Change in the duration and course of the menstrual cycle may indicate a health problem. Knowing at what levels the regulation of the cycle takes place, and the flow patterns of all processes, it is possible to prevent the development of dangerous changes in the female body.
Record content:
-
1 What is the menstrual cycle?
- 1.1 Duration
- 1.2 Permissible deviations
-
2 Levels of menstruation regulation
- 2.1 Level 1: cerebral cortex
- 2.2 Level 2: hypothalamus
- 2.3 Level 3: pituitary gland
- 2.4 Level 4: ovaries
- 2.5 Level 5: uterus
-
3 Phases of the menstrual cycle
- 3.1 Phase one
- 3.2 Second phase
- 4 Causes of an irregular menstrual cycle
- 5 What violations are there?
- 6 Relationship between menstruation and ovulation
- 7 Amenorrhea and its manifestations
- 8 Video about the levels of regulation of the menstrual cycle
What is the menstrual cycle?
The menstrual cycle refers to changes in the body that occur every month and contribute to the conception of a child.

The scheme of its regulation can be established throughout all stages of a woman's reproductive age, but after 2-3 years from the beginning of the first menstruation (maturation of the body to conception occurs by the age of 12-13), it acquires a constant character.
Duration
The menstrual cycle lasts on average 21 to 35 days. This value depends on the individual characteristics of the organism. The first day of the cycle is the 1st day of vaginal bleeding. Their duration is 3-7 days.
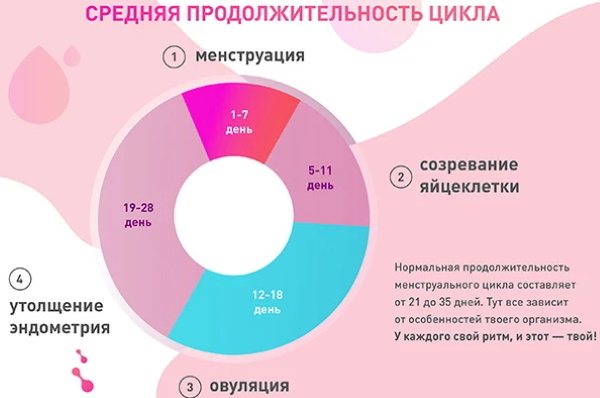
Menstrual flow should occur at equal intervals every month.
Permissible deviations
In case of a deviation of 7 or more days, it is recommended to contact your attending gynecologist for advice. This may indicate pregnancy or the appearance of pathological health disorders.
Levels of menstruation regulation
The levels of regulation of the menstrual cycle (the scheme of each of them will be described later in the article) represent 5 peculiar stages. The brain plays a major role in this complex process.
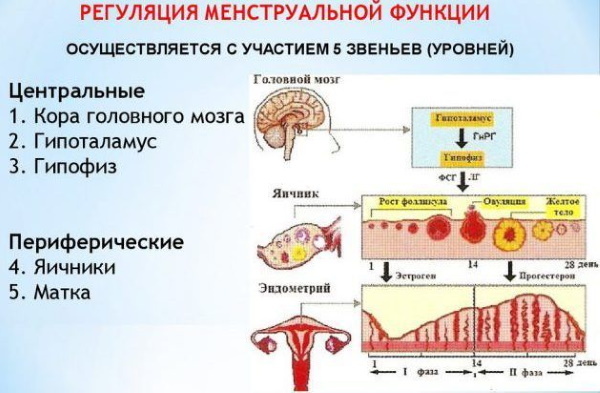
Certain biological processes take place at each level.
Level 1: cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex is responsible for the normal course of the entire menstrual cycle. It forms the emotional state of a woman, based on incoming external factors (for example, severe stress, fear of unplanned pregnancy, etc.).
In combination, psychological factors affect the cerebral cortex, as a result, the body can stop the production of hormones. The consequence of this is a delay in the start of a new cycle.
Failures can also occur through head injuries.
