Parkinsonism is a disorder in the brain, accompanied by trembling of the head, arms and legs, stiffness of movements and increased muscle tone.
Parkinsonism is a disorder in the brain, accompanied by trembling of the head, arms and legs, stiffness of movements and increased muscle tone.
Parkinson's disease is characterized by similar phenomena, but unlike it, parkinsonism can occur again( after craniocerebral injuries, poisonings, etc.).
Parkinsonism( trembling paralysis) is not an isolated disease, but a syndrome( a combination of symptoms).
Parkinsonism syndrome manifests itself in a number of neurological disorders.
Depending on the cause of the disorder, the following are identified:
- Primary( idiopathic) .In this case, the syndrome causes the death of dopamine neurons in the nervous system of the body. They regulate locomotor activity, their lack leads to impaired motor function.
- Secondary syndrome is provoked by external factors: taking medications, head injuries, infections, etc.
Parkinsonism is very common in old age. For the first time the condition was described in 1817 and was named after James Parkinson.
Quake paralysis occurs in every fifth person older than 80 years.
Contents
- Causes and risk factors
- Primary form
- Reasons for the secondary form
- What types of the syndrome are
- Clinical picture
- Individual approach - the basis of therapy
- General advice
- Complications
- It is possible to stop the development of the syndrome!
Causes and Risk Factors
The causes of primary and secondary forms are different.
Primary form of
Primary Parkinsonism is the most common form. Tremor paralysis is a symptom of neuronal damage and death.
One of the functions of neurons is the production of dopamine, responsible for the transfer of impulses that provide movement.
When the disease develops, dopamine production decreases, resulting in impaired transmission of impulses. The result is the 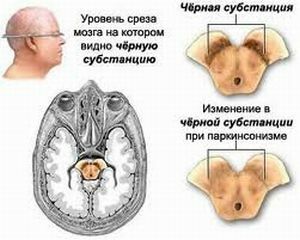 manifestation of parkinsonism symptoms.
manifestation of parkinsonism symptoms.
With age, a person's dopamine production decreases, but people suffering from such a disease lose a large part of the neurons.
The exact cause of neuronal destruction has not yet been identified.
Reasons for the secondary form of
Secondary Parkinsonism can be caused by a variety of causes. The disorder can develop after taking medications, traumatizing the head, infectious diseases, and tumor processes.
The disorder often occurs in people with signs of chronic cerebral circulatory failure.
Risk Factors:
- is frequently developed with the use of potent neuroleptics ( haloperidol, trifazine).The disorder can also develop with the treatment of mild antipsychotics( prochlorperazine).When taking atypical antipsychotics, the probability of the onset of the disease is minimized.
- often develops on the background of high doses of neuroleptic piperazine .
- Presence of background organic brain damage, craniocerebral trauma .
- The risk factors include age, sex, smoking e. In women, the syndrome occurs twice as often as in men.
- Family history of of Parkinson's disease.
- Schizophrenia at a young age.
- Cognitive Disorders .
- Diabetes mellitus .
 A vagoinsular crisis occurs when the work of the autonomic nervous system fails - the methods of treatment and symptomatology in our article.
A vagoinsular crisis occurs when the work of the autonomic nervous system fails - the methods of treatment and symptomatology in our article. The Louis-Bar syndrome kills the cerebellum and the cortex of the brain - how to alleviate the suffering of a doomed person?
What kinds of a syndrome are
Parkinsonism syndrome manifests itself in different ways:
- Parkinson's disease. occurs in 70% of cases of parkinsonism syndrome. The difference between this form and others lies in a one-sided beginning( for example, the disease first hits one arm, then the other).
- Medicinal. Most often is a consequence of the administration of neuroleptics and related drugs, calcium antagonists, reserpine, indomethacin, lithium preparations, etc. Symptoms manifest themselves during drug treatment and disappear several weeks after its completion.
- Toxic. Syndrome occurs when manganese, cyanide, methanol and other substances are poisoned. Most often, the changes are reversible, but with severe poisoning, prolonged maintenance of the symptomatology is possible.
- Vascular. Is manifested with ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke. To confirm the diagnosis, a computed tomography or MRI is performed.
- Post-infection .Develops after the transfer of infectious diseases( especially severe: for example, with the development of encephalitis, after syphilis).

- Post-traumatic .It develops as a result of head injuries, with permanent trauma to the brain( often in athletes).
- Tumor .Occurs in the presence of brain tumors.
- Idiopathic ( with an unknown cause).Formally included in Parkinson's disease, which manifests itself with similar symptoms( tremor, muscle stiffness), but does not have an exactly established cause.
Clinical picture of
Primary symptoms in parkinsonism syndrome are poorly expressed. The patient complains of weakness, apathy, insomnia.
Further obvious signs of the disease begin to appear:
- Tremor .It starts with a slight trembling of individual fingers or hands. A tremor of the legs may occur. Symptom is accompanied by a violation of coordination and sensitivity. Trembling increases with nervous tension and stress. During sleep, the tremor disappears.
- Deceleration of movements .It manifests itself in the form of awkwardness and lack of coordination. The gait is broken due to the stiffness of the leg muscles. This condition can cause pain and stiffness of movements.
- Imbalance of the .The severe form of the disease is accompanied by an inability to maintain balance.
- Loss of automatic movements .The patient can not smile, blink, wave his hands while walking. In some patients, a non-blinking sight is fixed. Some patients lose the ability to gesticulate.
- Speech disorder .The voice is illegible, quiet, monotonous.
- Impaired salivation, swallowing problems .This symptom is manifested in severe form of the disease.
- Dementia .Most often occurs at a late stage. The inability to understand, think and remember arises in a small number of patients.
Individual approach - the basis of therapy
 Treatment of Parkinson's Syndrome does not have a standard scheme.
Treatment of Parkinson's Syndrome does not have a standard scheme.
Each case requires an individual approach. In the secondary type of disease, the primary disease is first treated.
For example, the treatment of vascular parkinsonism requires surgical intervention( shunting).
Therapy involves the use of medications that have a positive effect on various nerve mediators( antidepressants, antipsychotics, anticholinergics).
In addition to taking medication, a special massage is prescribed, exercise therapy. It is extremely important that the patient does not stop taking physical activity.
If conservative treatment does not give proper results, brain neurostimulation is performed. In the chest area under the  , the skin is injected with a neurostimulator connected by electrodes to the brain.
, the skin is injected with a neurostimulator connected by electrodes to the brain.
In the treatment of severe disease, cardiac stimulation of the brain by means of a magnetic field is used. Electroconvulsive therapy is sometimes prescribed.
A new direction in the treatment of Parkinson's syndrome is transplantation of embryonic tissues and stem cells.
General advice
The key to successful treatment is to fulfill a few simple rules:
- clear execution of doctor appointments;
- thoughtful organization of work and leisure in order to prevent possible problems;
- compliance with the recommended diet;
- doing physical exercises;
- consultation with a psychologist and social workers on the problems that the patient may encounter, communication with other patients;
- no self-treatment.
Complications of
The disease can cause the following complications:
- immobility;
- inability to care for themselves due to severe symptoms;
- serious mental disorders( memory loss, loss of orientation in time and space).
Stop the development of the syndrome is possible!
The following measures will help prevent the disease:
- timely treatment of infections( taking antibiotics);
- detoxification( plentiful drink, intake of vitamins);
- control of blood pressure( if necessary - taking drugs that reduce blood pressure);
- administration of medications that can provoke the syndrome, in minimally effective doses and strictly according to the doctor's prescription;
- Avoid contact with toxic substances.