Child cerebral palsy or cerebral palsy is a term that in medical practice means a whole group of pathologies of the functioning of the nervous system resulting in a number of motor disorders. Cerebral palsy is considered a progressive disease that develops due to the lesions of certain areas of the brain or spinal cord during embryonic or neonatal development. In most cases, cerebral palsy is detected in children of the first year of life.
Warning! There are many reasons that can lead to the development of infantile cerebral palsy. As a result of one or several factors in the aggregate, partial or complete destruction of certain parts of the brain occurs.

Characteristics of cerebral palsy at 3 months
Characteristics of the causes of infantile cerebral palsy
| Group of diseases | Reason for the onset of the disease | Factors that led to the development of the disease |
|---|---|---|
| First | Congenital cerebral palsy | Genetically determined, congenital. Caused by severe genetic mutations and vices or pathology of intrauterine development. The brain of children in this case is underdeveloped, has insufficient number of convolutions, a number of brain structures may be absent. Occurs in approximately 9-11% of children
|
| Second | True acquired cerebral palsy | Pathology develops due to birth trauma, the harmful effects of toxic substances on the newborn, including anesthesia. Also, cerebral palsy can result in meningeal encephalitis of newborns. In most cases, children with this form of illness manage to adapt and develop their self-service skills. This form of the disease is revealed in 11-13% of patients |
| Third | Acquired cerebral palsy | Acquired cerebral palsy syndrome. Develops because of birth or other trauma, leads to paralysis, but the intelligence of these children remains intact. Patients have high chances of successful rehabilitation. The disease is detected in approximately 75-80% of children with cerebral palsy |
Attention! Child cerebral palsy can occur due to a violation of the genetic code of the fetus. However, this disease is not inherited and not inherited from a related lineage.

Pediatric cerebral palsy
Content of material
- 1 Features of the development of the disease
- 2 Skills and reactions in a healthy child of 3 months
- 3 Child's pathological reactions in three months
- 4 Signs of cerebral palsy in a child in three months
- 4.1 Forms of infantile cerebral palsy
- 5 In what casesshould I contact a specialist?
- 6 Signs of cerebral palsy in children with instrumental diagnostics
- 6.1 Video - Cerebral palsy. How to recognize the disease
Features of the development of the disease
There are a number of reasons that can cause the development of cerebral palsy in infants. It is quite difficult to establish the presence of the disease in the first three months of a child's life. Therefore, children, whose embryonic or early neonatal development occurred under the influence of pathological factors, should be closely monitored by the pediatrician and neurologist.
Warning! The most difficult diagnosis of cerebral palsy in premature infants or children with developmental lag, formed as a result of various diseases. In these cases, the child may delay the formation of age-specific reflexes.
The following factors are capable of provoking cerebral palsy during embryonic development:
- hypoplasia or placental abruption;
- mechanical damage to the fetus or placenta;
- embryo hypoxia;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases in a woman during gestation;
- Rhesus-conflict;
- fetoplacental insufficiency is a complex of abnormalities in the functioning of the placenta;
- infectious diseases transferred by a pregnant woman, including rubella, syphilis, gonorrhea and other STDs.

Causes of cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy during childbirth and during neonatal development can be caused by a number of reasons:
- damage to the brain structures at birth due to passing through a narrow pelvis or when applying forceps or a vacuum extractor;
- long anhydrous period;
- pathologically fast or protracted labor;
- birth of a child before 35 weeks of gestation;
- breech presentation of the fetus;
- newborn erythroblastosis;
- asphyxiation or aspiration with amniotic fluid;
- defects in the functioning of the cardiovascular, nervous or respiratory systems.

Causes of development of cerebral palsy
The disease can develop before or during childbirth, as well as in the first months of a baby's life. Therefore, it is necessary to pay attention in time to the emergence of anxiety symptoms, indicative of abnormalities in the child's brain and spinal cord.
Skills and reactions in a healthy child at 3 months
By the third month of life, the child has lost most of the reflexes peculiar to newborns, including the proboscis reflex and the palmar-oral reaction. You can check their presence as follows:
- You should put the baby on your back, then quickly and sharply touch his nasolabial fold. In the presence of a proboscis reflex, the children contract the circular muscles of the mouth, which causes the lips to open and stretch forward.
- The child should be on his back. You should gently push the baby's palm closer to the base of your thumb. In this case, the new-born mouth is slightly opened, the neck and arms are bent in the shoulders and elbows. Normally, the reaction lasts up to two months.
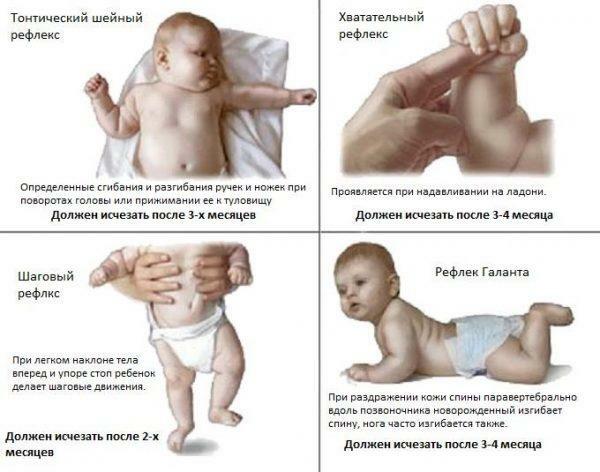
Reflexes of newborns are OK
Attention! In case of preservation of reflex data in a child in three months or later, it is necessary to consult a pediatric neurologist.
In this case, the infant should retain the reflexes of sucking and crawling. It is necessary to control how the baby takes the breast or the nipple: the muscles of the mouth in the child are regularly contracted and relaxed, the tongue is in the form of a "boat".
It is also necessary to pay attention to various skills that must be formed in a healthy baby by three months:
- The ability to focus on a fixed object or for 20-40 seconds to follow a bright moving toy. This skill indicates the normal development of oculomotor muscles.
- Head holding. The child needs to spread on the stomach, so that he, leaning on his forearms, kept his head raised for several minutes. A healthy baby stay in this position does not cause discomfort and allows you to study the environment.

Holding the child's head
- Forming speech skills. Children at the age of three months babble, publish a variety of sounds and sound combinations. At the same time, the child's speech activity is enhanced by interaction with parents or other close people.
- Mimicry is formed. Babies at this age can frown, laugh, squint, etc. Emotional response to events around and communication with people is manifested by active body movements, various grimaces, sounds, etc.
Some abilities can be formed in a child fairly quickly, while others develop somewhat more slowly. The reason for concern should be expressed physical difficulties that arise in the infant when trying to learn a particular skill.
Pathological reactions in a child in three months

Types of cerebral palsy
The basis of clinical symptoms of this disease in young children are various motor disorders. In the norm throughout the entire growth of the child, the basis of all his movements is the reaction of straightening and balance. The first reflex appears approximately 28-30 after birth, and the balance is formed from the sixth month of life. In this state of rest, the child is in the so-called flexion posture, that is, with the knees brought to the stomach. However, the infant should freely and arbitrarily bend and unbend the upper and lower limbs.
It should also pay attention to the preservation or appearance in a child at the age of three months of pathological reflexes. They indicate various dysfunctions of the central nervous system. The detection of such disorders is a symptom of cerebral palsy.
The palm-oral reflex, also called the Babkin's reflex, is expressed in all newborns. However, he must weaken by two months, and when the child reaches three months in the norm completely disappears or manifests itself only as separate components. With the defeat of the brain or spinal cord, the reflex of Babkin does not know how to tend to extinction, but only intensifies with time. In some cases, in this case, children open their mouths and bend their heads even if they touch the palms lightly.