Level 2: hypothalamus
The levels of regulation of the menstrual cycle (the diagram is represented by the production of the corresponding hormones) are continuously connected, so information from the cerebral cortex then enters the hypothalamus. It regulates the main body systems through the production of hormones.

The control centers are concentrated in the hypothalamus:
- emotions;
- human behavior;
- sleep;
- hunger;
- thirst;
- the genital area;
- vegetative reactions.
The hypothalamus is a complex of sensitive cells that produce substances called releasing factors. They contribute to the synthesis of hormones that ensure the normal functioning of the pituitary gland. It is at this level of regulation that the production of hormones responsible for the onset of the menstrual cycle can stop.
Level 3: pituitary gland
At this level, the pituitary gland is involved in the work, which produces growth hormones. It is these hormones that are responsible for the proper functioning and maturation of the ovaries, as well as the subsequent normal development of the formed fetus (if the process of conception has taken place). The anterior pituitary gland is responsible for regulating the menstrual cycle through hormones.
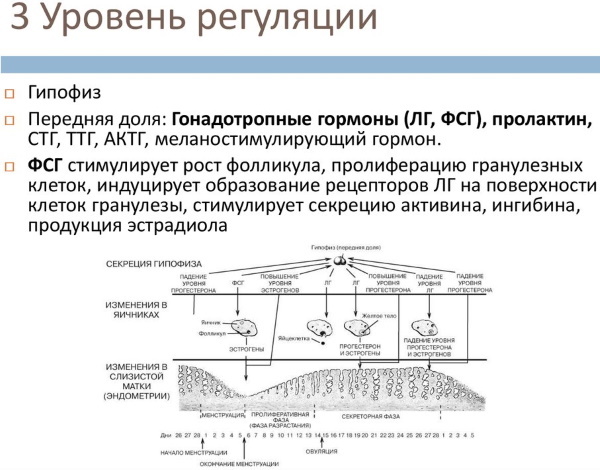
This is a complex process that takes place with the participation of:
- Hormones that activate breast growth and stimulate lactation (luteotropic hormones).
- Hormones that ensure the proper development of mature eggs and follicles (luteinizing hormone).
- Hormones that ensure the growth and maturation of follicles.
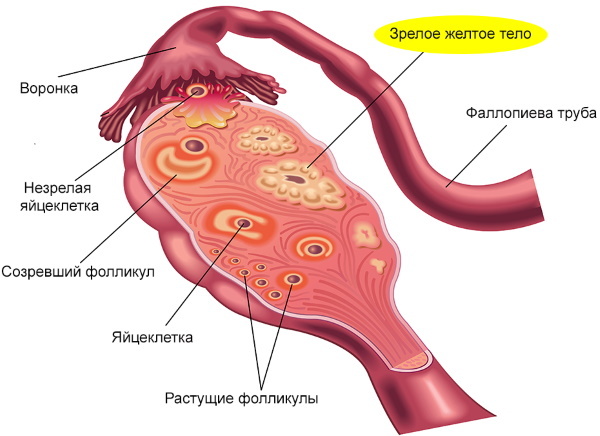
Level 4: ovaries
The ovaries have 2 main functions:
- Endocrine - there is a production of sex hormones (due to connections with the pituitary gland and hypothalamus).
- Generative - the formation of germ cells occurs.

These functions ensure the correct maturation, and then the development of the follicle, followed by the release of a mature egg from it.
Level 5: uterus
The levels of regulation of the menstrual cycle, the scheme of which is the same for all women, are completed by the processes of changes in the uterus. So, under the influence of hormones, the endometrium of the uterus changes depending on the phase of the cycle. Also, at this level of regulation, the fallopian tubes, the uterus itself and the tissues of the vagina are involved.
Phases of the menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is divided into several phases. Each of them is characterized by certain characteristics and condition of the female body, which is formed under the influence of the hormones produced.
Phase one
The follicular phase begins on the 1st day of menstrual flow and is pumped by ovulation.
During this period, there is:
- Development and maturation of follicles in the ovary.
- Rejection of the endometrial layer in the uterus, which is manifested by menstrual flow. During this process, the uterus begins to actively contract, so some women may experience pain in the lower abdomen.
