Gilbert syndrome is one of the varieties of hereditary pigmentary hepatosis. It is associated with a disturbance in the metabolism of bilirubin in the liver and the disease is called conditionally. It is more correct to consider it a genetically conditioned feature of the organism.
The pathology was named after the French physician Augustine Gilbert, who was the first to discover the syndrome. The disease is transmitted from parents to children - the source can be either the mother or the father. This type of inheritance is called autosomal dominant.
The disease is more common in men and occurs in 2-5% of the world's population.
Content
- 1 Gilbert's syndrome - what it is in simple words
- 1.1 Syndrome Cause Gilbert
- 2 Symptoms of Gilbert's syndrome, a photo
- 3 syndrome Diagnostics Gilbert
- 4 The treatment of the syndrome Gilbert
- 5 Diet for Gilbert's syndrome
Gilbert's syndrome - what it is in simple words
photo
symptomsThis is a congenital chronic disease, in which the utilization of free bilirubin in liver cells - hepatocytes is disrupted. Other names are benign, nonhemolytic family jaundice, constitutional hyperbilirubinemia.
- What is Gilbert's syndrome? In simple words, it can be described as the process of accumulation in the blood of bilirubin, which normally is converted in the liver and is excreted from the body with bile.
- What is the danger of Gilbert's syndrome? The prognosis of the disease is favorable - it does not lead to death and, leaking mainly in chronic form, does not bring pain and discomfort.
Many throughout life do not even suspect of the presence of disease until the blood does not show an increase in bilirubin.
But if the diet, regime or due to drug overdose and due to other factors is not adhered to, the course of the disease worsens and, sometimes, complications develop - cholelithiasis, pancreatitis, cholangitis, chronic hepatitis and extremely rarely liver failure. In simple terms, you may not suspect this disease( especially if there are no visible symptoms of "yellowing"), until you cross a certain line in the diet or treatment.
- E80.4.- Code of Gilbert's syndrome according to ICD 10( International Classification of Diseases).
The cause of the Gilbert syndrome
Bilirubin is formed during the breakdown of hemoglobin, and the primary unbound form of this substance is toxic. Normally, its metabolism consists of several steps:
- transport in the blood plasma to the liver;
- capture of its molecules by hepatocytes;
- transformation into a non-toxic, bound form( conjugation);
- biliary excretion, or in simple words - getting into the bile secret;
- the final destruction and excretion in the intestines, where bile comes from the gallbladder.
The cause of Gilbert's syndrome lies in the mutation of the gene UGT 1A1.He is responsible for the work of the enzyme, which transforms the bilirubin molecule into a non-free form. When the disease, its activity is reduced by about a third of the norm. This also accompanies:
- Decreased ability of hepatocytes to capture bilirubin;
- Failure in the functioning of the enzyme, which transports it to the membranes of the liver cells.
As a result, the first three stages of bilirubin metabolism are disturbed, it accumulates in the blood and, when exacerbated, leads to the development of symptoms of Gilbert's disease, which will be discussed further.
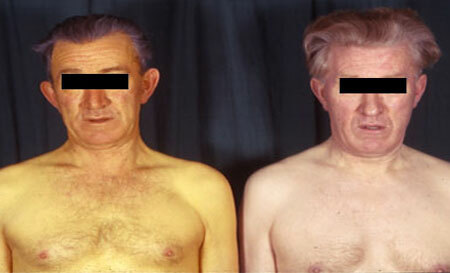
Symptoms of Gilbert's syndrome, photo
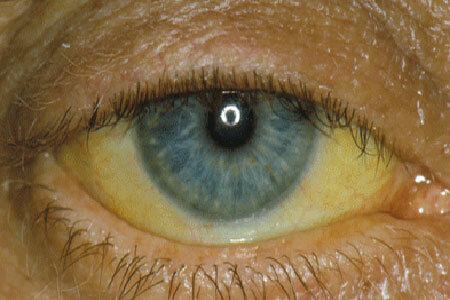
photo of Gilbert's syndrome
During the remission period the syndrome does not manifest itself. The first symptoms in most cases are found during puberty - from 13 to 20 years. At an earlier age, the disease manifests itself in the case of infection of the child with acute viral hepatitis.
Signs and symptoms of Gilbert's disease develop only with exacerbation, and in the vast majority of cases it is mild jaundice.
It manifests itself by staining the skin, mucous membranes and sclera in yellow - the so-called "liver mask".The severity of the hue is clearly visible when the level of bilirubin in the blood reaches 45 μmol / l or more. To jaundice is added the appearance of xanthelasm - yellow granular inclusions under the skin of the upper and lower eyelids, which is associated with connective tissue dysplasia.
About half of the patients complain of discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract:
- nausea;
- decreased appetite;
- belching;
- heartburn;
- flatulence;
- stool disorder.
Additional symptoms:
- weakness, dizziness;
- discomfort in the liver;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- swelling of the feet;
- lowering of blood pressure;
- shortness of breath and heart pain;
- anxiety, irritability;
- headaches.
