune system.
In medicine, the following classification of the disease is distinguished:
| Name | Description |
| Acute thrombocytopenia | Pathological processes are more often diagnosed in children. The duration of the disease is 6 months. Then the child recovers, the blood composition is restored. The risk of secondary recurrence of the disease is minimal. |
| Chronic purpura | The duration of the disease is more than six months. Chronic purpura is also diagnosed in adults. |
| Recurrent | The disease is characterized by a repetitive nature. The periods of exacerbation are followed by stages of remission. |
In each individual case, characteristic clinical symptoms appear, with which it is important to go to the hospital in a timely manner. Comprehensive diagnostics will allow you to establish the cause of the disease and draw up the most effective treatment regimen.
There are also the following forms of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura:
| Name | Description |
| Heteroimmune | The pathological condition develops as a result of the negative effects of viruses or after taking medications. The disease is characterized by damage to the platelet's own structure. |
| Autoimmune | Pathology occurs as a result of the production of antibodies by the immune system that attack its own platelets. The disease is often chronic and is characterized by periodic relapses. |
| Isoimmune | A rare form of thrombocytopenia, which develops as a result of the ingress of unfamiliar platelets into the blood (incompatibility between the platelets of the mother and child, transfusion). |
The classification of thrombocytopenia differs in the degree of the course of pathological processes, taking into account the provoking factor. Correctly selected therapy at an early stage will help to avoid complications and fully recover.
Symptoms of pathology
The clinical picture of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura will allow the doctor to determine the stage and degree of development of pathological processes. Assign the patient with the most informative examination, according to the results of which an effective treatment can be drawn up.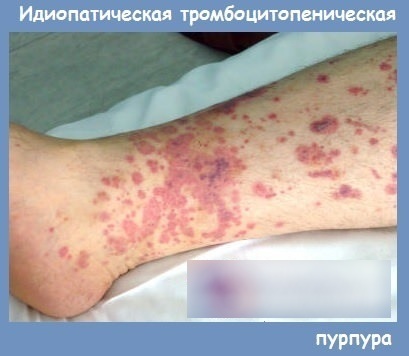
Given the course of the disease, the following clinical signs appear in patients:
| Name | Symptoms |
| Acute idiopathic purpura |
|
| Chronic form |
|
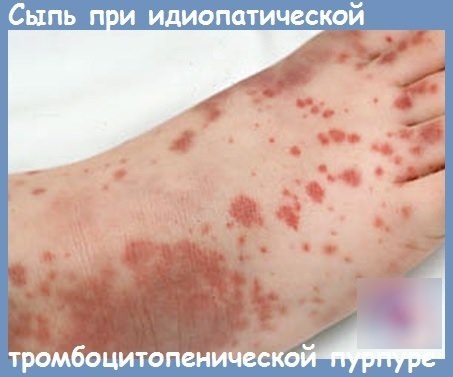
The rash that appears on the skin and mucous membrane of a patient with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura may be dry or wet. Fresh dots are purple in color. Old rashes take on a green or yellow tint.
In idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, patients develop bruises on their bodies, even after minor physical impact. The damaged skin surface does not heal well, the duration of bleeding increases.
Differential diagnosis
Patients need to undergo a comprehensive examination in order to establish an accurate diagnosis and, if necessary, draw up the most effective therapy regimen. Studies also make it possible to differentiate disorders, since many blood pathologies are accompanied by similar clinical symptoms (leukemia, systemic lupus erythematosus, infectious mononucleosis).
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (treatment at an early stage of the disease will help stop pathological processes) requires the following testing methods:
| Name | Description |
| Laboratory research |
|
| Hardware diagnostics |
|
Taking into account the results obtained after the diagnosis, the patient may need additional consultation with other specialized doctors (endocrinologist, gynecologist, urologist, oncologist, gastroenterologist).
Treatment of the disease
Therapy for idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura is carried out using complex methods. In the absence of pronounced symptoms, treatment is not carried out.
It is enough for the patient to avoid injuries and injuries, to give up contact sports. When a visible clinical picture appears, drugs are prescribed to patients. In the absence of medical contraindications, the use of folk remedies is allowed.
Medication
Conventional treatment for idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura aims to reduce the production of antibodies to platelets and prevent platelet binding. The doctor selects medications, taking into account the patient's condition and the individual characteristics of his body.
| Drug group | Name | Application |
| Glucocorticosteroids | Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone | The medicine is recommended to be taken orally at 20-30 mg 1 time per day. |
| Immunoglobulins | Octagam, Sandoglobulin | Medicines are given intravenously. They are needed to increase the level of platelets in the blood. The adult dosage is 0.8-1 g / kg body weight. The medicine is administered every 3-4 weeks. |
| Interferons | Interferon Alpha, Viferon | The dosage for an adult patient is determined by the condition of the person and the established diagnosis. The medicine is administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly. Patients are prescribed 30 million. IU per day for 16-24 weeks. |
| Cytostatics | Cyclophosphamide, Imuran | The drugs are administered intravenously or intramuscularly. An individual therapy regimen is drawn up for each patient. 200 mg every day or 400 mg every other day. 1 g every 5 days or 2-3 g every 2-3 weeks. |
| Angioprotectors | Dicinon, Adroxon | The standard dosage of the drug is 0.25-0.5 g. The drug should be taken orally 3 times a day for 5-14 days. |
| Immunosuppressants | Cyclophosphamide, Azathioprine | The medicine is administered intravenously through a dropper. The dosage depends on the condition and age of the patient and is determined by the doctor. Typically, patients are prescribed from 3 to 40 mg / kg. |
The drugs should be taken strictly as directed by the attending physician, since many of the active ingredients can provoke side effects. In the event of a possible cerebral hemorrhage and the appearance of neurological signs, patients are shown an infusion of platelets or plasmapheresis. In severe and emergency situations, surgical intervention is prescribed.
