Cause of thrombocytopenia of occurrence in adults, various pathologies often become. Much less often it is an independent disease. It is characterized by a decrease in the level of platelets (flat colorless blood elements). Pathology can provoke bruises and hematomas, disruption of organs and systems, and death.
Record content:
- 1 Views
- 2 Stages and degrees
- 3 Symptoms
-
4 Reasons for the appearance
- 4.1 Hereditary
- 4.2 Productive
- 4.3 Destruction
- 4.4 Consumption
- 4.5 Reallocations
- 4.6 Breeding
- 5 Diagnostics
- 6 When to see a doctor
- 7 Prophylaxis
-
8 Treatment methods
- 8.1 Medications
- 8.2 Traditional methods
- 8.3 Other methods
- 9 Possible complications
- 10 Video about thrombocytopenia
Views
Platelets keep blood in a liquid state, prevent the formation of clots, and protect the vascular walls from damage.
A decrease in the production of these elements leads to an increase in blood viscosity, the formation of blood clots, and hemorrhages. Normally, the platelet count should be less than 150,000 / macroliter. This value changes during the day - at night it is less, during the day it can reach a maximum.
Thrombocytopenia is classified according to the cause, nature of the disease, and the severity of symptoms. According to etiology, primary (idiopathic) is distinguished - as a separate pathology and secondary (acquired), developing against the background of various disorders in the body.
Also, thrombocytopenia is divided into two forms. In acute illness, the disease begins suddenly, the number of platelets decreases sharply. This phase can last up to six months. In the chronic form (over 6 months), symptoms appear and intensify gradually, as does a decrease in platelet concentration.
Thrombocytopenia (the causes of occurrence in adults and the development of the disease are described in the table) are of the following types: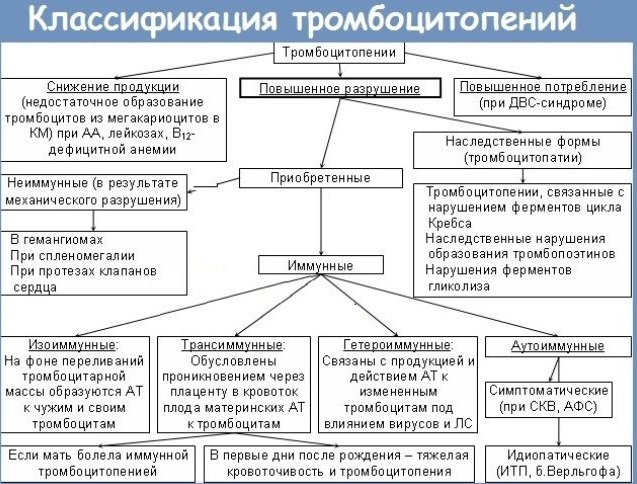
| A type | Development mechanism |
| Hereditary | It is caused by diseases arising from genetic mutations. |
| Productive | The group includes pathologies of the hematopoietic system, when the formation of the required number of platelets in the bone marrow is disturbed. |
| Destruction | It develops as a result of the strong destruction of platelets (in particular in the spleen). A smaller part of them breaks down in the liver, lymph nodes, vascular bed. Very rarely, the disease appears after vaccination against measles, flu, rubella, chickenpox. |
| Consumption | Platelets are activated in the vascular bed. As a result, the mechanism of accelerated blood coagulation is triggered. Platelet production is increased. If the cause of activation is not eliminated, the compensatory function of the bone marrow is depleted. |
| Reallocations | Normally, a third of platelets are in the spleen, and are released into the blood if necessary. Some diseases lead to splenomegaly. Then the number of flat cells in the spleen is retained up to 90%, which does not cause an increase in their production to compensate. |
| Breeding | It develops in inpatients. Often after a lot of blood loss. At risk are patients who receive a lot of blood, plasma and its substitutes, erythrocyte substance. In this case, there is no reimbursement of lost platelets. Then their concentration is significantly reduced and the work of the blood coagulation system is disrupted. |
Thrombocytopenia as an independent pathology is called Werlhof's disease or idiopathic purpura. This is a state of the body when it produces antibodies to its platelets. In other cases, thrombocytopenia is referred to as symptoms suggestive of other conditions.