Reflex Babkin
Galante reflex is also a symptom of the pathology of the nervous system. If you slide your finger along the child's spine, the baby archs back and straightens the leg from the side of the stimulus. Normally, by the end of the third month, this reflex should disappear.
Many other unconditioned reactions also fade away, on the basis of which conditioned-reflex skills are formed. However, central paralysis activates unconditioned reflexes, which, in combination with the disturbed muscle tone, lead to the formation of pathological movements. In infantile cerebral palsy, a grasping reaction persists, which forces the child to keep his fists clenched. Characteristically expressed are the reaction of support and automatic gait: a touch with the support provokes a sharp spasm of the muscles of the legs and trunk. The same physiological response in a child with paralysis is caused by a crawling reflex.
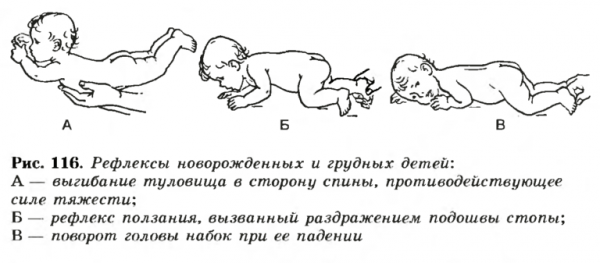
Reflexes of newborns
Attention! Specialists distinguish several dozen normal and pathological reflexes in children aged three months. In order to timely identify a malfunction of the nervous system in an infant, it is necessary to visit the pediatrician and neurologist on a regular basis.
Signs of cerebral palsy in a child in three months
There are also a number of signs, in addition to pathological reactions, which may indicate the development of a child's central paralysis. Most of these symptoms parents can notice at home during the daily care of the baby. In this case the manifestations of cerebral palsy fluctuate from slight awkwardness when moving to severe lesions, leading to complete paralysis of the patient. The severity of the disease directly depends on the degree of brain damage.
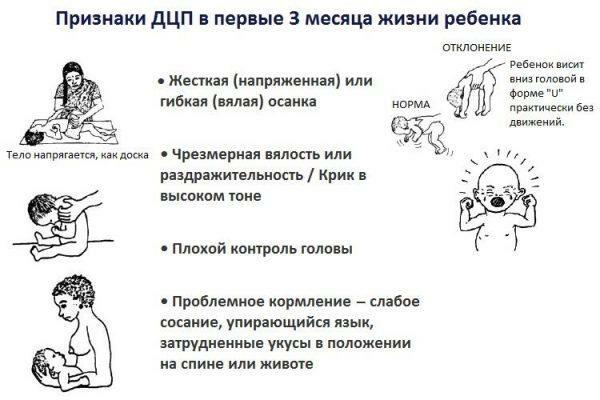
Signs of cerebral palsy in the first 3 months of
The following signs indicate the development of cerebral palsy in a child:
- Abnormalities of muscle tone. There may be a hyper- or hypotonic disorder. Spasms cause the child to constantly be in a tense, uncomfortable position for him. An attempt to bend the foot to a baby, plant or otherwise change the position of his body encounters a pronounced resistance. With hypotonia, children are flabby, can not hold their head, do not rise in position on the abdomen, are characterized by low mobility.
- Pathological movements. A child with cerebral palsy often has chaotic, discoordinated movements. Many infants suffer from sleep disorders because they wake themselves with uncontrollable swings of the hands or feet.
- Contractures of joints, that is limitation of their passive mobility. This symptom arises because of uneven tone in different muscle groups. It usually manifests itself by crying and crying of the child when trying to massage him or doing gymnastics.
- Convulsions. In young children, convulsions are usually poorly expressed. They can be noticed by abnormal abrupt movements of the baby's limbs.
- Trembling of hands and feet. Constant flexing and extension of the fingers or difficulty when trying to unclench the child's palm.
- Gref syndrome - hydrocephalic syndrome.
- No response to sound stimuli, hearing loss.
- Problems during feeding. Children with cerebral palsy at the age of three months have difficulty in swallowing and sucking. The movements of the lips and tongue can be too sluggish or stiff and chaotic. In a number of cases, aspiration and fluid outlet through the mouth or nose are noted.
- Strabism, that is, strabismus. Can be either unilateral or bilateral. Pathology arises from the weakness of the oculomotor muscles. In some cases nystagmus is noted - chaotic movements of the eyeball.