Folk remedies
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (treatment is carried out in a complex under the supervision of a qualified specialist) allows the use of recipes of healers and healers.
The therapy should be discussed with the attending physician hematologist. The components used can provoke an allergic reaction or individual sensitivity. Therefore, the treatment method must be adjusted with the attending physician hematologist.
Effective folk remedies:
| Name | Recipe | Application |
| Rose hip | Pour the dry fruits of the plant (1 tbsp.) With boiling water (1 l). Withstand the resulting solution for 10-12 hours and strain well. | The ready-made broth is recommended to be consumed throughout the day instead of tea. For taste, you can add natural honey or sugar in a small amount. Rosehip infusion slows down bleeding and strengthens the immune system. |
| Japanese sophora | Pour the fruits of the plant (1 tsp) with hot water (100 ml). Insist 1-1.5 hours and drain. | The resulting solution must be lubricated in areas where rashes are present. The procedures are recommended to be carried out 2 times a day, in the morning and in the evening. |
| Herbal collection | Mix in equal proportions yarrow flowers and leaves, shepherd's bag, dry cucumber lashes. Brew with boiling water (500 ml) 1 tbsp. herbal collection. Leave for 5-6 hours and drain. | The ready-made broth should be taken in 150-180 ml 3 times a day before meals for 20 minutes. |
| Viburnum bark | Pour with boiling water (300 ml) 4 tsp. pre-chopped bark. Put the resulting mass on medium heat and cook for another 30 minutes. Cool, strain and add warm boiled water to get a final 300 ml. | The ready-made solution is recommended to be consumed inside 3-4 times a day for 2 tablespoons. |
| Burnet medicinal | Grind the roots of the plant and pour 2 tbsp. boiling water (250 ml). Leave for 2-3 hours and strain. | The finished medicine is recommended to be taken warm inside. The adult dosage is 2 tablespoons. before meals in 20 minutes. For taste, you can add 1 tsp. jam or natural honey. Burnet medicinal has an astringent effect on bleeding. |

Sesame oil can help increase the level of platelets in the blood in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. The product is recommended to be consumed 3 times a day before meals for 1 tsp. Sesame oil also improves blood clotting.
Diet
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in complex treatment requires adherence to a certain diet. The dietitian doctor will help to make the menu, taking into account the patient's condition and the recommendations of the attending physician.
| Allowed Products | Prohibited foods |
|
|
Proper nutrition will help reduce the negative effect on blood vessels, the mucous membrane in the gastrointestinal tract, and also reduce the likelihood of an allergic reaction.
Surgical intervention
In the case when traditional therapy with medications did not give a positive result or in difficult situations when complications appear, patients are prescribed surgical treatment.
The main indications for splenectomy:
- the development of a severe form of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura at the stage of exacerbation, in which drug therapy does not help;
- the appearance of severe bleeding that threatens human life;
- pathological processes occur throughout the year;
- persistent thrombocytopenia (<10,000 mm3);
- the development of chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura with signs of bleeding, while the platelet count is <30,000 mm3.
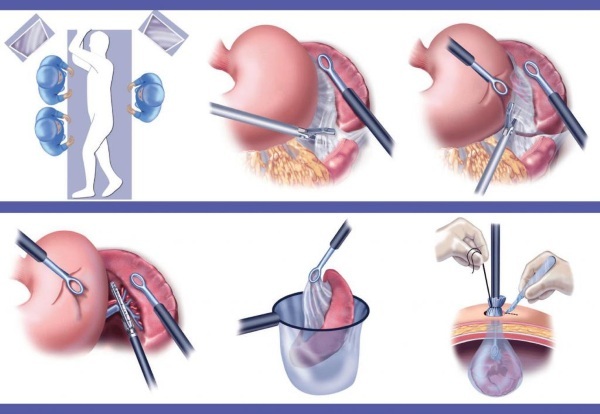
Surgery is also indicated for patients who lead an active lifestyle with frequent injuries and injuries. Surgical treatment is carried out in extremely rare situations and requires some preparation.
Prognosis and complications
Untimely or incorrectly selected therapy can lead to serious complications. The prognosis for idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura also depends on this. The likelihood of complications depends on the degree and extent of damage to the vessels of the brain, cardiovascular system and other internal organs.
The consequences of the disease are as follows:
- massive bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract;
- the acute form of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura provokes hemorrhagic stroke;
- detachment of the retina due to severe bleeding.
The most dangerous complications of idiopathic purpura are disability and death in particularly severe cases. Expressed pathological processes provoke serious changes in the form of hemorrhage in the brain tissue. With timely therapy, a full recovery occurs in 75% of cases in adults and 90% in children.
When the first signs of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura appear, self-treatment should not be undertaken. The pathology is insidious and requires a comprehensive examination, according to the results of which the specialist draws up a therapy regimen. Without medical care, the patient will face serious consequences, including death.
Video about the disease
Thrombocytopenic purpura. Etymology, pathogenesis, clinic, treatment: