1 Clinical picture
Peritonitis is an inflammatory process in the peritoneum. Peritoneum called the inner membrane of the abdominal cavity. The abdominal cavity is the space below the thorax, which is filled with internal organs. It contains a small amount of aseptic fluid.
Do you have gastritis?
GALINA SAVINA: "How easy is it to cure gastritis at home for 1 month. A proven method - write down a recipe. ..!"Read more & gt; & gt;
Recommended to consult
- Symptoms of duodenal gastrular reflux
- What is the diagnosis of IBS
- Symptoms of perforating ulcer
- Effective agent for gastritis and gastric ulcer
Inflammation of the peritoneum is referred to the group of acute surgical conditions under the generalized name "acute abdomen."
The disease is accompanied by a violation of the vital functions of systems and organs. It carries a threat not only to the health of the patient, but also to his life. Mortality from peritonitis is very high. The process is developing rapidly, so it is very important to provide medical assistance as soon as possible. Inflammation of the abdominal area is diagnosed in every fifth patient in a critical condition. Treatment of peritonitis requires urgent surgical intervention.
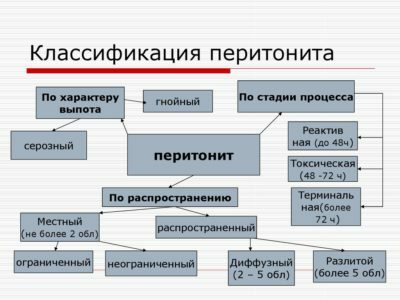
Classify peritoneal inflammation according to various criteria.
2 Variety of the disease according to the traumatic factor
Bacterial peritonitis occurs as a result of penetration of viable bacteria into the sterile abdominal cavity. In the development of the disease, the amount of penetrating infection, the pathogenic qualities of the microbes and the mechanism of the body's defense forces are of great importance. Infection can enter the abdominal cavity through blood or lymph or as a result of damage to the abdominal or pelvic organs.
The causes of peritonitis are different. With a variety of diseases of the intestine, inflammation of the peritoneum develops in 5% of cases. Intestinal pathologies include intestinal obstruction, intestinal diverticula( bulging of intestinal walls).
If peritonitis is found, its causes are often a consequence of diseases of the biliary tract( 10% of cases).
One of the most likely causes of bacterial peritonitis is appendicitis( inflammation of the appendix of the cecum).
It is often caused by perforation( the formation of a through hole) of a stomach or duodenal ulcer. The disease can also arise due to the development of diseases of the female reproductive system or due to trauma.

Aseptic peritonitis is provoked by irritation of the peritoneal tissue with aggressive substances of the body - blood, urine, bile, gastric juice or pancreatic juice. It very quickly becomes bacterial, because after a few hours the irritated peritoneal tissues are exposed to bacteria.
-
 IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
One of the varieties of the aseptic form is barium peritonitis. It develops as a result of the release of barium outside the intestine. This becomes possible during X-ray studies using a contrast agent containing barium. Barium variety of the disease is very rare, but every second person dies from it.
3 Types of disease by the mechanism of infection
Primary peritonitis is a rather rare phenomenon. It occurs as a result of infection from other organs. For example, it can appear as a complication of cirrhosis of the liver.
Secondary peritonitis develops due to organ damage due to ulcers, trauma or surgical intervention.
There is also a tertiary peritonitis( also creepy or persistent).This is the term purulent forms of the disease that appear during the treatment of secondary peritonitis. They have a weakly expressed character and develop gradually, in contrast to the primary and secondary forms.
4 Species of the pathology according to the extent of
distribution Local( local) peritonitis is localized around the organ or trauma, which is the focus of inflammation. Due to the quality of the peritoneum to the formation of fusion, the inflammatory process is often limited to a specific site. Although in some cases there is a flow of inflammatory fluid into adjacent areas. Local inflammatory process is limited to 2 or 3 of 9 anatomical areas of the peritoneum.
-
 Gastroenterologist. IMPORTANT: "I beg you, if you began to worry about abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, do not do gases. .."Read more & gt; & gt;
Gastroenterologist. IMPORTANT: "I beg you, if you began to worry about abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, do not do gases. .."Read more & gt; & gt;
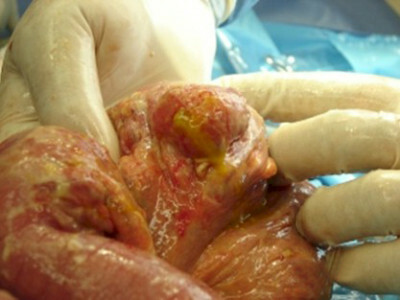
Under the widespread( diffuse) peritonitis is meant the involvement of 2 to 5 abdominal parts in the inflammatory process. It can capture up to 60% of the cavity.
If the lesion exceeds 60% of the peritoneum and extends over more than 5 regions, this inflammation of the abdominal region is called a common spill.
General( total) peritonitis occurs if there is a total inflammation of the abdominal cavity.

5 Classification of the disease by the nature of the peritoneum contents
The agents of purulent form of the disease are representatives of purulent microflora - staphylococci, gonococci and E. coli. Purulent peritonitis progresses rapidly and is accompanied by a powerful intoxication of the body. Toxicity of products of purulent flora activity causes serious disturbances in the human body. Mortality from purulent inflammation of the peritoneum is large. Some patients have a slow purulent peritonitis, as a consequence of treatment of the secondary form.
Serous peritonitis usually appears due to congestion of serous fluid. After 2-3 days, the fluid accumulates the plasma protein( fibrin) and the disease becomes serous-fibrinous. This form can develop into a purulent if purulent microflora is activated.
ADVICE FROM THE MAIN GASTROENTEROLOGIST
Korotov SV: "I can recommend only one remedy for the rapid treatment of Ulcer and Gastritis, which is now recommended by the Ministry of Health. .." Read testimonials & gt; & gt;
Fibrinous peritonitis occurs if a lot of fibrin accumulates in the fluid. Excessive amount of plasma protein leads to the appearance of fibrin films. This form of the disease is dangerous by the appearance of fusion of the abdominal cavity with nearby organs or tissues of the intestine.
Hemorrhagic peritonitis is a condition in which blood that enters the abdominal cavity is attached to the fluid. It pours out during trauma or when perforating( forming a through hole) ulcers.

Fecal peritonitis occurs when fluid in the abdominal cavity is contaminated with the contents of the intestine.
The inflammatory process of the peritoneum, which is accompanied by the accumulation of fluid, is called exudative( wet).When the process progresses, the volume of the liquid increases. Simultaneously with the accumulation of fluid in the peritoneum, the remaining organs lose water. As a result, the body begins to suffer from dehydration. The condition is aggravated by the general intoxication which occurs because of penetration in a blood of toxins from the liquid accumulated in an abdominal cavity.
6 How
is manifested The first and main manifestation of peritonitis is severe and acute pain. The most severe pain occurs if the inflammation in the peritoneum is caused by perforation of the stomach or duodenal ulcer. The nature of the pain syndrome resembles a sharp knife blow. Intensive pain is accompanied by pancreatic juice. Its effect on peritoneal tissue is comparable to a burn. Pain syndrome can cause a loss of consciousness in the patient.
The first signs of peritonitis are most often localized in one place. But after a few hours the pain spreads over the stomach. Sometimes the process can progress in the opposite direction - from the spilled the pain can become localized.

An alarm sign is the disappearance of the pain syndrome. This may indicate the accumulation of a large volume of fluid.
If peritonitis occurs, the symptoms may appear visually. A clear sign is the tension of the abdominal muscles. It occurs around the same time as the pain syndrome. Especially strong tension is felt during the perforation of the ulcer. The abdomen acquires a characteristic "flattish" state. It is so clearly manifested that it is observed without feeling.
Voltage is local. For example, only in the area of the gallbladder in the occurrence of biliary peritonitis. As the disease develops, the tension goes away. In weakened patients and in adults of advanced age, the stress may not appear.

Diagnosis of peritonitis is performed using the Shchetkin-Blumberg method. The patient is laid on the bed and asked to bend his knees to achieve the greatest relaxation of the walls of the abdominal cavity. In the area of presumed inflammation, the doctor presses on the stomach. The patient should feel pain. If the patient feels an increase in the pain syndrome with a sudden withdrawal of the hand, then the diagnosis of "peritonitis" is confirmed. If the intensity of pain has not changed, the result is negative. The application of the method may be hampered by the presence of tension in the abdominal muscles.
7 Stage
Reactive stage. This stage can end in 2 hours, but it can drag on for several days. An exception is acute purulent peritonitis, which progresses no more than a day. Characterized by the manifestation of local symptoms. General symptoms are observed only in their initial stage. Along with the pain syndrome, the patient raises the temperature to 39 ° C and above. His heartbeat accelerates, nausea and vomiting appear. If the pain syndrome is pronounced, the patient may have confused consciousness. His tongue becomes dry and covered.

Toxic stage. May last 2-3 days. At this time, signs of intoxication, metabolism and dehydration are clearly manifested. From the toxins affect the organs and systems of the body, especially the liver and lungs. Serious liver diseases can develop. Breathing is superficial and intermittent, blood pressure is lowered. Emotional vomituses acquire a sharp unpleasant odor. Cramps may occur. During this period, the pain and tension of the abdominal muscles is lost. There may be a swelling. If the patient does not immediately provide medical assistance, the terminal stage will begin.
Terminal stage. It develops approximately 4 days after the onset of the disease. By this time the patient is in the pre-coma. Symptoms of peritoneal inflammation in the thermal stage in adults, as in children, can be determined by their appearance. Eyes and cheeks look sunk. The skin dries and contracts, becomes pale with an earthy tinge and even cyanotic. Consciousness becomes clouded.
8 Consequences of
The complications of peritonitis are divided by the time of the onset of immediate and remote. Immediate symptoms occur immediately during or immediately after the illness in the form of sepsis, bleeding, coma, or death of the patient.
Long-term complications may occur several weeks after the disease in the form of a postoperative hernia or bowel disorders. After acute peritonitis, there is often an obstruction of the intestine. Women can develop gynecological diseases, there are difficulties when trying to become pregnant.

9 Treatment measures
Treatment at the initial acute stage of peritonitis is performed with the help of surgical intervention. An exception is a limited peritonitis of gynecological origin. The focus of inflammation is cleared and processed. But this is not always enough. After all, very often, by the time a patient calls for medical help, the disease acquires a general character, other organs and systems of the body are affected. In this case, the treatment of peritonitis is aimed at purifying the body of toxins. Drainage of the gastrointestinal tract is carried out, enterosorbents are appointed( substances capable of removing toxins from the body).
If the symptoms of peritonitis are moderately expressed, it is local and tends to die out, the treatment is performed conservatively. The patient is prescribed antibiotic therapy, bed rest and a caloric and vitaminized diet are needed.
If there is a suspicion of peritonitis, treatment should be carried out without delay.
- 1 Clinical picture
- 2 Types of the disease according to the traumatic factor
- 3 Types of the disease according to the infection mechanism
- 4 Variety of pathology according to the extent of
- 5 distribution Classification of the ailment by the nature of the peritoneum contents
- 6 How the
- 7 is manifested Steps
- 8 Consequences
- 9 Therapeutic measures
Doctors often frighten the diagnosis of "peritonitis".Peritonitis - what is it? Why is this disease considered so dangerous? Many associate it with appendicitis. Indeed, most often it is appendicitis that causes this disease.



