Diverticulosis is more often diagnosed in developed countries with a high life expectancy. The disease occurs with the same frequency in persons of any gender, regardless of body weight.
The risk of developing the disease increases with age, especially after 40 years, when the body's ability to withstand constant adverse factors - malnutrition, bad habits - is reduced. About the causes of diverticulosis of the intestine, about the symptoms and treatment of pathology read further.
Contents
- 1 Diverticulosis of the intestines - what is it?
- 2 Symptoms of intestinal diverticulum
- 3 Treatment of diverticulosis of the intestine, preparations
- 3.1 Diet for diverticulosis
- 4 Prognosis and prevention
Diverticulosis of the intestine - what is it?
Diverticulosis of the intestine is a pathology in which diverticulums appear on the mucosa, or protrusions of the organ wall to the sides. Such formations occur in different tubular and hollow organs, but are mostly formed in the digestive tract.
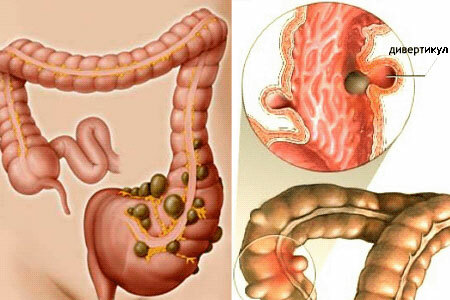
In the intestines more often develop multiple diverticula, in the esophagus and stomach - single.
Mechanism of the appearance of diverticulosis is as follows:
- in the diet there is a sufficient amount of dietary fiber( fiber);
- because of this the motor activity of the intestine is disrupted;
- because of constipation and constant swelling increases intestinal pressure, creating protrusions in the wall, or diverticula.
Another reason for diverticulosis is the weakness of the muscles of the intestinal wall. Sometimes it can appear during life due to trauma, inflammatory diseases. Most often, the weakened muscle layer is the cause of congenital diverticulosis.
Risk factors:
- genetic predisposition;
- permanent constipation;
- improper diet, excess of refined foods in the diet and fiber deficiency;
- disturbed circulation in the intestinal veins;
- old age.
Symptoms of diverticulosis of the intestine

Symptoms of diverticulosis of uncomplicated form include:
- Periodically occurring spastic abdominal pains, more often on the left, less often in the middle and below, can be sharp or aching.
- The pain intensifies after eating and can go on independently after a few hours.
- An attack of acute pain resembling manifestations of appendicitis occurs if the diverticula is in the sigmoid colon or in the right part of the intestine.
- Soreness can spread to the lower back, the sacrum, into the anus, the groin and the buttock zone.
- Pain most often disappears after bowel movement or accumulation of accumulated gases.
Associated signs of diverticulosis are:
- constipation - chronic or alternating diarrhea;
- excretion of a large amount of mucus from the anus;
- tenesmus - false urge to defecate;
- flatulence, fetid gases;
- feeling of incomplete liberation of the intestines after defecation.
One of the complications of diverticulitis is inflammation of protrusions - diverticulitis, resulting from stagnation of feces. The pain in the abdomen becomes permanent and pronounced, the temperature rises, blood can appear in the stool.
Inflammation of the diverticulum changes the indicators of urine and blood tests - they can detect lymphocytes, protein, erythrocytes.
Treatment of diverticulosis of the intestine, drugs
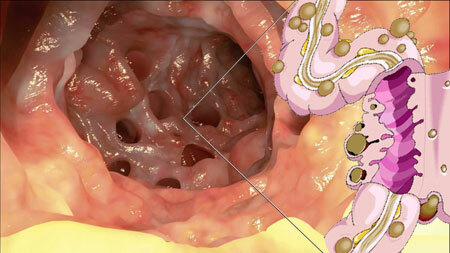
Diverticulosis without severe symptoms does not need special therapeutic measures. In this case, it is enough to observe a diet with a high content of vegetable fiber.
To treatment of diverticulosis of the large intestine without complications, when symptomatology appears in medical nutrition, the use of:
- antimicrobials of a broad spectrum of action;
- enzyme means for the normalization of digestion;
- antispasmodics;
- is laxative;
- preparations of oily and 5-aminosalicylic acid.
Therapy is performed on an outpatient basis, and hospitalization is needed only if there is no effectiveness of taking medications within 3-4 days. This applies to acute and complicated diverticulosis, in which the treatment regimen is as follows:
- antibiotics are prescribed;
- rinses the stomach, and the intestines are cleaned with siphon enemas;
- uses freshly frozen plasma;
- is infused with colloidal and crystalloid solutions.
Inflammation of diverticulum shows antibacterial drugs from the group of sulfonamides( sulfamethoxazole), cephalosporins( cephalexin), lincosamides( Clindamycin) and metronidazole. Antibiotic therapy is carried out for 7-10 days.
The operative removal of the part of the intestine affected by diverticula is shown in the case of:
- of severe intestinal obstruction;
- severe internal bleeding;
- formation of perforations accompanied by retroperitoneal phlegmon or peritonitis;
- appearance of intestinal fistula.
Diet in diverticulosis
The nature of nutrition in diverticulosis of the intestine provides for an increase in dietary fiber. Effective in this regard, products with a bran content - they help reduce intestinal pressure.
The healing effect is provided by the use of pure bran, which is introduced into the menu gradually over 2-6 months, starting at 5 g per day and reaching 35-40 g. They need to be filled with hot water and after swelling drain the remaining water. Then the bran is added to yogurt, kefir, cereals, dishes from vegetables, soups.
Vegetable fiber is needed for:
- increasing the viscosity of food in the small intestine;
- binding and retention of water in the stool, which reduces the intestinal wall tension;
- accelerate the progress of food through the intestines;
- absorption of toxic compounds;
- reproduction of useful microorganisms.
Products , which must be included in the diet:
- wheat and buckwheat porridge with vegetable oil;
- soups from vegetables on chicken or beef broth;
- kefir, fermented milk and other dairy products;
- bread with bran or wholemeal wheat flour;
- baked fruits and vegetables( pumpkin, apples, zucchini, pears, eggplants, tomatoes).
A similar diet because of a significant amount of dietary fiber during the first 3-4 weeks can increase abdominal pain. Therefore, to ease the condition, the diet is supplemented by taking antispasmodics - Mebeverin, No-shpy, Bukopan, Meteopazmila.
The source of plant fiber is also the preparations, which include shells of seeds of oval plantain, in which, in addition to fibers, the percentage of mucous substances is high. They have a softer, gentle effect on the intestines, and the risk of developing spasmodic pains and flatulence is minimal.
Examples of means: Mukofalk, Isago, Solgar Psillium, Fiberlex. Pure bran and preparations on their basis do not need to be taken with uncomplicated forms of diverticulosis, if the menu has enough fresh fruits, vegetables and greens.
Intestine should receive enough liquid - pure water, juices - at least 1200 ml per day. The best principle in the diet for diverticulosis is a separate diet, in which one meal is not recommended to combine proteins and carbohydrates. This contributes to the better absorption of food and the improvement of general well-being.
Prohibited:
- white bread made from fine flour;
- coffee and strong tea;
- pasta;
- rice and semolina porridge;
- chocolate, cocoa;
- fat, sausage, fatty foods;
- jelly.
One-off portions should be small, and the number of meals per day - 5-7.Admissible ways of cooking - for a couple, by baking or cooking. It is also important to thoroughly chew food.
Prognosis and prevention
Diverticulosis of the intestine, whose treatment began in a timely manner, has a favorable prognosis. With the development of the complications, the first attack is cured in 2/3 of the patients, and the third - only in 1/20.Therefore, when any symptoms of this disease appear, it is important to undergo a thorough examination.
Prevention of diverticulosis is as follows:
- Nutrition with a high content of dietary fiber and water;
- Physical activity;
- Prevention and timely treatment of constipation.
It is also important in time to identify any pathology of the digestive system and regularly visit a gastroenterologist.