The author of the article is Chuklina Olga Petrovna, general practitioner, therapist. Work experience since 2003.
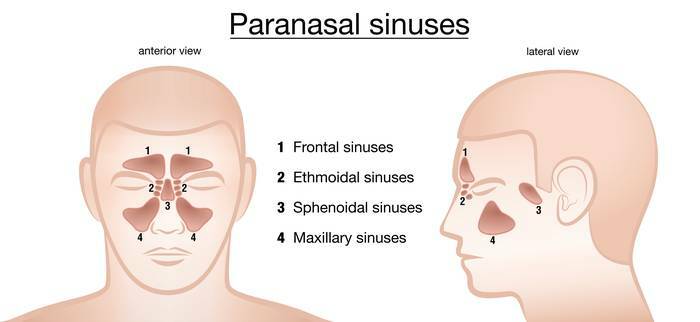 Frontitis is an inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane of the frontal sinus. This is one of sinusitis (inflammation of the paranasal sinuses). According to statistics, an average of 10% of the adult and 4-5% of the child population suffer from some kind of sinusitis.
Frontitis is an inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane of the frontal sinus. This is one of sinusitis (inflammation of the paranasal sinuses). According to statistics, an average of 10% of the adult and 4-5% of the child population suffer from some kind of sinusitis.
Forms
Frontit can be:
- acute (duration of the disease less than 4 weeks);
- subacute (duration of the disease 4 weeks - 3 months);
- chronic (the duration of the disease is more than 3 months);
Acute frontal sinusitis is subdivided into:
- acute catarrhal frontal sinusitis - moderate nasal discharge, nasal congestion, discomfort in the brow region; there may be a recovery or transition to another form;
- acute purulent frontal sinusitis - there is an accumulation of pus in the frontal sinuses;
Also, frontal sinusitis can be one- or two-sided.
Causes
Frontitis is subdivided into:
- rhinogenic (occurs after rhinitis - runny nose);
- hematogenous (if the infection gets through the blood);
- post-traumatic (occurs after injuries to the bones of the skull in the area of the frontal sinuses);
- allergic (develops as a result of an allergic reaction);
- polyposis (develops in the presence of polyps in the nasal cavity).
Frontitis symptoms
With an acute front:
- nasal congestion (up to the absence of breathing through the nose);
- pain, heaviness in the brow region;
- nasal voice;
- decreased or loss of smell;
- increased body temperature;
- headache in the frontal region, which intensifies when bending forward, in the prone position, when tapping in the brow region, when coughing;
- general malaise;
- yellow or greenish discharge from the nose.
With chronic frontitis:
- periods of exacerbation are manifested by symptoms as in acute frontalitis;
- during periods of remission, symptoms are less pronounced;
- decreased sense of smell;
- pain is less pronounced, more often of a permanent nature;
- discharge from the nose in the form of thick mucus, often in the morning after waking up;
- heaviness in the brow region.
Diagnostics
When collecting an anamnesis, the doctor pays attention to the following factors:
- the presence of a long runny nose; a history of acute frontal sinusitis;
- transferred ARVI;
- polyps nasal cavity.
To clarify the diagnosis, the following procedures are carried out:
- rhinoscopy - examination of the nasal mucosa, allows you to see signs of inflammation;
- X-ray examination is a very informative method that allows you to detect frontal sinusitis and helps distinguish between a catarrhal or purulent process (darkening with catarrhal frontitis and fluid level with purulent);
- endoscopic examination - examination of the nasal cavity using a small video camera; allows you to see redness and swelling of the mucous membrane, the presence of polyps.
- computed tomography, more often to identify complications during the spread of the process;
- diaphanoscopy - a special light is placed in the patient's mouth and the sinuses are examined (now rarely used);
- ultrasound examination of the area of the frontal sinuses.
Differential diagnosis
Similar pain can be with trigeminal neuralgia.
With neuralgia, the pain has a sharp, burning character, proceeds in the form of attacks. The pain occurs suddenly, and a violation of sensitivity in the area of pain is also characteristic.
Frontitis treatment
Treatment is carried out by an otolaryngologist, less often a general practitioner and a therapist.
Treatment of acute frontal sinusitis
Outpatient treatment is indicated for acute uncomplicated frontal sinusitis.
In such cases, apply:
- plentiful drink
- vasoconstrictor spray or drops - used to reduce mucosal edema and improve mucus discharge; (snoop, rhinonorm, otrivin, etc.);
- antihistamines - to remove the allergic component (cetrin, back, zyrtec);
- sprays containing antibacterial drugs (polydex with phenylephrine, isofra);
- drugs that help liquefy mucus and help remove it (acs, fluditec);
- with purulent frontitis, systemic antibiotics are indicated (amoxicillin 500 mg - 3 times / day, cefuroxime 400 mg 1 time / day).
Antibiotic therapy (taking antibiotics) is carried out for about 7-10 days, and the drug continues to be taken after the symptoms disappear.
Procedures for acute frontalitis
- rinsing the nose with a method called "cuckoo". A medical solution is poured into one nostril to the patient, and the contents are sucked out from the other nostril using suction; the patient at this time says "cuckoo" so that the solution does not get into the throat.
- physiotherapy is carried out at the stage of recovery and in the presence of a good outflow from the sinus; the use of electrophoresis, UHF is possible.
Important. With timely and high-quality treatment, the duration of disability is 7-14 days. With the development of complications, the need for inpatient treatment, the duration of disability increases significantly.
Inpatient treatment is indicated
- with the ineffectiveness of outpatient treatment;
- with severe course;
- with the development or threat of development of complications.
With stagnation of pus, trepanopuncture can be performed (puncture of the frontal sinus, washing and injecting drugs into the sinus cavity). Trepanopuncture is performed only in a hospital setting. Also, surgical treatment is carried out with the development of intracranial and ocular complications.
Treatment of chronic frontal sinusitis
In case of exacerbation, treatment is carried out as in acute frontalitis.
In the absence of exacerbation, in remission:
- sprays containing hormonal drugs (nazonex, etc.);
- rinsing the nasal cavity with saline solutions;
- treatment of allergic diseases;
- surgical treatment for anatomical defects (curvature of the septum, developmental anomalies);
- steam inhalation with menthol and eucalyptus oil.
Complications
The most common complications of frontal sinusitis are:
- frequent inflammatory diseases (pharyngitis, laryngitis);
- sleep apnea syndrome (stopping breathing at night);
- labored breathing.
Such complications arise in the case of delayed or incorrect therapy.
With malicious ignorance of treatment, in the treatment of folk methods without medication support, extremely serious complications are possible:
- spread of the process into the cranial cavity (development of meningitis, encephalitis, brain abscess);
- osteomyelitis (purulent inflammation of the bones of the skull);
- sepsis (spread of infection into the bloodstream, then throughout the body).
Prevention of frontal sinusitis
- timely treatment of diseases of the nasal cavity (polyps, cysts, curvature of the septum);
- timely treatment of rhinitis, acute respiratory viral infections, allergic diseases;
- treatment of acute frontal sinusitis to avoid the development of a chronic form;
- strengthening of immunity and prevention of acute respiratory diseases.

