 Tumor of the bone is the appearance of neoplasms in the bones.
Tumor of the bone is the appearance of neoplasms in the bones.
The disease is very rare - it accounts for about 1% of cancer patients. Most often affected by the bones of the legs and skull.
Bone cancer is a collective concept, combining both primary neoplasms( osteosarcoma, osteoma) and secondary ones, resulting from metastases from other organs.
What is osteoblastoma?
- Diagnosis
What is osteoblastoma?
Osteoblastoma is a benign neoplasm of bone tissue, one of the types of osteoma.
Most often this disease begins in childhood and adolescence up to 30 years, only in 10% of cases this disease was registered in older people.
Men are exposed to him more often than women twice.
Develops in comparison with osteoid osteoma quickly and in size varies in the range of 2-10 cm.
Usually proceeds painlessly, but it can also be accompanied by blunt pains and other symptoms when exposed to neighboring organs and tissues. Treatment is usually surgical, but it can not be removed if it does not cause discomfort and is not a cosmetic drawback.
Often this disease is confused with osteophytes. Osteophytes are bone growths that appear with age in almost 100% of the population and are not related to tumors.
Tumor varieties
There are 2 types of osteoblastoma:
- The quaint consists of a large number of multinucleated cells. As a rule, it has a favorable outlook.
- Aggressive - the disease occurs with relapses and is very common in people older than 30 years. Having clear boundaries, it, nevertheless, can penetrate into adjacent bones, rapidly increasing in size.
How can education be caused?
The reasons for the appearance of education are not fully determined.
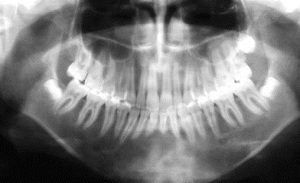
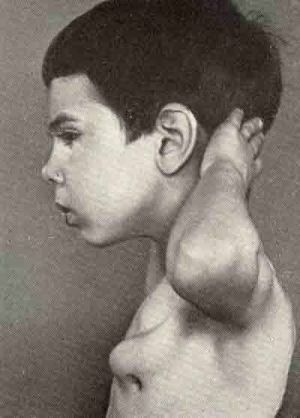
In the photo of the mandibular osteoblastoma
, trauma, systematic repeated effects( eg, cavalry syndrome in riders), hypothermia can provoke the development of the disease.
The most common reasons are:
- heredity( the probability of transmission of the disease to children around 50%);
- congenital pathology;
- injury;
- inflammation;
- syphilis in the advanced stage;
- rheumatism;
- impaired calcium metabolism.
Risk factors are permanent colds and inflammatory diseases, reduced immunity, metabolic disorders.
A major role is played by the systematic receipt of the same injury, this is often found in athletes during training or shooters.
The disease begins to manifest itself at a young age, while the body is still growing. With age, the growth is increasing.
Tumor localization
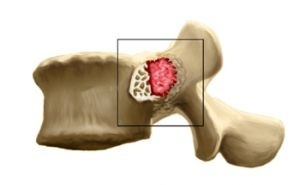
In most cases( about 50%), osteoblastoma is localized in the spine, leading to the development of scoliosis.
Also the pathologies are susceptible to humeral, femoral, tibia. It can develop in places of attachment of tendons and joints, as well as in the area of the fingers and toes.
Detect and diagnose a tumor
A small tumor can be invisible for a long time, it manifests itself as the appearance of a solid cone, usually painless.
When compressing nerves or blood vessels, there may be a feeling of discomfort, pain, sensation of foreign body.
Often completely asymptomatic and can be detected only on an X-ray.
Depending on the location of the osteoblastoma, the symptoms also differ:
- With localization on the bones of the skeleton , it is possible to draw muscle pains, impairment of motor activity, discomfort or pain during movement. Possible the development of inflammatory joint diseases.
- When the skull of is affected, headaches, nosebleeds, difficulty breathing, sore throat may appear. Perhaps the occurrence of dizziness, epileptic seizures, the fall of vision, the lowering of the eyelid, the bulging of the eyeball. When the jaw bone is affected, the motor function decreases.
- The most dangerous development of the tumor inside the skull is .This is fraught with consequences such as memory loss, hormonal failures, increased intracranial pressure, the development of epileptic seizures and the disruption of other body functions, depending on the area of the brain being exposed.
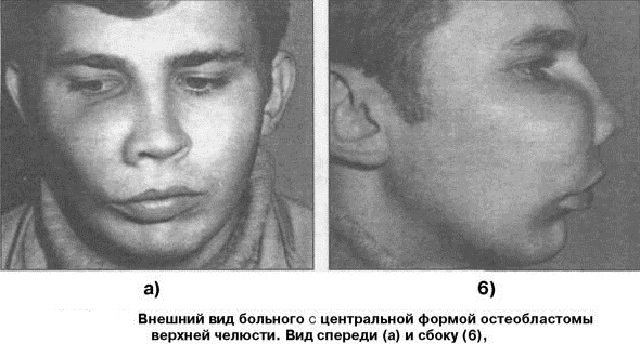
Diagnosis
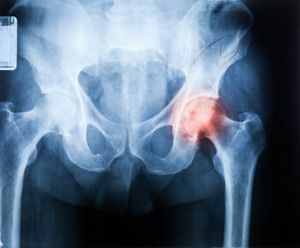
Based on the clinical picture, the doctor prescribes a radiographic examination. In the picture, the focus will be oval, swollen, surrounded by a small aureole of sclerosis.
The study will show the affected area, dimensions and accompanying pathologies.
As the main method of diagnosing osteoblastoma, radiography is effective in the study of medium and large neoplasms.
It will help determine the type of tumor - hard, spongy or cerebellar, and also the degree of its impact on other tissues, the presence of destruction of the bone structure.
Additional diagnostic methods are aimed at clarifying the diagnosis and are effective for small tumors. These include:
- computed tomography;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- histological examination;
- bone scintigraphy.
Treatment methods
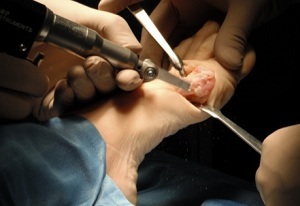
Osteoblastoma is surgically removed, this method is indicated in the following cases:
- neoplasm interferes with the functioning of body systems;
- is a cosmetic defect;
- there is a delay in development or deformation of bones;
- began to increase rapidly in size( extremely rare).
 Mostly, systematic observation is shown. In the case of development of concomitant effects( pain, joint problems), symptomatic treatment is indicated. Often prescribe anti-inflammatory and pain medications.
Mostly, systematic observation is shown. In the case of development of concomitant effects( pain, joint problems), symptomatic treatment is indicated. Often prescribe anti-inflammatory and pain medications.
To avoid recurrence, removal occurs with truncation of a healthy portion of the bone.
Surgical removal is of two types:
- Surgical intervention .Depending on the location of the neoplasm, surgery is performed by traumatologists, orthopedists or specialists in maxillofacial surgery.
- Evaporation of .Removal of neoplasm with a laser. This method is less traumatic, and the rehabilitation period is much shorter.
Since the size of the lesion is large enough - it can reach 10 cm - often after removing it requires plastic.
What are the chances of success?
Operations conducted in childhood tend to have a favorable outlook.
Recurrences of the disease after surgery occur in 20% of cases.
Osteoblastoma can cause secondary osteogenic sarcoma - this occurs in 25% of patients.
Removal of a large tumor, or located in a conspicuous place, is fraught with cosmetic defects. Small neoplasms are removed without a trace, and large tumors require a second stage of treatment - plastic surgery.
Preventative measures
Specific prevention does not exist. It is necessary to maintain the body in shape, to observe the diet and sleep. It should be remembered that in people with a good metabolism and a strong immune system, the risk of developing the disease is much lower.
If bone seals are found, consult a doctor and keep them under observation. 
Osteoblastoma is a benign new growth in the bone, which makes itself felt in childhood and adolescence. It develops for a long time and can give relapses or in rare cases to be modified into a malignant one.
Dangers do not represent if it does not affect nearby organs and does not affect the body's functions. Treatment of the disease is only surgical. With timely treatment in medical centers and attentive to their health, the negative consequences of the development of the disease are easily avoided.