Stages and degrees
The degree of thrombocytopenia is determined by the concentration of platelets in the blood and the severity of bleeding:
-
Lightweight. The platelet count is 50,000 - 150,000 in 1 microliter of blood. This is sufficient for the normal state of blood vessels and to prevent bleeding. At this stage, a wait and see tactic is used. Treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause of thrombocytopenia. No drug therapy is required.
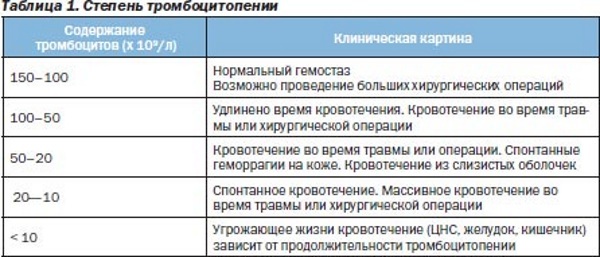
- Average. The platelet count is 20,000 - 50,000 in 1 microliter of blood. Small bleeding appears in the mucous membranes, from the nose, gums. Bruises and injuries provoke micro-effusions into the skin. Medicines are prescribed only when the risk of bleeding and ulceration increases.
- Heavy. The level of platelets in 1 microliter of blood is less than 20,000 units. This stage is characterized by sudden severe bleeding. Other symptoms become more pronounced. However, the general condition of the patients is normal and does not correspond to the severity of the disease.
The initial stage of thrombocytopenia is often discovered by chance - during the treatment of diseases or preventive examination. During this period, external signs are not visible.
Then, hemorrhages appear on the mucous membranes and the body. Gradually, they become more pronounced, the area of the lesion increases. At the last stage, anemia begins, the risk of bleeding into the brain increases, which leads to death.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of thrombocytopenia are bleeding from the nose, gums, internal organs, and the brain. This is due to a violation of the enzyme responsible for blood clotting. At the same time, the permeability of the vascular walls increases. Symptoms begin to appear after a decrease in the rate of platelets in one microliter - 50,000.
Signs of thrombocytopenia:
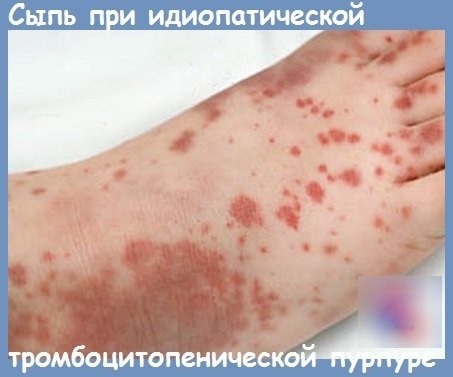
- Hemorrhages in mucous membranes and skin. They appear as small red spots. There are more of them in places where clothes are attached. The spots do not appear as pimples, are painless, and do not disappear with pressure. They can be single manifestations or appear in whole areas from 3 mm in diameter to several centimeters. The bruises are of a different color. The early ones are blue and red, the passing ones are yellow or greenish.
- Bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract. They appear when the strength of the capillaries of the mucous membrane is broken, injured by hard food. Blood comes out with feces or vomit. Heavy bleeding can be life threatening.
- Nosebleeds. There are many capillaries in this mucosa. Lack of platelets provokes their permeability, which causes profuse bleeding. It can appear as a result of sneezing, microtraumas, colds, foreign body entering the nose. Bleeding can last up to 10-15 minutes.
- Hematuria (appearance of blood in the urine). Appears when the walls of the capillaries of the mucous membranes of the urinary tract and bladder are weakened. With insignificant blood loss, they can be determined only in laboratory conditions, since outwardly the urine seems to be of a normal color. With increased thrombocytopenia, urine turns red.
- Bleeding gums. Normally, it is absent or insignificant. With thrombocytopenia, it is very pronounced, the blood flows for a long time.
- Bleeding after surgery, tooth extraction. Normally, the damaged area fills the blood clot, which prevents its further flow. With thrombocytopenia, this process can take a long time.
-
Profuse menses. They normally last 3-5 days. In this case, no more than 150 ml of discharge flows out (together with the old layer of the endometrium), up to 80 ml of blood is lost. With thrombocytopenia, these values increase greatly. Bleeding can occur even between periods.