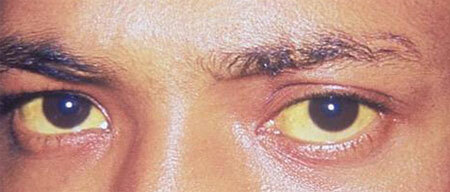
When the exacerbation of the syndrome often changes the color of the discharge - urine acquires a darker shade, and the feces become colorless.
During the life of the provocateurs, exacerbations of the disease are:
- Violation of the supporting diet, starvation;
- Drinking alcohol or drugs;
- High physical activity;
- Stress, overwork;
- Viral infections( influenza, herpes, HIV and others);
- Acute forms of existing chronic pathologies;
- Overheating of the body, hypothermia.
The intake of large quantities of certain drugs also affects the exacerbation of the genetic syndrome of Gilbert. These include: Aspirin, Paracetamol, Streptomycin, Caffeine, glucocorticosteroids, Levomycetin, Cimetidine, Rifampicin, Chloramphenicol.
Diagnosis of Gilbert's syndrome
After the examination and collection of anamnesis( complaints, medical history), a laboratory examination is performed. The attending physician sends tests for Gilbert's syndrome, among which there are special diagnostic tests:
- Fasting. The first sample of bilirubin is taken on an empty stomach in the morning before the test, the second - after 48 hours, during which a person receives with food not more than 400 calories per day. When the disease level of bilirubin for two days increases by 50-100%.
- Test with phenobarbital. If Gilbert's syndrome occurs, taking this medication for five days leads to a decrease in bilirubin in the blood.
- Test with nicotinic acid.40 mg of substance is administered intravenously, and if the percentage of bilirubin increases, the result is considered positive.
Other diagnostic methods:
- urine test for the presence of bilirubin;
- biochemical and general blood test;
- molecular diagnostics of DNA;
- blood test for the presence of viral hepatitis;
- analysis for strobobilin - in Gilbert's syndrome this product of bilirubin decay in the stool is not detected;
- coagulogram - evaluation of blood clotting.
Diagnosis of Gilbert syndrome includes such methods as ultrasound and computed tomography of the abdominal cavity, liver biopsy and elastography( the study of hepatic tissue for the detection of fibrosis).
Tactics for the treatment of Gilbert's syndrome
During remission, which can last many months, years and even a lifetime, special treatment is not required. Here the main task is to prevent an aggravation. It is important to follow the diet, the regime of work and rest, do not overcool and avoid overheating the organism, exclude high loads and uncontrolled taking of drugs.
Treatment of Gilbert's disease with the development of jaundice involves the use of medicines and diet. From medicines are used:
- Barbiturates - reduce the concentration of bilirubin in the blood;
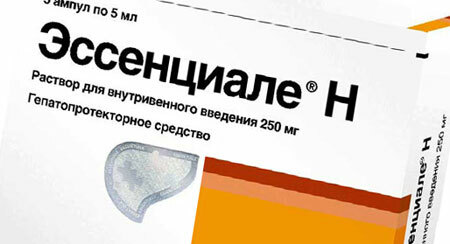
- Hepatoprotectors( Essentiale, Ursosan, Karsil, thistle extract) - support liver function;
- Cholagogue preparations( Hofitol, Karlovy Vary salt, Holosas) and herbs with a similar action - accelerate the movement of bile;
- Enterosorbents( Polysorb, Enterosgel, activated charcoal) - help to remove bilirubin from the intestine;
- Means for the prevention of cholecystitis and cholelithiasis.
Teenagers may be prescribed flumecinol instead of strong barbiturates. It is taken in small doses and at bedtime, as it causes drowsiness and lethargy.
Physiotherapy measures include the use of phototherapy, in which blue bulbs destroy bilirubin accumulated in the skin.
Thermal procedures in the area of the stomach and liver are inadmissible.
If necessary, symptomatic treatment of vomiting, nausea, heartburn, diarrhea and other disorders of the digestive system. It is necessary to take vitamins, especially group B. Along the way, sanation of all foci of infection in the body and therapy of pathology of the bile ducts are carried out.
If the level of bilirubin in the blood reaches a critical level( above 250 μmol / l), then blood transfusion and albumin administration are indicated.
Diet in Gilbert's syndrome
Therapeutic diet includes using the menu of table №5, at which:
- different kinds of groats are allowed;
- lean meat and fish;
- fruits and vegetables - fresh and boiled;
- skimmed yogurt, cottage cheese, yogurt, fermented baked milk;
- dry biscuits, wheat bread;
- freshly pressed non-acidic juices, weak tea, compote;
- vegetable soups.
Prohibited:
- buns;
- fat, fatty meat;
- spinach;
- mustard, pepper, other spices and spices;
- coffee;
- spinach and sorrel( since they contain oxalic acid);
- chocolate, cocoa;
- eggs;
- alcoholic and carbonated drinks;
- ice cream, fatty milk, sour cream, cheese.
Vegetarianism is contraindicated.
Compliance with the diet in Gilbert's syndrome not only alleviates the condition during jaundice, but also reduces the risk of exacerbations.