 The essence of epilepsy is that the nerve impulses of the brain impair conductivity. Neural connections in the brain of the patient are violated. As a result, a person suffers from epileptic seizures of various kinds and origins.
The essence of epilepsy is that the nerve impulses of the brain impair conductivity. Neural connections in the brain of the patient are violated. As a result, a person suffers from epileptic seizures of various kinds and origins.
Partial epilepsy has its own characteristics, if the generalized form affects both hemispheres in the brain, then the partial becomes the result of the defeat of only its individual parts.
Aggravating factors
Most neurologists believe that the cause of partial epilepsy can be a complex of various factors. The main reason is the genetic predisposition. That is why the first symptoms of the disease manifest themselves in childhood or during adolescence.
The cause of partial seizures of epilepsy can be such factors:
- neoplasms that appeared in the brain( they can be both benign and malignant);
- abscesses, bruises, cysts;
- all possible changes in blood vessels: malformations, aneurysms;
- violation of the cerebral circulation( for example, in stroke, ischemia and other pathologies);
- penetration of neuroinfections( syphilis, encephalitis, meningitis, etc.);
- congenital pathological changes in the nervous system;
- various head injuries.
These factors can trigger the onset of epilepsy or aggravate seizures. Under the influence of any of these factors in a certain area of the brain, neurons begin to give pathological signals with a changed intensity.
Over time, this affects negatively all cells that surround the pathological zone. This provokes the development of epileptic seizures.
Localization of a disorder in the brain area
The classification of partial epilepsy is based on the detection of an area in the brain with an increase in activity during the seizure period. By the way, the picture of a specific fit will largely be determined by the location of the focus of pathological excitability of neurons.
Possible location of the outbreak:
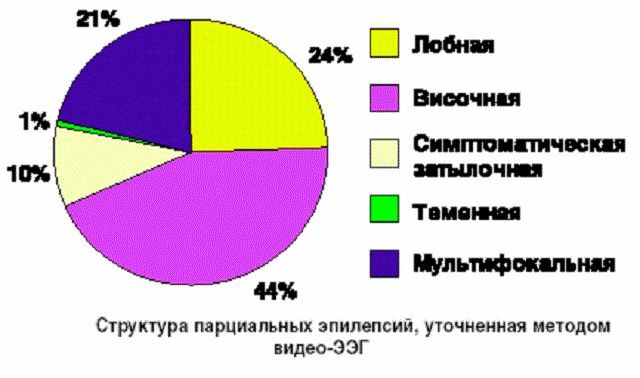
- Temporal .This is the most common type of partial epilepsy( about 50% of all cases of the disease is provoked by the pathological activity of neurons in the temporal zone).
- Frontal .Deservedly takes the second most frequent place( 24-27%).
- Occipital ( about 10% of all patients with this form of epilepsy).
- The Dark .It occurs least often( 1%).
How to determine the exact location of the source? Now it is very simple. EEG( electroencephalogram) will help.
Diagnosis is most often performed during the period when the patient is at rest or asleep( polysomnography).But the most accurate result is given by EEG directly during the next attack. It is almost impossible to wait for it. Therefore, the attack is provoked by the introduction of special drugs.
Types of seizures and their symptoms
Partial epilepsy in each patient manifests itself in purely individual attacks. But there is an accepted classification of their basic types. With simple partial attacks, the patient's consciousness remains fully or partially. This state has different forms of manifestation:
- can observe not very intense contractions of the muscles of the legs, arms, facial muscles, the patient feels numbness, tingling, the so-called "goose bumps" on his skin;
- the patient turns in a certain direction of the eye, head, and sometimes the entire body;
- salivation is observed;
- the patient performs chewing movements, grimaces;
- stops the speech process;
- there is pain in the epigastric region, heartburn, heaviness, peristalsis becomes worse, flatulence appears;
- may have hallucinations: taste, olfactory, visual.
Approximately one third of patients have complex partial seizures, in which a person loses consciousness. Such patients are often quite aware of what is happening, but are not able to speak, answer the questions posed.
Often after a regular attack, the patient experiences a phenomenon of amnesia. He forgets everything that happened.
Symptoms of complex partial seizures:
- The patient appears strong anxiety, fear of death .
- He concentrates on the events that occurred or the words hears, experiences strong experiences because of them.
- A completely familiar environment for the patient begins to be perceived as unfamiliar to him. Or maybe, on the contrary, pursue the feeling of "deja vu" .
- The patient perceives what is happening, as something unreal .He can perceive himself as a hero of a book, a film he has seen, or even watching himself, as if from a side.
- Automatisms of .These are certain intrusive movements. What exactly the movement will appear in the patient, depends on what zone in his brain is affected.
- In small periods between seizures, a person at the initial stage of development of partial epilepsy feels quite normal. But with time, more and more manifest symptoms of brain hypoxia or the underlying pathology of .There are headaches, sclerosis, personality changes, dementia( dementia) is observed.
Consider the manifestation of each type of disease in more detail.
Lesion of the frontal lobes of the brain
Partial epilepsy in the frontal lobes has the characteristic symptoms: 
- simple seizures;
- complex seizures;
- secondary generalized paroxysms;
- is a combination of these seizures.
Seizures last for 30-60 seconds, often repeated. One can observe their seriality. Often they happen at night. In 50% of patients, the seizure begins without an aura before it begins.
Frontal epilepsy has its own peculiarities:
- seizures are quite short( up to 1 min);
- after the end of complex seizures there is a minimum of confusion;
- very quickly come secondary attacks;
- it is often possible to observe motor disturbances( uncharacteristic automatic gestures, trampling in one place);
- at the beginning of an attack of automatism are very common;
- the patient often falls. Forms of frontal epilepsy:
- Motor .It manifests itself in the form of convulsions in the limbs, aura before the attack, Todd's paralysis may occur, often secondary generalization occurs.
- Front( frontal-polar) .It manifests itself in the form of painful memories, the sense of time changes, thoughts swim, often there are failures in memory.
- Cingular .Characterized by hyperemia of the face, increased motor activity, blinking, a state of affect.
- Dorsolateral .The patient turns his eyes, head and even his torso in one direction, for the time of an attack loses speech, and there is often a secondary generalization.
- Orbito-frontal .
- The operative .
- Additional motor zone .
Temporal form of disorder
Temporal partial epilepsy manifests itself in such attacks:
- simple;
- complex;
- secondary generalized;
- of their combination.
Very often, with a temporal form, there are complex partial seizures with automatisms and a frustrated consciousness.
Very often, before an attack in the case of a temporal form, the patient feels an aura:
- olfactory;

- flavoring;
- visual;
- somatosensory;
- vegetative-visceral;
- auditory;
- is mental.
Types of temporal epilepsy:
- Paleocortical .The patient can freeze with a completely immobile face, his eyes remain wide open, pointing at the same point. There is a feeling that he just "stares" at something. The consciousness can be switched off, but at the same time the motor activity remains. For example, a patient can touch their buttons on clothes. Often the patient can simply fall down without the appearance of seizures( syncopal temporal).
- Lateral .During seizures speech, vision, hearing are broken, auditory and visual hallucinations appear.
Patients with occipital form of epilepsy are tormented by visual hallucinations, impaired vision, discomfort in the eyeballs, curvature( deviation) of the neck, they often blink.
Complex of therapeutic measures
 Partial epilepsy is an incurable disease. The essence of treatment is reduced to reducing seizures. To achieve remission, antiepileptic drugs are prescribed( Carbamazepine( standard drug for all possible forms of epilepsy), Lamictal, Depakin, Topiramate).
Partial epilepsy is an incurable disease. The essence of treatment is reduced to reducing seizures. To achieve remission, antiepileptic drugs are prescribed( Carbamazepine( standard drug for all possible forms of epilepsy), Lamictal, Depakin, Topiramate).To get the maximum result, the doctor can combine the drugs. If the medication fails to work, perform a neurosurgical operation.
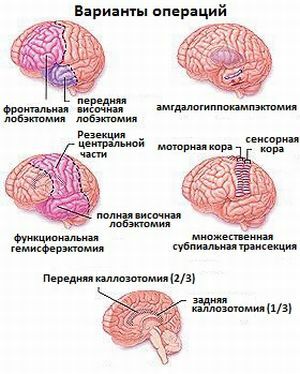
The operation is resorted to only if all methods of conservative treatment are not successful, and the patient suffers from frequent seizures.
Trepanation of the skull occurs in the zone that caused epilepsy. The neurosurgeon neatly excludes everything that irritates the cerebral cortex - the membranes that are changed by scars, exostoses. Such an operation is called meningoencephalolysis.
The Horsley operation is performed more rarely. Her technique was developed by the English neurosurgeon Horsley in 1886.In this case, the affected cortical centers are scooped out.
If partial seizures of epilepsy provoke scars on the substance or shells of the brain, the results of such an operation do not bring the desired result.
When the irritating effect of scars on the brain is eliminated, seizures may temporarily stop. But very quickly in the area of the operation again formed scars, and even more massive than the previous ones.
After surgery, Horsley may be attacked by a monoparality of the limb that has been removed from the motor centers. At the same time seizures stop. Over time, paralysis passes, it is replaced by monoparesis.
Forever in the patient there is some weakness in this limb. More often than not, seizures reappear with time. Therefore, surgical intervention is not the first-choice method for partial epilepsy. Preferably conservative treatment.
The essence of the prevention of all kinds of epilepsy is as follows:
- should avoid craniocereberal trauma;
- should avoid intoxication;
- needs to treat infectious diseases on time;
- should not have children, if both parents suffer from epilepsy( this at times increases the risk of developing diseases in their children).