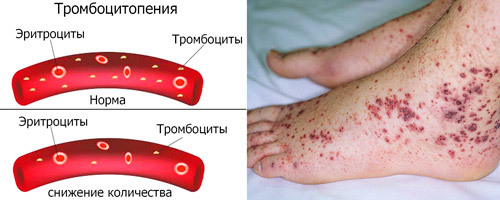
The first symptom of thrombocytopenia is the appearance of hemorrhages on the mucous membranes, bruises under the skin with slight injury to soft tissues. There may be a rash on the body, arms and legs, increased bleeding of the gums.
Gradually, these symptoms become more pronounced, the area of the lesions is extensive, and their duration ranges from hours to several days. When the platelet count drops dramatically, internal bleeding occurs, which can lead to death.
Reasons for the appearance
Thrombocytopenia (causes of occurrence in adults can be external and internal) can develop as a result of injuries, diseases, disorders of physical processes.
Hereditary
Platelet deficiency (blood abnormality) is detected from birth.
The reasons can be:
- May-Hegglin disease. A rare genetic pathology of an autosomal recessive type. If at least one parent is sick, the probability of the risk of transmission to the child is 50%. The process of platelet division in the red fluid of the bone marrow is disrupted. As a result, the number of giant cells decreases. In addition, the process of formation of leukocytes is disrupted, leukopenia develops.
- Bernand-Soulier's disease. Giant, but not working platelets are formed, which are quickly destroyed in the spleen, without having time to attach to the walls of the arteries. The child is inherited only if the pathology is diagnosed in both parents. The disease manifests itself in early childhood.
- Wiskott-Aldrich pathology (transient). It produces very small platelets with an irregular structure. As a result, the period of their decay and vital activity decreases. This provokes the appearance of inflammation on the skin, a decrease in immunity, which increases the risk of contracting viruses and infections. Pathology is typical only for boys until adolescence.
- TAR syndrome. A rare condition in which the radial bones are absent. The gene responsible for megakaryocytes mutates, resulting in a platelet deficiency.
- Amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia. The gene that is supposed to be responsible for the appearance and formation of megakaryocytes mutates and deforms. As a result, platelet production is impaired. This is an autosomal disorder that is common in infants.
Genetic diseases are diagnosed during infancy and early childhood.
Productive
The group includes pathologies of hematopoiesis, in which the formation of flat elements in the inert brain is disturbed.
Thrombocytopenia (the causes of occurrence in adults are presented below) is formed due to diseases:
-
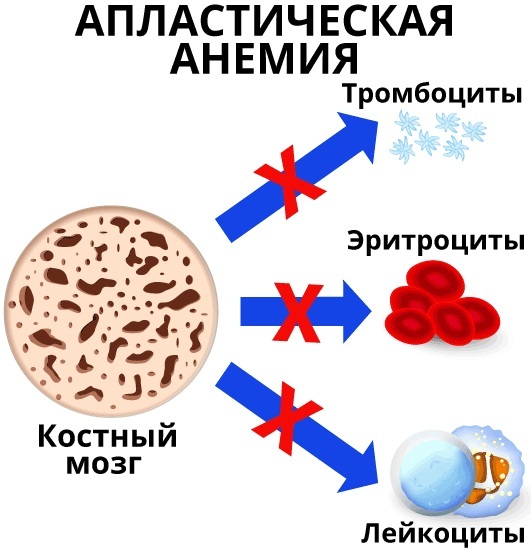
Aplastic anemia. With it, hematopoiesis in the bone marrow is suppressed. As a result, the level of platelets and leukocytes decreases. Anemia can be triggered by high levels of radiation, medicines, HIV infection, and environmental pollution.
- Cancer tumors. At the final stage, metastases spread throughout the body, which disrupts platelet production and displaces hematopoietic cells.
- Megaloblastic anemia. It occurs against the background of a deficiency of folic acid. The work of DNA fragments, which are responsible for the storage of genetic information, the formation and development of blood cells, is disrupted. Mucous membranes are also at risk.
- Radiation. It has a destructive effect on the hematopoietic system, causes various mutations, the development of hemoblastosis.
- Myelodysplastic syndrome, polycythemia vera. A group of tumors, due to which hematopoiesis in the bone marrow is disturbed. Cell reproduction is accelerated, but their maturation is disrupted. As a result, they cannot work normally, and the process of self-destruction begins.
- Cytostatic drugs. They are used to treat various tumors. The drugs slow down the growth of neoplasms, but often hematopoietic disorders become side effects.
- Acute leukemia. Oncological pathology arising on the background of mutations in bone marrow stem cells. They begin to share rapidly and cannot fulfill their functions. The tumor fills the red fluid in the brain, eliminating all hematopoietic cells.
- Alcoholism. In high concentrations, ethyl alcohol has a depressing effect on the hematopoietic system. As a result, the concentration of leukocytes, erythrocytes, platelets decreases. More often this process occurs with constipation, when the effect on the bone marrow lasts a long time. However, this thrombocytopenia is usually temporary and resolves after a few days. But with constant long-term binges, the changes become irreversible.
-
Myelofibrosis. Against the background of the disease, stem cells mutate, fibrous tissues are formed. They gradually fill the entire space of the bone marrow, displacing vital elements. A distinctive ability is the development of the same pathological processes in the spleen and liver.

High sensitivity to drugs may be the cause. It is not found in everyone, but this feature of the body becomes an obstacle to the formation and maturation of platelets. However, such a reaction rarely develops in humans.
Destruction
In this case, a rapid disintegration of platelets occurs. More often in the spleen, but with some pathologies - in the liver and lymph nodes.
Causes:
-
Idiopathic purpura (otherwise called autoimmune thrombocytopenia). At the same time, the concentration of platelets decreases, but the rest of the blood composition does not change. Vaccinations, hypothermia, medications can be provoking factors. Sometimes infections, excessive sun exposure are the cause of the development of purpura. The production of antibodies begins, which destroy platelet antigens. As a result, their lifespan is reduced to several hours.
- Evans-Fisher Syndrome. It occurs due to systemic diseases (such as arthritis, hepatitis, or lupus erythematosus), but sometimes without predisposing diseases.
- Viral pathologies (in particular influenza, rubella, measles, chickenpox). This starts the production of antibodies that destroy platelets.
- Medicines. Components of some drugs can bind to antigens in blood cells and platelets. As a result, the production of antibodies is triggered in the body. After the drug is discontinued, the platelet count is gradually restored.
- Post-transfusion thrombocytopenia. Appears after blood transfusion. In this case, significant destruction of platelets is observed. Since foreign cells are transferred to the patient, the body begins to produce antibodies in response. This process appears 7-8 days after transfusion.
Thrombocytopenia destruction can occur in neonates. But this condition develops if the child's platelets contain antigens that are absent from the mother. Then antibodies penetrate the fetal placenta and destroy its flat blood cells. As a result, the child is born with severe thrombocytopenia.
Consumption
The mechanism of pronounced blood coagulation is triggered. In response to increased consumption of platelets, their increased production begins. As a result, the compensatory capabilities of the red fluid of the bone marrow are quickly depleted.
The reasons are:
- Hemolytic uremic syndrome. It is found mainly in children. This is a condition in which bacterial toxins enter the bloodstream, damaging blood vessels. Platelets are activated and adhere to damaged areas, forming microscopic blood clots. In this case, blood microcirculation is disturbed. Intestinal infections are more common. Also, the syndrome can be caused by some systemic pathologies, genetic predisposition and medications.
- Thrombocytopenic purpura. The disease develops due to a deficiency in the blood of prostacyclin (a substance that prevents clotting). It is necessary to prevent platelets from sticking together and forming clots, damage to blood vessels, and the development of hemolysis.
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation. The condition develops as a result of large damage to tissues and organs, provoking a violation of blood clotting. This leads to the formation of many blood clots. They clog the vascular lumen, disrupting the blood supply to organs and tissues. Heavy bleeding begins, often leading to death.
Also, even allergic reactions to external stimuli, decreased immunity, and oncological diseases can become the cause.
Reallocations
Normally, a third of platelets are concentrated in the spleen. They are released into the blood when necessary. Some disorders and diseases provoke splenomegaly (delay in the spleen of platelets up to 90%).
Thrombocytopenia (the causes of occurrence in adults are infectious) can be a consequence of:
- infections;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- alcoholism;
- lupus erythematosus;
- lymphomas, leukemias.
With prolonged splenomegaly, most platelets are destroyed. Compensatory reactions develop in the bone marrow. Also, this type of thrombocytopenia appears with hemangioma (benign neoplasm). After its removal, the disease disappears.