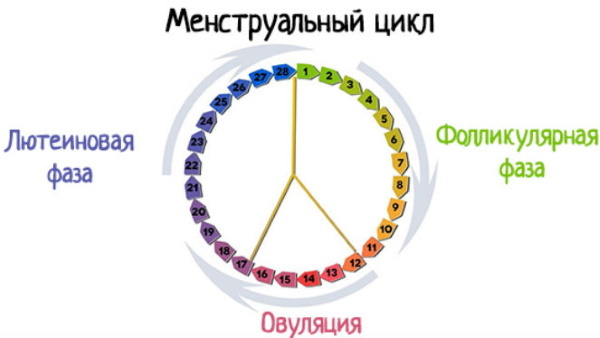
In the process of maturation, the follicle synthesizes hormones that contribute to the restoration of the rejected layer of the endometrium. After maturation, the follicle opens and an egg cell ready for fertilization comes out of it (ovulation occurs).
The duration of the phase depends on the individual characteristics of the organism and the duration of the cycle, so it can last from 7 to 22 days.
For example, with a 28-day cycle, phase 1 has a duration of 14 days. During this period, the body needs a sufficient intake of B vitamins and folic acid. These substances normalize hormonal balance. A sufficient amount of zinc is also required - it improves the growth and development of the egg.
Second phase
The luteal phase occurs after ovulation.
Changes in the body during this period are presented in the table below:
| Changes | Peculiarities |
| Corpus luteum formation | This formation appears at the site of a mature follicle in the ovary. Its main function is to prepare the female body for bearing a child, as well as to ensure the correct course of pregnancy. For this, the corpus luteum synthesizes the hormone progesterone. |
| Thickening of the endometrium of the uterus | Under the influence of progesterone, the lining of the uterus begins to thicken so that the fertilized egg can easily attach and develop correctly. |
If conception has occurred, then the corpus luteum continues to develop and produce hormones. If the egg is not fertilized, then the corpus luteum will gradually atrophy. At the end of the phase, a woman may experience a deterioration in well-being, sudden mood swings (PMS syndrome develops). The reason for this is the lack of magnesium, calcium and vitamin D.
Causes of an irregular menstrual cycle
Often the reason for the failure of the menstrual cycle is a violation of the psycho-emotional state of a woman. Constant stress, overwork, mental trauma can cause a number of other health problems.
Also, irregularity of the cycle can provoke:
- Treatment with hormonal drugs.
- Miscarriages, abortions.
- Diseases of the organs of the genitourinary system and their complications (can manifest themselves in the form of fibroids, tumors).
- Diabetes.
- Malnutrition, abuse of junk food.

- Infectious diseases of various etiologies.
- Inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs.
- Severe diseases of the endocrine system and possible complications after them (for example, dysfunction of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands).
- Incorrect placement of the intrauterine device.
- Non-compliance with the daily regimen.
It is possible to speak of a violation when changes in the menstrual cycle occur over several cycles.
What violations are there?
Violations are classified according to several factors:
- Duration of menstrual flow. If they last less than 2 days, then this violation is called oligomenorrhea. If the discharge is observed for 8 days or more, this is called polymenorrhea.
- Cyclicity. Menstruation can be frequent (the cycle duration is only 21 days), rare, very rare (menstrual flow is no more than 4 p. per year), and may be absent for more than six months.
- The amount of blood secreted during menstruation (scant or profuse discharge).
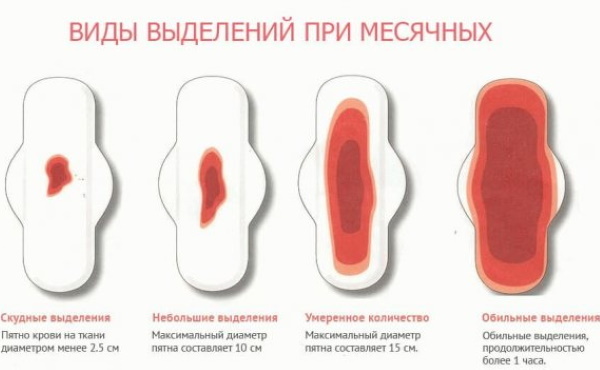
- Influence on the well-being of a woman (the common name for dysmenorrhea). Violations are manifested in the form of headaches, feelings of nausea, vomiting, pain in the lower abdomen, bad mood.