- Violations of facial expressions. A child with paralysis has problems trying to control the facial muscles. This manifests itself as an erased, smoothed or overly expressed, rough mimicry. In cerebral palsy, the following disorders are often observed: a smile on one side of the mouth;ptosis, that is sagging, centuries;constantly open mouth, etc.
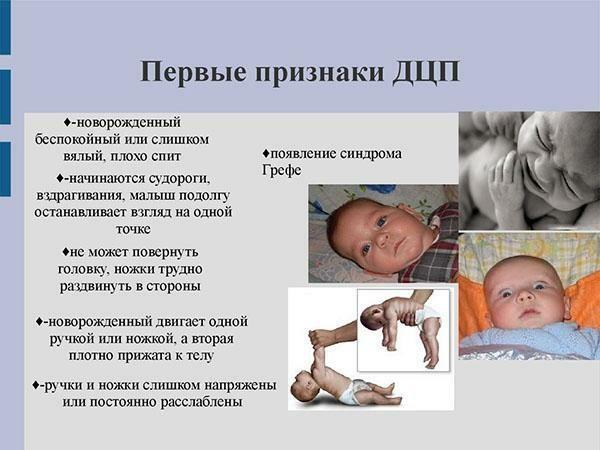
First signs of cerebral palsy in a newborn
Forms of infantile cerebral palsy
In medical practice, four main forms of cerebral palsy are distinguished, each of which has the characteristic features:
- Spastic paralysis. A baby with this type of disease develops a pronounced hypertonic muscle. When palpation of the limb from the affected side, rigid, passive movements are severely limited. The child is able to hold a rattle or other thing in the affected hand.
- Choreoathetoid paralysis. This form of the disease is observed in about 15-20% of patients. Is manifested chaotic muscle twitching. At the same time, limb movements are sharp, poorly controlled.
- Ataxic paralysis. With this type of cerebral palsy, the child can not coordinate his own movements. He is able to roll over on his stomach, hardly holds the rattle, can not grab the toys suspended above him.
- Mixed form occurs in about a third of patients and includes various subspecies of infantile cerebral palsy.
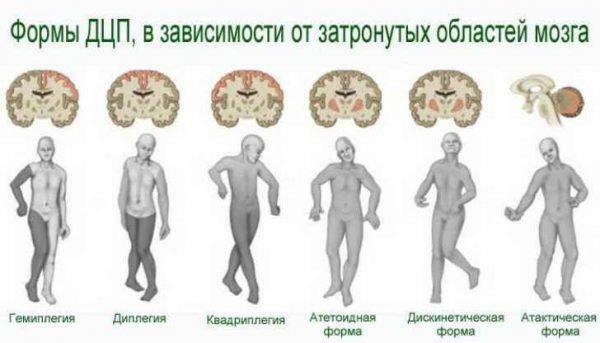
Forms of cerebral palsy
Attention! There are also different types of paralysis depending on the severity of motor disorders. The most common is spastic diplegia - the defeat of the muscles on both sides, while the lower limbs are more affected.
When should I contact a specialist?
Brain lesions in children may occur in an erased or mild form. Therefore, timely diagnosis of the disease should pay attention to the alarming signs:
- The child is constantly tense, unable to move his arms and legs freely.
- The baby has a permanent weight deficit.
- Movements of the baby seem chaotic and sharp or lethargic, vermicular.
- The child has regular problems with stool, constipation. Some children with cerebral palsy can not stiffen during defecation.
- The baby constantly screams and cries, especially during gymnastics and massage.
- The child is hard to hold. He seems tense or limp and lethargic.
- Baby does not eat well, does not take breast, chokes with milk.

Symptoms of cerebral palsy
Symptoms of cerebral palsy in children with instrumental diagnostics
It is often impossible to accurately determine the presence of cerebral palsy according to the results of a physical examination in a child at three months of age. To accurately identify organic changes in the brain and exclude various genetic diseases allow instrumental research. Encephalography and neurography are aimed at differentiation of cerebral palsy from myopathy, ataxia-telangiectasia, etc. To identify atrophy of optic nerves, tumors, cysts and areas of ischemia, hydrocephalus or brain underdevelopment, MRI is prescribed under anesthesia and neurosonography.
Children's cerebral palsy is a complex of diseases caused by disorders in the work of various structures of the brain and spinal cord. The disease manifests itself in various paresis and paralysis, a violation of muscle tone, a lag in physical and motor development. In children at an early age, cerebral palsy can be identified by a number of characteristic symptoms: preservation of pathological reflexes, violation of sucking, limitation of mobility, etc. When identifying such signs in a baby, it is necessary to urgently turn to a pediatric neurologist.