Breeding
Dilution thrombocytopenia is diagnosed in patients in the hospital - after operations, transfusion, severe blood loss. In this case, platelet replacement does not occur. As a result, their concentration decreases so much that normal blood clotting is disrupted.
The causes of thrombocytopenia, depending on the stage:
| Stage of the disease | Causes |
| Moderate |
|
| Sharp |
|
| Expressed |
|
The cause of thrombocytopenia in adults is often cancer, in particular, chemotherapy. The risks are increased with the use of platinum and gemcitabine preparations. Radiation therapy leads to the suppression of the work of the red bone marrow and a strong decrease in platelets. The risk increases significantly after chemotherapy.
Diagnostics
Basically, the symptoms of thrombocytopenia indicate not an independent disease, but other pathologies, disorders of the body.
Therefore, the following are used for diagnostics:
- KLA (complete blood count), which allows additional study of individual cells;
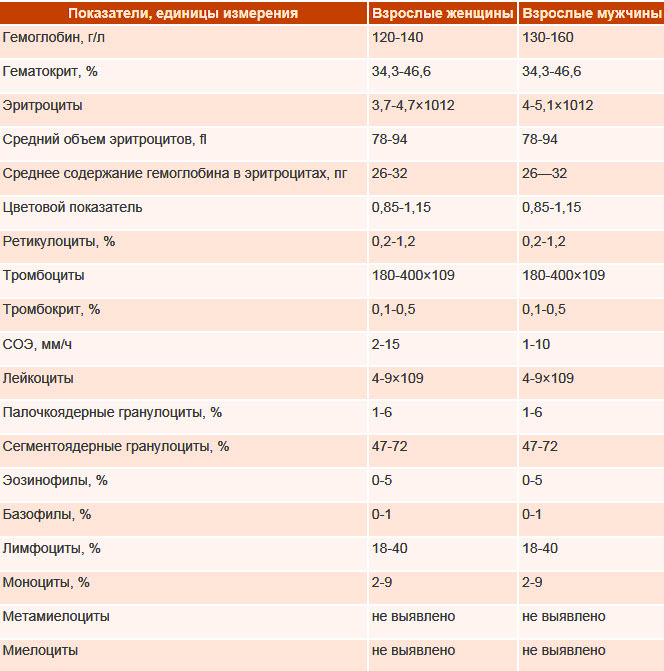
- Duke determination of bleeding time;
- assessment of the rate of blood clotting;
- puncture of the red fluid of the bone marrow (10-20 ml of the substance is taken with a needle and its smears are examined under a microscope);
- detection of antibodies in the blood;
- genetic research (helps to detect mutations in parents and relatives);
- Ultrasound (examines the size and structure of the spleen, liver, reveals tumors);
- MRI (allows you to get a layer-by-layer image of organs and blood vessels).
In hereditary thrombocytopenia, genetic testing can help identify the defective gene. It is different for each disease. In thrombocytopenia of consumption, the criteria at the beginning and end of the disease are compared. In addition to those listed, other studies are not required.
In the clinic, upon presentation of an insurance policy, diagnostics and treatment are carried out free of charge. In private clinics, the cost of services ranges from 1,700 rubles. It depends on the region, equipment, doctor's experience.
When to see a doctor
Thrombocytopenia is treated by a hematologist. Referral to it is given by the therapist. A doctor should be consulted if sudden subcutaneous hemorrhages appear (incl. on mucous membranes), spontaneous nasal bleeding, when bruises and hematomas appear on the body after a light blow.
Also, the therapist refers the patient to a hematologist with an unfavorable general blood test, if the platelet count differs from the established norm.
Prophylaxis
Since thrombocytopenia can be a hereditary disorder, people at risk are not recommended to exercise. You need to try to avoid falls, injuries, factors that can provoke bleeding. It is important to eat right so as not to disrupt the work of internal organs, in particular the liver and spleen.
Undergo preventive medical examinations annually. Prevention rules are especially important for people who have one or more parents with thrombocytopenia.
Treatment methods
Therapy is prescribed depending on the severity of the disease, its cause. First, a general examination, samples are carried out, analyzes are taken and examined by instrumental methods. In addition to drugs, alternative therapy methods can be used, a special diet is prescribed.