Relationship between menstruation and ovulation
Before ovulation, the endometrium (a layer of cells on the walls of the uterus) grows under the influence of hormones. Closer to the onset of ovulation, this layer thickens, preparing to receive a fertilized egg. During ovulation, a zygote is formed in the endometrial cells - this is a special secret that facilitates the process of attachment and ingrowth of a fertilized egg.
And if conception does not occur due to ovulation, a sharp decrease in sex hormones occurs in the body. This causes the uterus to contract. As a result, endometrial cells remain without blood supply and begin to die off - new menstrual flow begins and, accordingly, a new cycle.
Amenorrhea and its manifestations
Amenorrhea is a woman's condition in which there is no menstrual flow for six months or more. She is one of the symptoms of disorders in a woman's body.
Amenorrhea can be caused by:
- Incorrect or defective structure of the reproductive organs.
- Malignant and benign neoplasms.
- Failure of the reproductive system.
- Endocrine diseases.
- Genetic disorders.
- Large sports loads.
- Getting uterine herbs.
- Sudden weight loss.
- Severe stress.

This disorder occurs only in 2-3% of women of reproductive age.
Its symptoms (except for the absence of menstruation) are:
- An increase in testosterone, which is accompanied by rapid weight gain, intense hair growth.
- A sharp increase in sweating.
- Headaches.
- General weakness and fatigue.
- Irritability.
Amenorrhea can have several types, the description of which is presented in the table below:
| Forms of amenorrhea | Features, how is it manifested |
| Primary | It manifests itself in young girls who have not yet had menstrual flow. This disorder occurs mainly due to delayed puberty. Also, a violation can cause exhausting physical activity, diets, severe psycho-emotional state. In some cases, amenorrhea can be hereditary - if the teen's mother has menstrual flow after 17 years. But usually primary amenorrhea occurs before the age of 14, and in the absence of signs of secondary amenorrhea - up to 16 years. |
| Secondary | The most common form is 70% of all types of amenorrhea. It is characterized by the absence of menstrual flow for more than 6 months. In women, a normal cycle is established, which for certain reasons is disrupted. As a result, menstrual flow stops. Most of the cases of this disorder are associated with malfunctions of the hypothalamus-pituitary-ovary system. |
| Uterine | It develops as a result of injury to the mucous membrane of the uterus. It can be caused by abortion, tissue burning, as well as postoperative and postpartum complications. At the site of injuries, adhesions are formed, causing complete or partial obstruction in the uterus. This can lead not only to the development of amenorrhea, but also to infertility. |
| Lactation | It is a natural period in the life of a woman who breastfeeds her baby. During lactation, the level of a substance responsible for milk production increases. As a result, the process of synthesis of pituitary hormones is suppressed. The duration of this form of amenorrhea ranges from 2 months to 1 year. After the end of breastfeeding, the woman's menstrual cycle will gradually recover. |
| Physiological | This type of amenorrhea occurs after menopause and during pregnancy. It is a normal physiological process and therefore does not require treatment. |

Amenorrhea is divided into several stages based on severity.
Allocate:
- 1st stage - no menstrual flow for less than 1 year.
- 2nd stage - menstrual bleeding is absent from 1 to 3 years.
- 3rd stage (chronic) - there is no menstrual flow for more than 3 years or more.
Knowing the flow pattern of the menstrual cycle will help to avoid the occurrence of many female diseases. If it is violated at a certain level of regulation, you should not ignore the symptoms that arise - you should immediately seek advice from a gynecologist.
Video about the levels of regulation of the menstrual cycle
What is the menstrual cycle, how does it happen:



