1 Etiology of the disease
The pancreas is a vital secret producing organ, which contains enzymes that ensure normal digestion. In addition, this body produces insulin and glucagon, which control the level of sugar in the blood. Most cases of development of acute pancreatitis are associated with alcohol use or with the presence of a history of cholelithiasis.
There are a number of factors that contribute to the emergence and development of this acute pathology. These include:
- herpes viruses;
- infection with campylobacteria or mycoplasma;
- abdominal surgery;
- reception of hormonal preparations, which negatively affects the pancreas;
- pancreatic injury;
- organ development defects;
- hereditary predisposition;
- cholecystitis;
- gastroduodenitis;
- hepatitis;
- cystic fibrosis.
Acute pancreatic inflammation causes damage to the functioning of enzymes that are produced by this organ. If in norm they are activated only in the digestive tract, then in a similar pathology the mechanism of their work is violated, and they begin their activity in the pancreas itself, which leads to digestion of the body's own tissue. The result of this complex process is inflammation of the pancreas, accompanied by edema of the organ tissue and the damage of the parenchyma vessels.
2 Clinical manifestations of
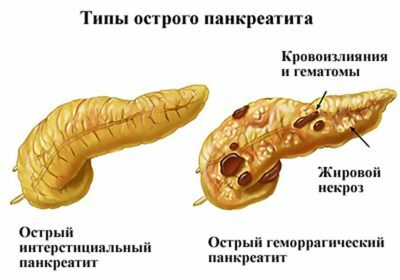
Symptoms of the disease depend on the form in which it occurs, mild or severe. In mild form, minimal organ damage is observed. The disease is expressed mainly by edema, which is easily treated and has a favorable outcome. In the case of severe course, severe disorders and local complications develop in the form of necrosis, infection, abscess formation or cyst.
The most common symptoms are unexpected, they are as follows:
- Acute intense pain in the navel. She can irradiate in the lower back and remind of the character of heartache, as she shoots her shoulder. This syndrome builds up gradually and can cause painful shock.
- Indomitable nausea and vomiting, which does not bring relief to the patient. In some cases, vomit can contain blood.
- The incessant hiccough. It is the result of irritation of the diaphragmatic nerve.
- Severe bloating. It occurs because of the disruption of the functioning of the transverse colon. At palpation, soreness is noted.
- Changing the stool. It can be frothy, with a sharp unpleasant odor and contain particles of food. But there are also constipations with bloating.
- Loss of consciousness, severe pallor.
- Increased temperature and frequent heartbeat.
-
 IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
In its development, acute pancreatitis passes through 3 phases. The first is an enzymatic one, it includes the initial 5 days of the disease. During this period, pancreonecrosis may develop. Then there is a 2 phase lasting for the next 7 days. It is characterized by the formation of peripancreatic infiltrate. The third phase begins with 3 weeks from the onset of the disease and can last for months. Characterized by the development of sequestration - a purulent complication.
Recommended to read
- Chronic gastroduodenitis code for ICD-10
- What is pancreatic diffusion
- Pancreatic pancreatic necrosis forecast
- Effective agent for gastritis and gastric ulcer
3 Diagnosis and treatment of pathology
Diagnosis of acute pancreatitis is carried out on the basis of various methods: patient complaints, physical examination, laboratory tests, instrumental research. According to the results of a clinical blood test, it is possible to detect an increase in red blood cells, a decrease in hemoglobin level, an increase in leukocytes and ESR.
-
 Gastroenterologist IMPORTANT: "I beg you, if you began to worry about abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, do not in any way do gases. .."Read more & gt; & gt;
Gastroenterologist IMPORTANT: "I beg you, if you began to worry about abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, do not in any way do gases. .."Read more & gt; & gt;
With the help of ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity organs, pancreatic swelling and stones in the ducts are detected. To confirm the diagnosis, a magnetic resonance imaging of the pancreas is performed. During the diagnosis, it is necessary to differentiate acute pancreatitis from acute appendicitis or cholecystitis, perforated ulcer of the stomach or intestine, intestinal obstruction or gastrointestinal bleeding.
This disease requires urgent hospitalization of the patient. The primary therapeutic goal is to reduce the pain syndrome and reduce the burden on the diseased organ. Then it is necessary to achieve the regeneration of the pancreas. Conservative treatment includes the restoration of acid-base, protein and water-electrolyte balance. To do this, salt and protein infusions and detoxification therapy are carried out. For the prevention of infectious complications, the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics is indicated. To remove the pain, novocaine blockades are carried out and antispasmodics are prescribed.
During an acute period the patient must observe hunger. In addition, proton pump inhibitors and pancreatic enzyme deactivators are prescribed.
ADVICE FROM THE MAIN GASTROENTEROLOGIST
Korotov SV: "I can recommend only one remedy for the rapid treatment of Ulcer and Gastritis, which is now recommended by the Ministry of Health. .." Read testimonials & gt; & gt;
Surgical treatment is performed in the following cases:
- formation in the pancreas of the cyst or abscess;
- formation of foci of necrosis;
- detection of stones in ducts;
- is a congestion in or around the pancreas.
In the postoperative period, intensive rehabilitation therapy is conducted, aimed at preventing and preventing purulent-septic complications. Severe form of pancreatitis can lead to death of the patient. Therefore, the prognosis of the disease directly depends on the form in which it occurs, how quickly medical aid was provided, and whether pathology is accompanied by complications.
- 1 Etiology of the disease
- 2 Clinical manifestations
- 3 Diagnosis and treatment of pathology
The international code and classification of diseases assigns a code for ICD 10 K.85, which is inflammation of the pancreas, to acute pancreatitis. This rapidly developing disease is characterized by organ damage by its own enzymes. Pathology threatens the patient's life if timely medical assistance is not provided. Such a dysfunction of the pancreas is very common and occurs with the same frequency in men and women.
Do you have pancreatitis?
Natalia Ronina: "How did I manage to beat pancreatitis at home for 1 week, paying 30 minutes a day? !" Read more & gt; & gt;