Mild thrombocytopenia does not require hospitalization or medication. If moderate severity is detected, therapy is carried out at home. Physical activity is limited, medications are prescribed. In severe thrombocytopenia, hospitalization of the patient is required.
This condition threatens human life, and treatment is carried out under the constant supervision of doctors. Also, all people with heavy bleeding are subject to compulsory hospitalization, regardless of their location and platelet level. This increases the risks of cerebral hemorrhage and death.
Medications
Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating the cause of thrombocytopenia, hemorrhagic manifestations, treatment of diseases that provoked bleeding.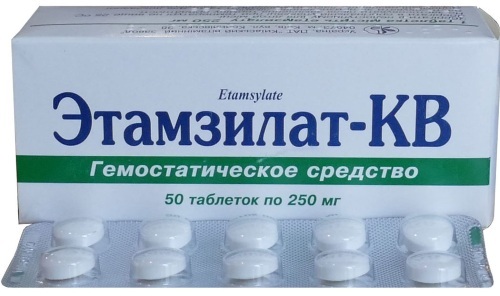
| Drug name | Indications | Mechanism of action | Dosage, method of administration |
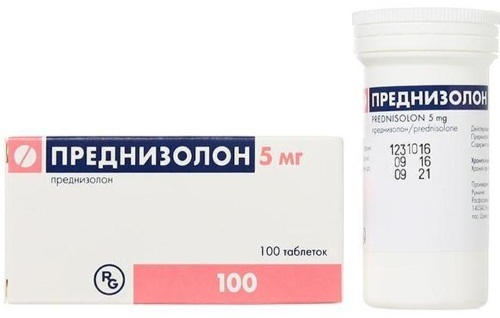
| "Prednisolone" (20-180 rub.) |
Autoimmune form, secondary thrombocytopenia and antibody formation |
|
At the beginning of treatment, 40-60 mg per day (for 2-3 doses). The dosage can be increased up to 5 mg. The course of therapy is a month. When remission is achieved, the dose is gradually reduced - by 2.5 mg per week, until the drug is completely discontinued. |
| Immunoglobulins (from 500 rubles) |
|
The amount of the drug is calculated depending on the body weight - 400 mg / 1 kg. Take once a day. The course of treatment is 5 days. | |
| "Vincristine" (from 1500 rub.) |
Stops cell division. Used for tumors, reduces the production of antibodies to platelets. | Prescribed if a large amount of antibodies is found in the blood or other drugs are ineffective. "Vincristine" is administered intravenously, once a week at the rate of 0.02 mg / 1 kg. The course of treatment is a month. | |
| Vitamin B12 ("Cyanocobalamin") (from 30 rubles.) |
Essential for the synthesis of platelets and erythrocytes | Prescribe 300 mg once a day | |
| "Eltrombopag" (from 27000 rub.) |
To reduce the risk of hemorrhage in idiopathic disease | Artificial analogue of thromboetin. Stimulates the formation of megakaryocytes, increases the concentration of platelets. | It is prescribed in tablets, 1 time per day, 50 mg. If there is no effect, the dosage is increased to 75 g. |
| "Etamsilat" (from 110 rub.) |
Any thrombocytopenia other than the initial degree of disseminated intravascular coagulation | The drug accelerates the formation of blood clots in the injured area. Reduces the permeability of the vascular walls, restores normal blood microcirculation. | It is prescribed in tablets of 500 mg, three times a day, after meals |
| "Depo-Provera" (from 100 rubles) |
Assigned to women with heavy menstrual bleeding caused by thrombocytopenia | The drug reduces the production of luteinizing hormone in the pituitary gland. This delays menstruation. | The drug is administered intramuscularly, 150 ml, every 3 months |
With thrombocytopenic purpura, immunomodulators are prescribed ("Timolin" (from 500 rubles), "Splenin" (from 80 rubles)). If megaloblastic anemia is detected, vitamin B12 and folic acid are prescribed.
When corticosteroids are prescribed, but after the first course of treatment, positive dynamics are not observed, then such further treatment is considered futile. To stop bleeding, use "Ditsinon" (40-430 rubles), "Vikasol" (20-70 rubles).
Traditional methods
Folk remedies for the treatment of thrombocytopenia can only be used as an adjunct. If other pathologies are the cause of the disease, then drug treatment is required.
| Direction of treatment | Herbs, products | How to cook, take |
| To strengthen the immune system |
|
If aloe is used, then fresh leaves are harvested. Keep them in the cold for 2 weeks. Then squeeze the juice and mix it with honey in a 1: 2 ratio. Consume 1 tsp. l. daily. The course is 3 weeks. Onions and garlic should be included in the diet daily. Currant leaves can be added to tea every time. From the rest of the herbs, infusions or decoctions are prepared, which must be drunk daily. |
| Restore normal blood composition |
|
Plants are taken in any quantity and brewed like tea. You need to drink the infusion daily. Sesame oil also helps to restore blood formation. Beets are boiled and eaten or squeezed out of raw juice. It is mixed 1: 1 with water and I drink 1 tsp. l. in a day. |
| To strengthen the vascular walls, prevent bleeding |
|
Parsley and berries can be eaten daily. Collect the rest of the herbs (at your discretion). It is brewed like tea and drunk daily. Collection example: take chopped dry chamomile, mint and shepherd's bag (20/40/40 g each). Then 1 tbsp. l. raw materials to brew 300 ml of boiling water. Filter and drink in the morning and evening, 100 ml each. |

Before using folk remedies, you need to consult your doctor.
Other methods
Additional non-drug treatment includes surgery and therapeutic measures:
- Bone marrow transplantation. An effective method of treatment with a significant decrease in the number of platelets. Before the operation, cytostatics and drugs to suppress the immune system are prescribed in large doses. The goal is to prevent the body from reacting to a donor brain transplant and the destruction of tumor cells in the hematopoietic system.
- Spelenectomy (splenectomy). If radical treatment is required, it can be removed. The indications for surgery are relapses of the disease after drug withdrawal, their ineffectiveness within a year. In most cases, after splenectomy, the platelet count is normalized, and the clinical manifestations disappear.
- Transfusion therapy. This is a transfusion of donated blood, platelets or plasma. However, the procedure can cause dangerous side effects, from infection to anaphylactic shock and death. Therefore, transfusion is done only if the patient's life is at risk (risk of cerebral hemorrhage, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome). The procedure is carried out under the supervision of doctors, in a hospital.
With thrombocytopenia, it is necessary to adhere to proper nutrition. It must be balanced. The presence of carbohydrates, proteins and fats in the diet is a must.
The menu also includes products to replenish minerals and vitamins. You can not eat coarse food, it is important to chew large pieces thoroughly so as not to injure the mucous membrane and prevent bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract. Eliminate alcohol, very hot and cold drinks, meals.
Possible complications
The main complications of thrombocytopenia are bleeding and hemorrhage. More serious consequences may appear depending on their intensity and localization.
The most dangerous are:
- Post-hemorrhagic anemia. It develops as a result of profuse bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract. The main danger is that it is not always possible to detect anemia in time. As a result, bleeding lasts for several hours and is often repeated. If a person loses more than 2 liters of blood, it can lead to death.
- Hemorrhage in the eyes. The retina is soaked in blood. Red spots appear in the eyes, vision deteriorates. The patient may go blind.
-
Brain hemorrhage. This is a rare but most dangerous complication. It often occurs spontaneously. In 25 percent, patients die.
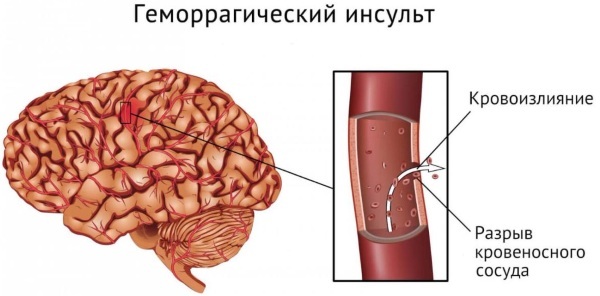
Hemorrhagic stroke
Bleeding may also open after surgery, extraction of teeth, tonsils.
When thrombocytopenia occurs in adults, the prognosis depends on the stage and duration of the disease that caused its causes, the presence of complications. Running diagnostics can lead to death. People who have thrombocytopenia need to donate blood for a general analysis every six months.
Video about thrombocytopenia
Immune thrombocytopenia in children:




